A basic metabolic panel (BMP) is a helpful and common test that measures several important aspects of your blood, like electrolytes and blood sugar. Healthcare providers often use it as a go-to blood test to assess your general physical health. It can also help diagnose, screen for and monitor certain health conditions.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
A basic metabolic panel (BMP) is a blood test that measures eight different substances in your blood. The panel provides helpful information about your body’s chemical balance and metabolism (how your body transforms the food you eat into energy).
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Healthcare providers often use a BMP as a go-to blood test and to help diagnose, screen for or monitor certain health conditions.
A basic metabolic panel measures the following substances in your blood:
A BMP also measures the following four electrolytes:
Advertisement
Healthcare providers often order a basic metabolic panel to get a broad assessment of your overall physical health. With eight individual measurements, it can check several body functions, including:
A BMP can provide helpful information in many different situations, including:
You’ll likely need to fast for at least eight hours before your basic metabolic panel blood test. Fasting means not eating or drinking anything except water. Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions when they order the test for you.
You can expect the following during a blood test:
The entire procedure usually takes less than five minutes.
After a healthcare provider has collected your blood sample, they’ll send it to a laboratory for testing. Your provider will then share the results with you.
Blood tests are a very common and essential part of medical testing. There’s very little risk to having blood tests. You may have slight tenderness or a bruise at the site of the blood draw. This usually resolves quickly.
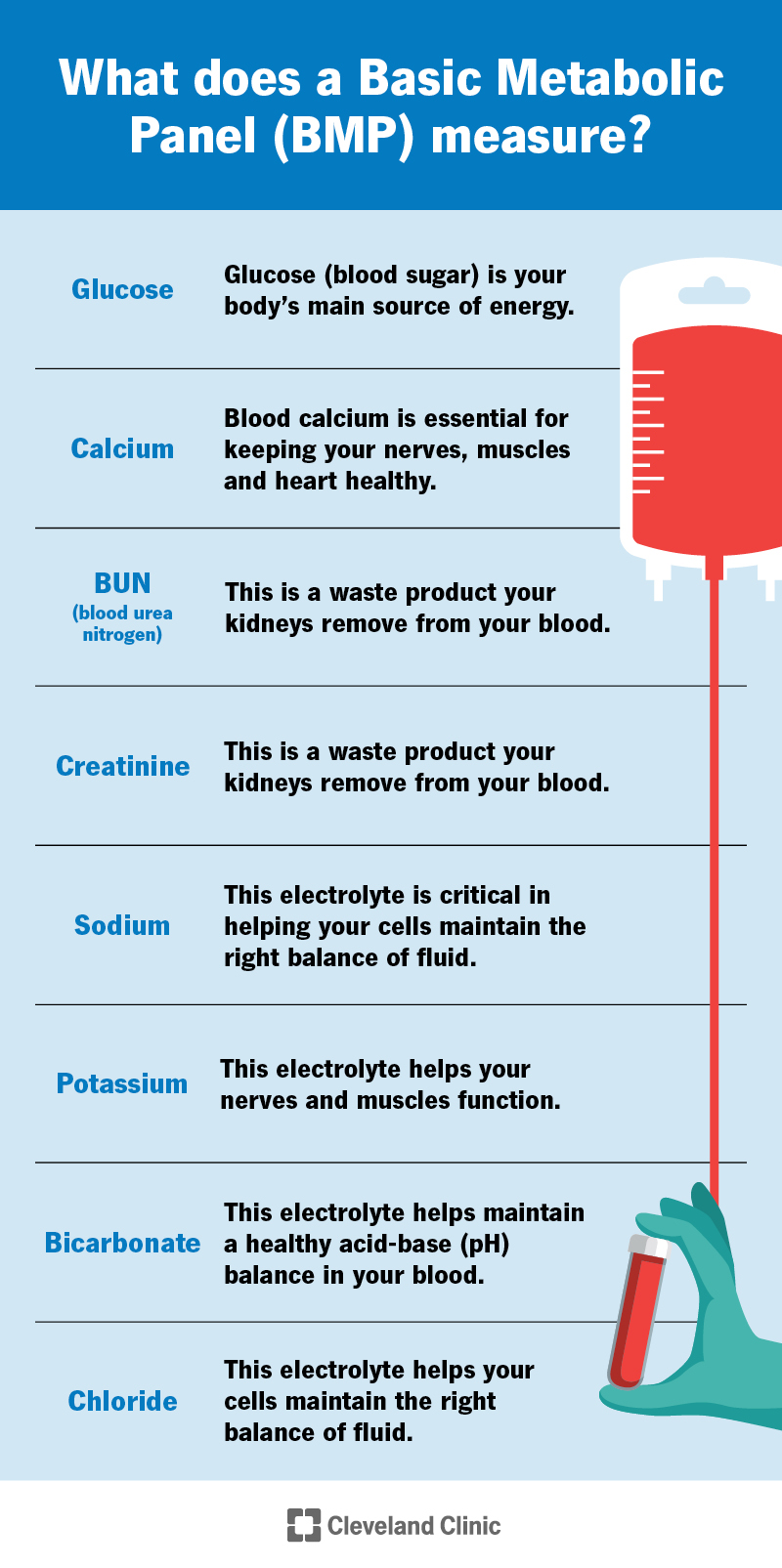
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/22020-basic-metabolic-panel-bmp)
In most cases, you should get the results of your BMP within one to two business days, though it could take longer.
If you’re receiving care in an emergency room and get a BMP, your care team should have the test results within hours.
Blood test reports, including basic metabolic panel test reports, usually provide the following information:
Laboratories may have different reference ranges for each aspect of a BMP. When you get your blood test results back, there will be information that indicates what that lab’s normal ranges are.
Advertisement
In general, normal ranges for a BMP include:
If you have any questions about your results, be sure to ask your healthcare provider.
If you have an abnormal result, your healthcare provider will likely recommend additional tests to confirm or rule out a specific diagnosis. Providers rarely make a diagnosis solely based on the results of a BMP.
If any single BMP result or a combination of results falls outside of the normal range, it may point to — but not guarantee — many different, long-term (chronic) health conditions, including:
A BMP can also help diagnose acute (sudden and severe) conditions, like:
If one of your BMP results is abnormal, it doesn’t necessarily mean that you have a medical condition. Other factors — like the foods you eat, certain medications and health conditions — can affect your test results. There could’ve also been an error in the processing of the test.
Advertisement
Your healthcare provider will consider your medical history and current medications when they assess your results. They’ll let you know if you need further testing.
A basic metabolic panel (BMP) is a helpful and common blood test that broadly assesses your physical health. Know that having an abnormal level in one of your BMP results doesn’t necessarily mean you have a medical condition. Many other factors can affect your results. Approximately 1 in 20 healthy people will have a result outside of the normal range. Your healthcare provider will let you know if you need further tests. Don’t hesitate to ask your provider questions. They’re available to help you.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s primary care providers offer lifelong medical care. From sinus infections and high blood pressure to preventive screening, we’re here for you.
