Spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD) is a separating or tearing of a layer of your coronary artery. This slows blood flow to your heart. It can cause acute coronary syndrome, angina (chest pain) or a heart attack. You need immediate care for this life-threatening condition. Women are most at risk.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
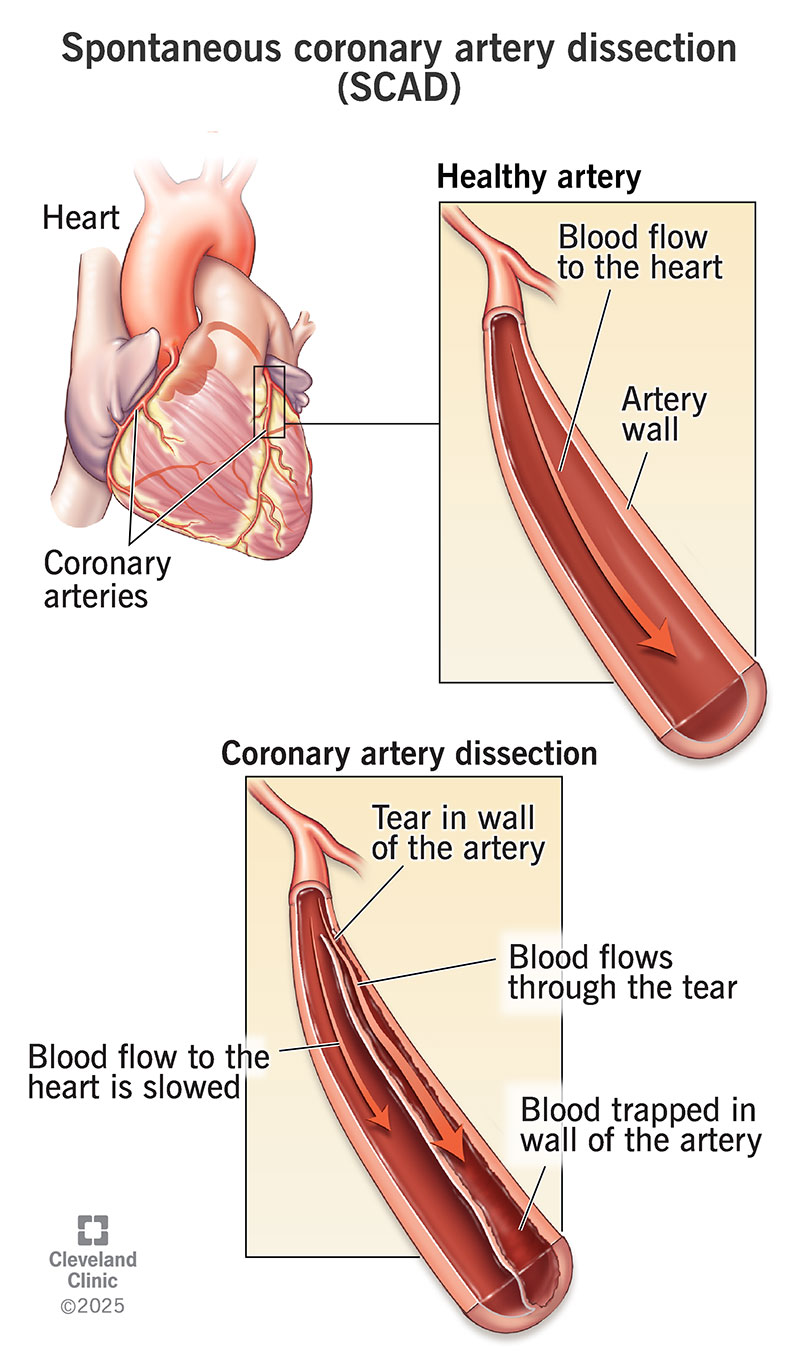
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/17503-spontaneous-coronary-artery-dissection)
Spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD) is when a coronary artery wall separates or tears without warning. The tear can occur in any one of the three layers of the coronary artery wall. Blood seeps between the layers, which trap it. This makes the artery bulge inward. The bulge blocks or slows blood flow to your heart. This reduces how much blood gets to your heart, which can cause chest pain.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
SCAD increases your risk of (and can cause) acute coronary syndrome. This term includes conditions that lead to a sudden drop in blood flow to your heart.
Medical experts aren’t sure how many people have this condition. They think there are people who have coronary artery dissection but don’t have a diagnosis. Some cases are too subtle for tests to detect. SCAD may account for up to 4% of all cases of acute coronary syndrome.
SCAD symptoms are like those of a heart attack. The most common symptom is chest pain or pressure. Other symptoms include:
Coronary artery dissection is an emergency. It can lead to a heart attack. Call 911 if you experience these symptoms.
Experts aren’t sure why spontaneous coronary artery dissection occurs. It’s different from a plaque rupture and traditional atherosclerotic disease. Many people who develop this artery tear don’t have risk factors for heart disease.
Possible stressors or triggers may include:
Advertisement
Most people who have a spontaneous coronary artery dissection are females in their 40s and 50s. Males account for fewer than 1 out of 10 cases.
People with certain conditions may be more prone to coronary artery dissection. These conditions include:
Following these steps may lower your risks:
A lack of blood flow from spontaneous coronary artery dissection can cause a heart attack. When your heart isn’t getting enough blood because of SCAD, it can’t pump enough blood to your body, either (heart failure). This can lead to cardiogenic shock.
When your heart muscles can’t get enough blood, they can’t beat properly. This can lead to an abnormal heart rhythm and sudden cardiac death.
If you have chest pain or other signs of a heart attack, your provider may use these tests to make a SCAD diagnosis:
Spontaneous coronary artery dissection treatment may include medicine or procedures.
SCAD treatment includes medicines like:
Most SCADs heal without intervention. But a little more than 1 out of 10 people with this condition need better blood flow. They need urgent care in a hospital for this. These treatments may include:
Because of the risk of another SCAD or heart attack, you may be in the hospital for three to five days. With treatment, a tear heals in most people in several weeks. Recovery is longer if you have a procedure.
Call 911 or your local emergency service number if you think you’re having a heart attack. You should call your provider if you have:
After a coronary artery dissection, you’ll need regular follow-ups with a heart specialist. This may include imaging tests.
Advertisement
You may want to ask your healthcare provider:
Most people with SCAD improve with medicines and have a good prognosis (outlook).
But spontaneous coronary artery dissection increases your risk of:
If you’ve had an artery tear, you may need to restrict certain physical activities to prevent another. Also, your healthcare provider may recommend cardiac rehab. This improves your heart health and teaches you how to move safely.
People rarely die from a spontaneous artery dissection.
Having chest pain can be scary. Most people don’t expect this if they have a low risk of heart problems. But you should call 911 or your local emergency services number anytime you have heart attack symptoms. Your provider will closely monitor your heart health. If you feel anxiety about this coming back, talk to your provider. They may direct you to resources that can help.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
When you need treatment for coronary artery disease, you want expert care. At Cleveland Clinic, we’ll create a treatment plan that’s personalized to you.
