Hemorrhagic strokes are medical emergencies. They happen when a blood vessel in your brain breaks and bleeds. They require immediate treatment and can be fatal. Call 911 (or your local emergency services number) immediately if you think you’re experiencing symptoms.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
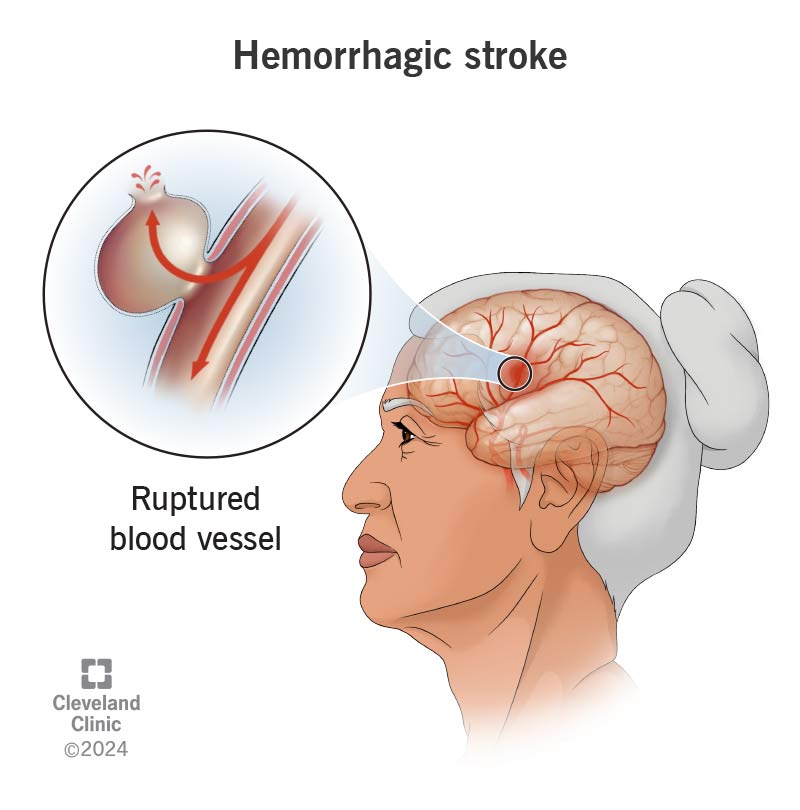
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/hemorrhagic-stroke)
A hemorrhagic stroke is a life-threatening emergency that happens when a blood vessel in your brain breaks (ruptures) and bleeds. A “hemorrhage” is the medical term for bleeding inside your body.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
The bleeding disrupts normal circulation in your brain and prevents it from getting the blood and oxygen it needs to survive and function. The stroke also adds extra pressure inside your brain, which can damage or kill brain cells.
Hemorrhagic (pronounced “hem-or-AJ-ICK”) strokes are particularly dangerous because they cause severe symptoms that get worse quickly. Without fast medical attention, these strokes often cause permanent brain damage and can be fatal.
If you think you or someone you’re with is having a stroke, immediately call 911 (or your local emergency services number). The sooner someone is diagnosed and treated, the more likely it is they’ll survive a stroke. Every second counts.
The symptoms of a hemorrhagic stroke can include one or more of the following:
Hemorrhagic strokes can cause lots of different symptoms. To recognize the warning signs in yourself or a loved one, remember the acronym BE FAST:
Advertisement
A transient ischemic attack (TIA) — sometimes called a “mini-stroke” — is like a stroke, but the effects are temporary. These are often warning signs that a person has a very high risk of having a true stroke soon. A person who has a TIA needs emergency medical care as soon as possible.
Anything that damages or breaks blood vessels in your brain can cause a hemorrhagic stroke. Having high blood pressure (hypertension) is the most common cause. That’s especially true if your blood pressure is very high or stays high for a long time.
Other conditions that can cause a hemorrhagic stroke include:
Hemorrhagic stroke can happen in one of two ways:
Anyone can experience a hemorrhagic stroke, but you have a higher risk if you:
You may have a higher stroke risk if you have a health condition that affects your circulatory system, including:
A healthcare provider will diagnose a hemorrhagic stroke with a neurological exam and tests, including:
Advertisement
The two main treatments for hemorrhagic strokes are medications and surgery.
There are many medications that providers use to treat hemorrhagic strokes. They work in one of two ways:
Accumulated blood from a stroke puts too much pressure on brain tissue around the bleeding blood vessel. You might need emergency surgery if the stroke increases your intracranial pressure. Your surgeon will remove the extra blood and relieve the pressure buildup on your brain.
Stroke rehab is an important part of treating a hemorrhagic stroke. You’ll need rehab to help you adjust to changes in your brain and body. You might need to regain abilities or adjust to new or different disabilities. You might need a combination of:
Advertisement
It’s hard for experts to estimate a life expectancy or survival rate for hemorrhagic strokes. That’s because everyone’s body and health are unique.
Strokes can be fatal, and they can cause permanent disabilities. But there’s no one standard recovery timeline or outlook that’s accurate for everyone.
Hemorrhagic strokes are more likely to be fatal than ischemic strokes. But that doesn’t mean you’ll definitely have a worse outcome than any other person.
Everyone’s body responds differently to a stroke. What you can expect (the prognosis) after a stroke depends on a few factors, including:
Your provider will tell you what to expect. They’ll help you set recovery goals and expectations that fit your unique health and situation.
Advertisement
Maintaining a healthy blood pressure level is the most important way to prevent a hemorrhagic stroke. If you have high blood pressure, your healthcare provider can help you manage it. They’ll suggest medications and changes to your daily routine that can keep your blood pressure in a safe range.
Other things you can do to reduce your risk of having a hemorrhagic stroke include:
Recovering and rehabbing after a stroke is hard work. Once you and your provider finalize your treatment plan, follow it as closely as possible. In general, you should:
Call 911 (or your local emergency services number) if you think you’re experiencing stroke symptoms again. Another stroke has an even higher risk of being fatal or causing severe complications. Don’t wait to call for help.
People who’ve had a stroke have an increased risk of other potentially serious complications, including:
Call emergency services or go to the ER if you think you’re experiencing any symptoms of these complications.
Hemorrhagic strokes can have a big impact on your life. Anything that can permanently affect your brain can be scary. If you think you’re experiencing stroke symptoms, get help right away. The faster a provider diagnoses and treats it, the better.
Once you’re safe and stable, you’ll start rehab. It’s hard work, but it’s worth it. Don’t ignore how you’re feeling, and share any frustrations with your providers and therapists. Your recovery might happen in small steps, but don’t forget to celebrate all of your successes.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
After a stroke, it’s essential to get treated right away. Cleveland Clinic’s stroke care specialists can help you manage recovery and improve your quality of life.
