A magnetic resonance angiogram (MRA) is a noninvasive test that allows your healthcare provider to see your blood vessels and blood flow. They can use an MR angiogram to diagnose a condition, like atherosclerosis or blood clots. They can do MRA testing with or without a contrast dye. An MRA is an alternative to an invasive angiogram.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
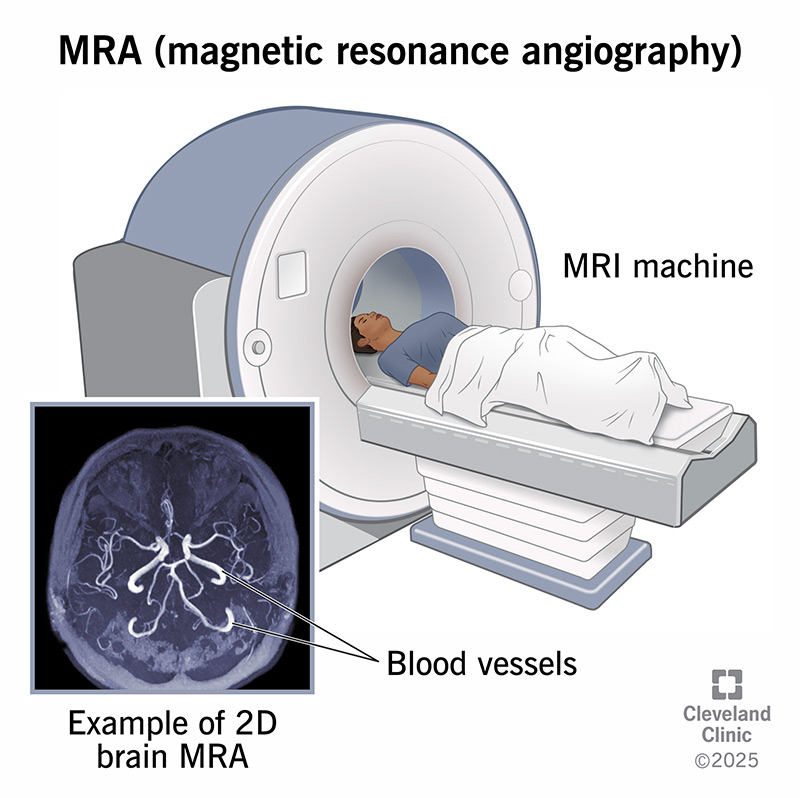
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/mra-illustration)
Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is an imaging test that shows your blood vessels and blood flow. An MRA is a type of MRI that focuses on your blood vessels (arteries and veins) specifically.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
An MRA can detect narrowing, widening or blockages in your blood vessels in a noninvasive way. This is unlike typical angiography, which involves inserting a catheter (tube) into a blood vessel to reach an artery.
Your healthcare provider can use MRA testing to diagnose a vascular problem, like a narrow artery. They can also use the information from an MRA to monitor changes in blood vessels and plan surgery.
They can use a magnetic resonance angiogram to look at your:
Your provider can use an MRA test to diagnose multiple conditions, including:
A brain MRA can detect the following issues:
Healthcare providers may also use a brain MRA to evaluate secondary headaches.
Different types of magnetic resonance angiography include:
Advertisement
Magnetic resonance angiography uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to create images. Your provider can see these images on a computer. Unlike an X-ray, an MRA doesn’t use radiation. It gets information from the energy your body gives off in a magnetic field.
Your healthcare provider will ask certain questions and go over your health history before a magnetic resonance angiogram, including if:
Follow your provider’s instructions for eating, drinking and taking medicine before your MRA test.
If you’re going to take a sedative before the scan, you’ll need someone to drive you home after.
In general, during an MRA, you can expect the following:
An MRA usually takes 20 to 60 minutes to complete.
MRA is safe and noninvasive, overall. It doesn’t use radiation. An MRA doesn’t put anything into your body other than a contrast dye. If you’re at risk of problems from the dye — like if you have kidney failure — you can have the scan without it.
Advertisement
Some people can have side effects from the contrast dye, like a headache, upset stomach or an allergic reaction. This is rare.
If you took a sedative to relax, you’ll need someone to drive you home. If you didn’t take a sedative, you can drive yourself and go back to work or other activities right away.
It will most likely take a few days for a radiologist to review your MRA scan and send the results to your healthcare provider. Contact your provider if you don’t hear back after a week.
Your healthcare provider will tell you if you have an issue in your blood vessels or another area they were examining. Based on your symptoms, they may have been looking for a certain condition. An MRA can confirm a condition and show how severe it is.
If you read the report, you may see the term “unremarkable.” This means the test was normal — they didn’t find anything concerning.
The machine that’s involved in an MRA can be intimidating. But you can wear headphones to soften the noise and take a sedative if the tight space makes you uncomfortable. The only thing you’ll feel going into your body is an IV if you’re receiving a contrast dye. An MRA gives your healthcare provider valuable information about your body. This helps them make a diagnosis, so you can get the care you need.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
When your heart needs some help, the cardiology experts at Cleveland Clinic are here for you. We diagnose and treat the full spectrum of cardiovascular diseases.
