Your pancreas is a large, tadpole-shaped gland situated deep in your belly. It plays an important role in digestion and blood sugar regulation. Pancreatic disease can be hard to diagnose due to the location of the organ. But there are things you can do to reduce your risk for these conditions.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
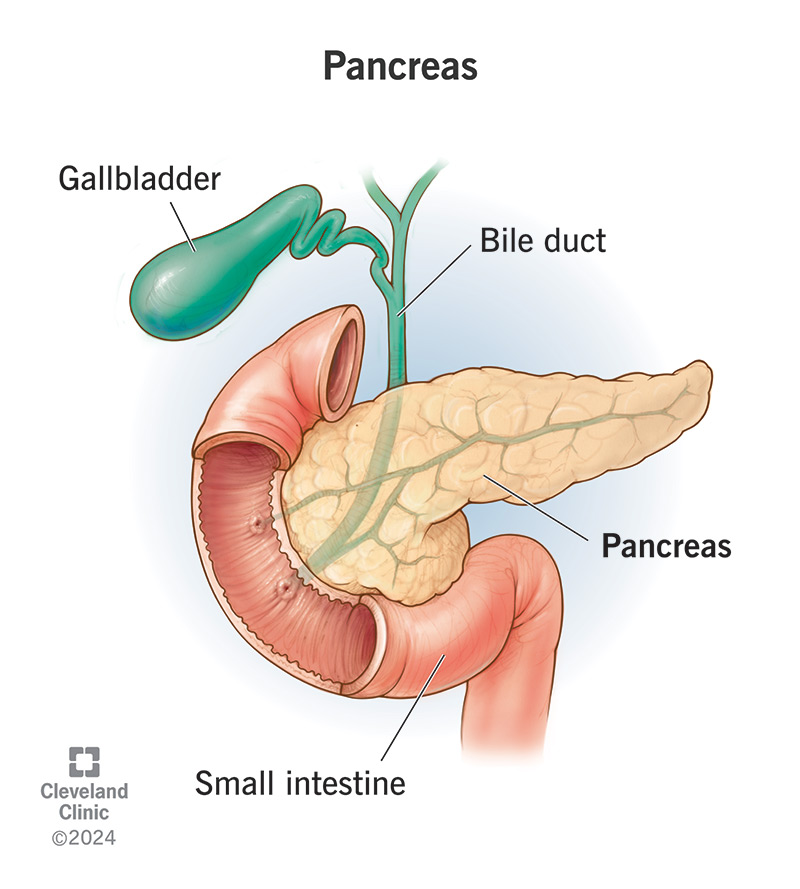
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/Images/org/health/articles/21743-pancreas.jpg)
The pancreas is a large gland in the back of your abdomen (belly). It’s part of your digestive system and your endocrine system. Your pancreas is a dual organ — like a factory with two production lines. It makes:
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Your pancreas helps with digestion and releases hormones that regulate your blood sugar. It also plays a role in supporting other organs like your heart, liver and kidneys.
Your pancreas makes about 1 to 4 liters (L) of enzyme-rich juice each day to help you digest the foods you eat. The exact amount varies depending on how much food you eat.
After you eat, you probably don’t think much about how your food gets digested unless you develop indigestion. But several organs actually work together to help you break it down. Here’s how it works when food enters your stomach:
Your pancreas makes hormones (like insulin and glucagon) that help control the levels of sugar in your bloodstream. When your blood sugar is too high, your pancreas makes insulin to lower it. When your blood sugar is too low, your pancreas makes glucagon to increase it.
Advertisement
Your body needs balanced blood sugar to run properly, and to keep organs like your heart, liver, kidneys and brain working well.
Your pancreas sits behind your stomach and in front of your spine. Your gallbladder, liver and spleen surround your pancreas.
The head of your pancreas is on the right side of your body. It’s tucked beside the curve of your duodenum — that’s the very first part of your small intestine, where your food goes when it leaves your stomach. The tail of your pancreas extends over to the left side of your body, near your spleen.
Parts of the pancreas include the:
Your pancreas resembles a tadpole — thick on one end and thin at the other, and the outer texture is bumpy like a cob of corn. It’s around 6 inches (in) long — about the length of your hand.
How much does the pancreas weigh?
On average, a healthy human pancreas weighs around 91.8 grams (0.20 pounds). That’s about the same as a deck of playing cards.
The following disorders can affect the pancreas:
Symptoms of pancreas problems may include:
Because your pancreas sits deep in your abdomen, it’s not easy for providers to check it through a physical examination. So, they may use pancreas function tests like:
Advertisement
Your provider may use surgery to look for issues in your pancreas.
Healthcare providers treat pancreas conditions in different ways, depending on the condition:
Some people may need a pancreas transplant or pancreatectomy (surgical removal of some or all of their pancreas). Less commonly, people may have a transplant of islets of Langerhans cells (pancreatic cells that make insulin and glucagon) into their liver to maintain insulin function.
You can help reduce your risk of pancreatic conditions by:
Advertisement
Yes, you can live without your pancreas. But you’ll need to take enzyme pills to digest food and insulin shots to control your blood sugar for the rest of your life. Though pancreatic removal is rare, surgeons may remove your entire pancreas if you have pancreatic cancer, major injury to your pancreas or severe pancreatitis.
Chances are, you don’t think about your pancreas much unless you develop a condition that affects its function. Tucked away in the back of your belly, your pancreas is like a factory with two production lines — each focused on different jobs. Getting the proper nutrition and avoiding things like smoking and drinking too much can help keep your pancreas healthy for the long haul.
Advertisement
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic's health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability, and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic's health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability, and up-to-date clinical standards.
If you have issues with your digestive system, you need a team of experts you can trust. Our gastroenterology specialists at Cleveland Clinic can help.
