Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) is a rare vascular disease involving abnormal cell growth in artery walls. It most commonly affects arteries that supply blood to your kidney and brain. The symptoms of FMD vary depending on the affected arteries. But high blood pressure is a common symptom. Severe cases can lead to aneurysm and stroke.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
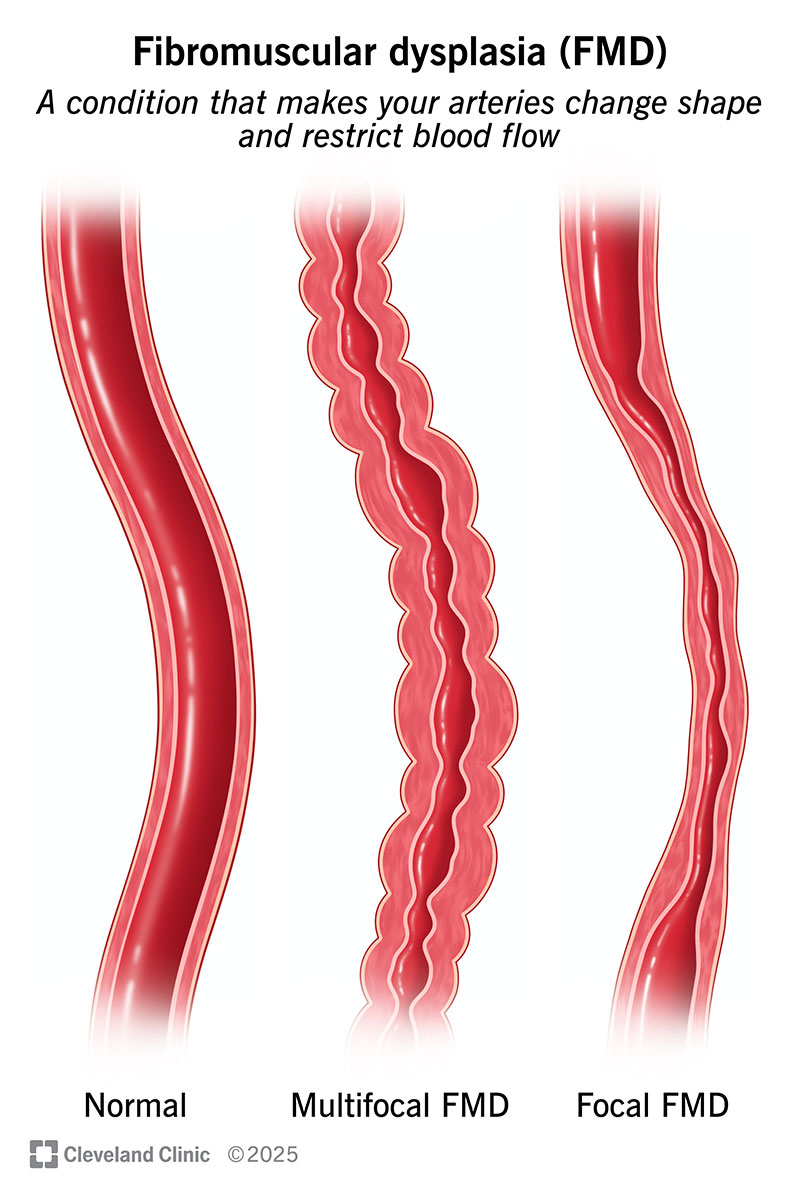
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/17001-fibromuscular-dysplasia-illustration)
Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) is a rare condition that makes your arteries narrow, bulge or develop a beaded appearance. This can restrict blood flow, which can lead to health complications.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
FMD commonly affects your renal and carotid arteries. But it can affect any artery in your body.
Anyone can develop FMD. But more than 90% of cases are in females.
There are two types of fibromuscular dysplasia, based on the appearance of your arteries during diagnostic tests:
FMD symptoms vary based on which arteries are affected. If you have a mild case, you might not have any symptoms.
Symptoms of FMD may include:
Scientists don’t know what causes FMD, but some cases have been linked to:
Advertisement
Fibromuscular dysplasia may be associated with other conditions, including:
FMD can lead to serious complications, like:
It’s important to learn the signs and symptoms of these complications.
Your healthcare provider may find signs of FMD during a routine physical examination. Or your provider may discover it while looking at the results of imaging tests for other reasons.
If your provider suspects the condition, a vascular ultrasound and/or angiography can diagnose it.
Some people don’t get an FMD diagnosis until they have an artery dissection or aneurysm rupture.
There’s no cure for FMD. FMD treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing complications. It varies depending on the affected arteries and the severity. Options may include:
You’ll need to have regular appointments to check on your arteries. It’s also important to make sure your treatment is working.
Your healthcare provider will educate you about symptoms that need immediate medical attention. This varies depending on the affected arteries.
There’s not a lot of research on how fibromuscular dysplasia affects life expectancy. In general, research shows that it doesn’t get worse over time. But it can lead to serious complications, like artery dissection and stroke.
Your healthcare provider will give you a better idea of what to expect based on your unique situation. You can help take charge of your health with the following strategies:
You may want to join advocacy organizations and support groups. These opportunities can connect you with other people who have the same condition. They also may help raise awareness of FMD.
Living with fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) requires you to stay on top of your health. But you’re not alone. Your healthcare team will help you develop a plan to manage symptoms and complications. They’ll tell you about warning signs to look out for. And they’ll recommend lifestyle changes that can help manage issues like high blood pressure. Lean on them for support.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Vascular disease may affect your life in big and small ways. Cleveland Clinic’s specialists treat the many types of vascular disease so you can focus on living.
