A CT angiogram is a test that checks for blockages and other problems in your arteries. It’s a CT scan with the added benefit of contrast dye. A healthcare provider injects the dye into a vein in your arm. The dye flows through your blood vessels and makes them look bright on the CT images. This means it’s easier to see blood flow and spot issues.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
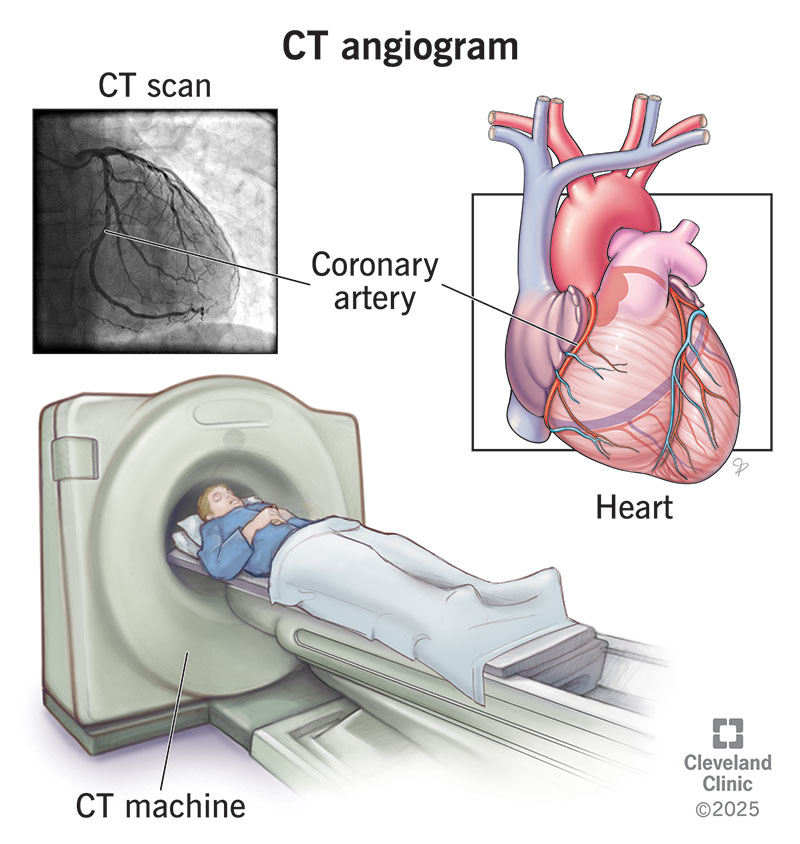
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/16899-ct-angiogram.jpg)
A computed tomography (CT) angiogram is a test that makes detailed pictures of your blood vessels and nearby tissues. The most common reason to have a CT angiogram is to see if you have narrowed or blocked coronary arteries (coronary artery disease). When done for these reasons, the test is sometimes called a coronary CT angiogram, or CCTA.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
But a CT angiogram is useful for many other purposes, too. For example, it can help diagnose:
Your provider may also use a CT angiogram to plan a procedure or surgery. For example, they might look at your coronary arteries before a procedure such as a heart valve replacement, heart bypass surgery or stent placement.
Technically, a CT angiogram is the picture the test produces. And CT angiography is the name of the imaging technique. But people often use both terms to refer to the test you go in to get. You might also see this test called CTA.
Advertisement
All CT scans produce detailed, 3D images of the inside of your body. This is because a scanner takes hundreds of 2D (flat) pictures. Then, a computer puts all these pictures together to form high-quality 3D images. But contrast dye is what makes the difference between a CT scan and CT angiography.
The combination of CT scanning and contrast dye produces “lit up” images of your blood vessels. Your healthcare provider can rotate each 3D image. It’s a bit like holding a model of your blood vessel in their hand. They can see each part of the vessel from different angles. This lets them get a close-up view to pinpoint any problems and plan treatment.
CT angiography is less invasive and has fewer risks than traditional angiography. For a traditional angiogram, a catheter moves inside your blood vessels until it reaches the part providers want to see. You don’t need this catheter for a CT angiogram. Based upon your age and other medical conditions, you may not be an ideal candidate for a CT angiogram and may still require a more invasive traditional angiography procedure.
The healthcare provider who requested your CT angiogram will tell you how to prepare. In general, you should tell your provider:
Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions to follow. These will tell you:
When you arrive, you’ll put on a hospital gown. You’ll also need to remove any jewelry or metal objects that you’re wearing. These could interfere with the test.
CT angiography is typically quick and painless. However, it does require an IV catheter to be inserted into your arm. You’re awake and don’t need anesthesia. You’ll lie on an exam table that moves through a large ring that looks a bit like a doughnut. You’re not as enclosed as you would be for an MRI.
During the test, you’ll need to stay very still so the scanner can take good pictures. A specially trained healthcare provider called a radiologic technologist will perform your test. They’ll explain each step and tell you exactly what you need to do (like when to hold your breath). Here are the general steps:
Advertisement
Advertisement
You can expect to be in the testing room for about 20 to 60 minutes, including prep time. You’ll spend about one to two minutes in the scanner. This should go by fast. But you might need to go through the scanner more than once so your provider can get all the pictures they need.
Depending on your needs and concerns, CT angiography may have some disadvantages. These include:
When your test is done, you can return to your usual routine. You should drink lots of water and other liquids. This helps flush the contrast dye out of your system.
CT angiography produces detailed images of your blood vessels and nearby tissues (including capillary beds). These images can show a wide range of issues, like plaque buildup, aneurysms and more. A radiologist will review and interpret these images. They’ll share the findings with the healthcare provider who requested your test. Your provider will schedule a time to go over the results with you.
Advertisement
You may need follow-up visits with your provider. You may also need further testing. Your provider will explain next steps. Don’t hesitate to ask questions about the results and what they mean for you.
Call your provider if:
No matter how many times someone says a test is quick or painless, you still might be nervous. That’s OK. It’s normal to get a bit worked up before any sort of exam. But remind yourself that a CT angiogram is there to help you. It lets your provider see what’s going on inside your blood vessels. The results can help you and your provider plan any needed treatments to support your health.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
When your heart needs some help, the cardiology experts at Cleveland Clinic are here for you. We diagnose and treat the full spectrum of cardiovascular diseases.
