A hematoma happens when you have blood pooling someplace inside your body. Most hematomas aren’t serious, and you can commonly see them in the form of surface bruises. But when hematomas are deeper or bigger, they can become serious. And knowing when they need care can make a lifesaving difference.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
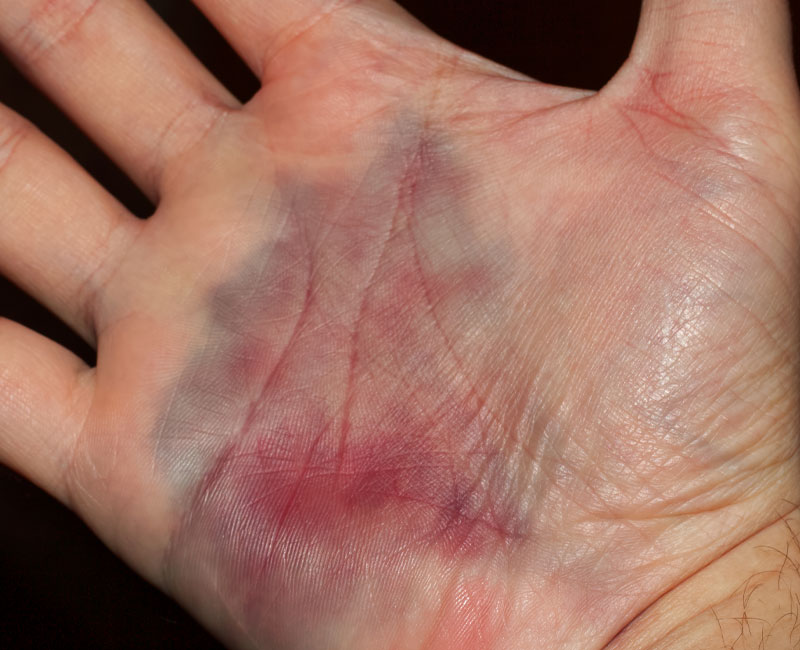
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/hematoma.jpg)
A hematoma is a closed wound where blood collects and fills a space inside your body because it can’t flow or drain out. And if blood fills a space, it can start pushing surrounding tissues outward. Minor hematomas are common, and you can have them almost anywhere in your body.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Hematomas are a concern when they’re larger, press on surrounding tissues or happen because of dangerous conditions. But smaller ones in noncritical places usually go away and aren’t a cause for worry.
There are several specific types of hematomas, mostly organized by where they happen. They include, but aren’t limited to, the following:
The bigger a hematoma is, the more likely it is to cause symptoms. They’re also likely to cause symptoms when they fill small spaces or are next to critical tissues. Some common symptoms of a hematoma include:
Advertisement
Hematomas inside your head are dangerous because there’s limited space for blood to fill. Blood filling that space will start pressing on your brain, eventually damaging it.
Warning symptoms from hematomas in your head include:
Internal bleeding inside your chest or abdomen that causes a large hematoma can also cause warning symptoms. They include:
Traumatic injuries are a key cause of hematomas. Blunt force trauma can easily cause them because bleeding inside your body doesn’t have anywhere to go.
But penetrating injuries can also cause hematomas. When you have some kind of penetrating injury, your body plugs the opening as soon as possible through a process called hemostasis. But if bleeding continues inside your body after the opening seals, hematomas can develop.
Some specific, injury-related conditions that can cause hematomas include:
You can also develop hematomas from internal bleeding with conditions that don’t involve an injury or external cause. Conditions that can do that include:
Advertisement
Hematomas usually don’t cause complications unless they involve a lot of bleeding. Complications that they can cause include:
Other complications may be possible, depending on your health history and other factors. Your healthcare provider is the best person to tell you more about your specific complication risks.
A healthcare provider can diagnose a hematoma using a physical exam and imaging tests. A physical exam is especially useful if there’s been an injury. During these exams, your provider will look for visible skin changes, listen with a stethoscope and feel (palpate) with their hands. Palpating is especially useful because hematomas feel different from normal, healthy tissues. Your provider may also ask questions about your symptoms, how and when they started, etc.
Imaging scans are helpful for finding hematomas because they let healthcare providers see inside your body. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the best at showing hematomas, especially deeper ones. But MRIs take a lot longer than other scans, so providers may use the following:
Advertisement
Depending on factors like your symptoms and health history, your provider may recommend other tests. They can tell you more about how these tests can help.
Smaller hematomas usually don’t need treatment or are treatable with simple home remedies. For simple surface bruising or a sprained or twisted joint, use the RICE method:
When hematomas are more serious, treatment starts with managing dangerous effects or complications. Examples include transfusing blood to make up for severe blood loss, or doing CPR to keep blood circulating if your heart stops.
When you’re not in imminent danger, treatment focuses on addressing whatever caused the hematoma. Examples include:
Advertisement
Your provider may recommend other treatments, depending on the details of your situation. They can explain the various options in detail and tell you about any possible complications or side effects.
What you can expect from a hematoma can vary depending on several factors. Its size and cause, your health history and many other factors can affect what you experience. Your healthcare provider can tell you more about what you can and should expect for your specific case. They can also tell you about the outlook for your condition and what you can do to improve it.
Most hematomas aren’t preventable because they happen unpredictably. But there are a few things you can do to reduce the odds of having them.
Hematomas can also happen from other chronic conditions. Talk to your healthcare provider about ways to prevent hematomas if you have a chronic condition that might cause them.
Taking care not to aggravate or worsen an injury that caused a hematoma is a key part of taking care of yourself. If you give it time to heal, that’s usually all you’ll need. If you have questions or concerns about how to help a hematoma heal, you should talk to a healthcare provider. They can tailor the information they provide so it’s accurate and helpful for your situation.
You should talk to or see a healthcare provider about hematomas if you have:
You should get emergency medical care if you have any symptoms of dangerous conditions that involve hematomas. These symptoms include, but aren’t limited to, the following:
Some questions you may want to ask your healthcare provider include:
Hematomas can range from minor to serious. The main things that determine how serious a hematoma is include:
A hematoma can be a bruise from bonking your shin on a piece of furniture or a dark purple spot underneath the nail of a toe that just got stepped on. But when hematomas are bigger, deeper or happen with certain symptoms, you shouldn’t ignore them.
If you have questions or concerns, talk to your healthcare provider. Timely diagnosis and care can make a lifesaving difference for severe hematomas. And the right response to self-treat and recover can help minor bumps and bruises fade away as your body heals.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Need care fast? Cleveland Clinic’s Express Care and Urgent Care locations treat everything from sprains to sinus infections — no appointment needed.
