A blood glucose test measures the level of glucose (sugar) in your blood. The test can involve a finger prick or a blood draw from your vein. Healthcare providers most commonly use blood glucose tests to screen for Type 2 diabetes, which is a common condition.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
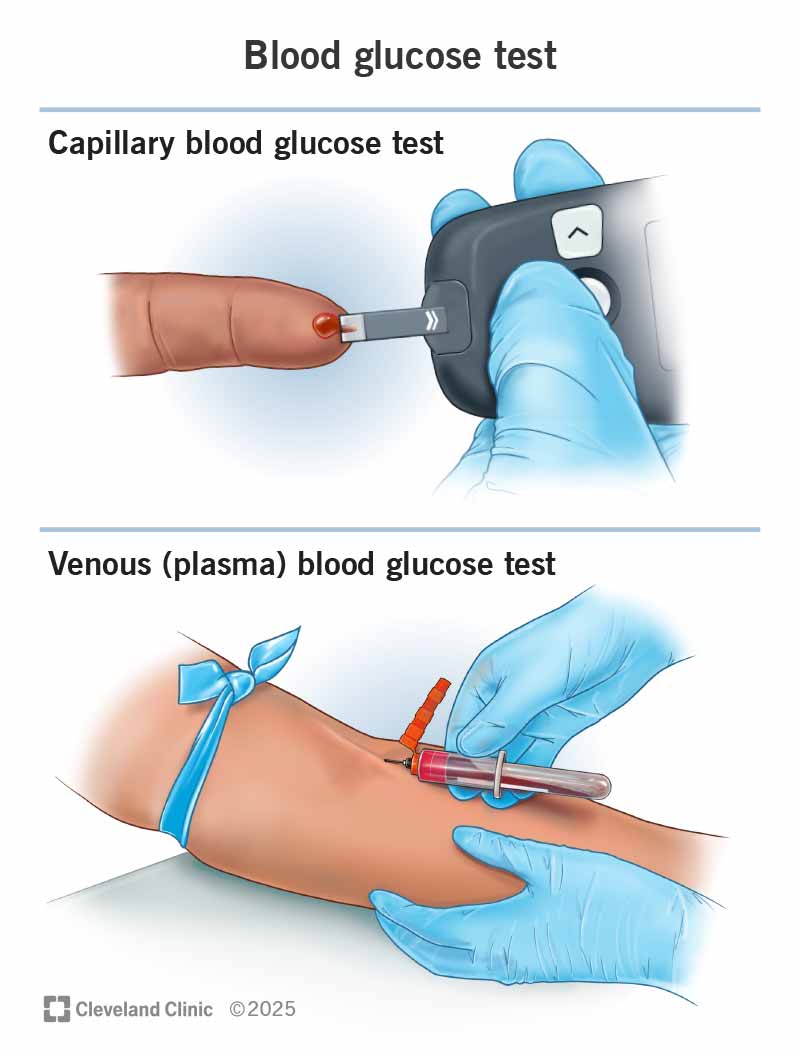
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/12363-blood-glucose-test)
A blood glucose test mainly screens for diabetes by measuring the level of glucose (sugar) in your blood.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
There are two main types of blood glucose tests:
Venous blood glucose tests are generally more accurate than capillary blood glucose tests.
Other types of blood glucose tests include:
Some glucose (sugar) comes from carbohydrates in the food and drinks you consume. Your liver releases some, as well. Glucose is your body’s main source of energy. Your blood carries glucose to all your body’s cells.
Advertisement
Several bodily processes help keep your blood glucose in a healthy range. Insulin, a hormone, is key to maintaining healthy blood sugar.
If you have high glucose levels (hyperglycemia), it usually means you have diabetes. Diabetes develops when your pancreas doesn’t make any or enough insulin, or your body isn’t using insulin properly.
There are four main reasons why you may need a blood glucose (sugar) test:
The most common use of a blood glucose test is to screen for Type 2 diabetes (T2D). If you have risk factors, your provider will likely recommend regular screening no matter your age. The American Diabetes Association recommends regular screening for anyone age 35 or older.
If you’re getting a fasting blood glucose test, don’t eat or drink anything except water for eight to 12 hours before the test.
If your blood glucose test is part of a basic or comprehensive metabolic panel, you may also need to fast for several hours before your blood draw. In any case, your provider will let you know if you need to follow any special instructions.
You can expect the following during a venous glucose test, or blood draw:
You can expect the following during a capillary blood glucose test (finger prick):
Advertisement
In most cases, you should have your venous blood glucose test results within one or two days.
Capillary blood glucose tests show the results within seconds via the glucose meter.
A healthy blood glucose level for someone without diabetes is 70 to 99 mg/dL (3.9 to 5.5 mmol/L).
Values between 50 and 70 mg/dL (2.8 to 3.9 mmol/L) for people without diabetes can be “normal,” too.
If your blood glucose level is 100 to 125 mg/dL (5.6 to 6.9 mmol/L), it usually means you have prediabetes. People with prediabetes have up to a 50% chance of developing Type 2 diabetes over the next 5 to 10 years. But you can take steps to try to reverse prediabetes.
If your fasting blood glucose level is 126 mg/dl (7.0 mmol/L) or higher on more than one testing occasion, it usually means you have diabetes. People with Type 1 diabetes usually have very high blood glucose levels (200 mg/dL, or 11.1 mmol/L, or higher).
In either of these cases, your provider will likely order an A1c test before making a diagnosis. An A1c shows your average blood sugar over a few months.
Other causes of high glucose levels may include:
Advertisement
A blood sugar result of 70 mg/dL or lower is considered too low for most adults who have diabetes.
Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) episodes are common in people with Type 1 diabetes. They can also affect people with Type 2 diabetes who take certain medications. They’re much less common in people who don’t have diabetes.
If you don’t have diabetes, low blood glucose levels may be a sign of:
These conditions typically cause frequent low blood sugar episodes. A single low blood sugar test result usually isn’t a cause for concern in people who don’t have diabetes.
Seeing an abnormal test result can be stressful. Know that having a high or low glucose level doesn’t necessarily mean you have a medical condition and need treatment. Healthcare providers rely on more than a single blood glucose test to diagnose diabetes and other conditions. Don’t hesitate to ask your provider questions. They’re available to help you.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Whether you’ve been living with diabetes for years or you’re newly diagnosed, you want experts you can trust. Our team at Cleveland Clinic is here to help.
