Urinary urgency is when you suddenly have to pee, and you feel like you can’t hold it. There are many possible causes, including UTIs. But it’s important to have a healthcare provider make an official diagnosis so you can get the most appropriate treatment.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
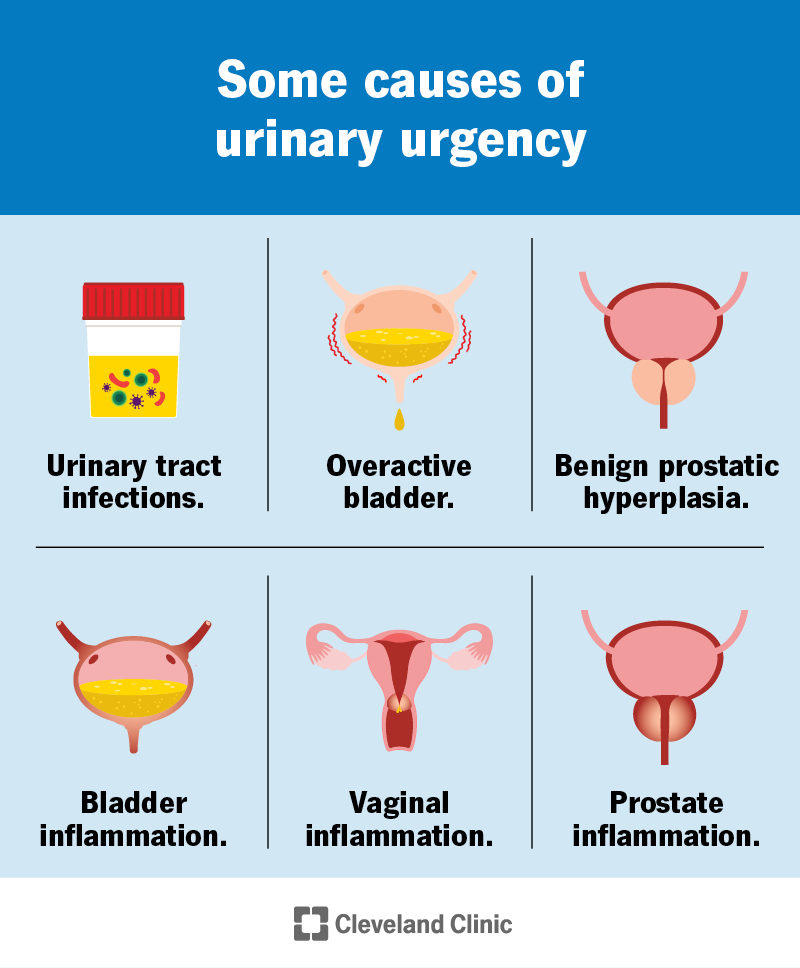
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/Images/org/health/articles/urinary-urgency)
Urinary urgency is a sudden, uncontrollable need to urinate (pee). Once you feel the need to pee, you have a very short amount of time to get to a bathroom before you leak pee (urinary incontinence).
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
There are many possible causes of urinary urgency. But the good news is that most causes aren’t serious, and healthcare providers can often treat the cause.
Some of the most common causes of urinary urgency include:
Other causes of urinary urgency may include:
Other factors may contribute to urinary urgency but may not be the main cause. This may include:
Advertisement
Treating urinary urgency depends on its cause. But you may be able to help manage it with:
You may need to drink fewer fluids and avoid alcohol and caffeinated drinks, such as coffee, tea or soda pop. Quitting smoking and maintaining a healthy weight for you can also help.
It can help to keep a bladder, fluid and food diary to try to identify patterns or triggers. Record everything you eat and drink and also when you pee or feel a strong urgency. See if the bladder problems correlate with certain foods or drinks.
You use the bathroom at set times throughout the day to prevent your bladder from getting too full, such as every two hours. It’s important that you pee to empty your bladder, even if you don’t feel like you have to go.
Kegel exercises (pelvic floor exercises) help strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. A pelvic floor physical therapist will teach you the proper techniques and may use biofeedback to ensure you’re working out the proper muscles.
Medications can help treat many different causes of urinary urgency. A healthcare provider may prescribe antibiotics to get rid of a UTI, alpha-blockers to relax your prostate muscle or anticholinergic or beta-3 adrenergic medications to relax your bladder muscles.
A provider may recommend specific treatments according to your urinary urgency cause. You may need a urinary catheter to drain your bladder.
Botulinum toxin (Botox®) shots in your bladder or functional electrical stimulation (nerve stimulation) can help treat an overactive bladder.
There are also many procedures to reduce the size of your prostate.
It depends on what’s causing urinary urgency. But your symptoms may get worse, and you may develop urinary incontinence.
Untreated UTIs may spread to other parts of your body, including your kidneys or prostate. In rare cases, they may even cause sepsis.
Urinary urgency can have a big impact on your quality of life. It’s a good idea to talk to a healthcare provider if you have urinary urgency symptoms.
You should also reach out to a provider if you have urinary urgency and you:
A healthcare provider will usually:
Advertisement
They may also recommend tests, including:
Many different conditions may feel like a UTI but aren’t. These include:
Urinary urgency is a common symptom of many different conditions. But it can be a challenge for many people to talk about changes to their bathroom habits, even to a healthcare provider. However, a provider can determine the cause of urinary urgency and work with you to develop the best treatment plan without judgment. They’ll reassure you that while urinary urgency is common, you shouldn’t feel embarrassed.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s primary care providers offer lifelong medical care. From sinus infections and high blood pressure to preventive screening, we’re here for you.
