Leiomyosarcoma (LMS) is a type of soft tissue sarcoma. It’s a rare, aggressive cancer that starts in the smooth muscles of your hollow organs (like your bladder, stomach, uterus, intestines or blood vessels). Treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy and targeted therapy. Outlook is more favorable when detected and treated early.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
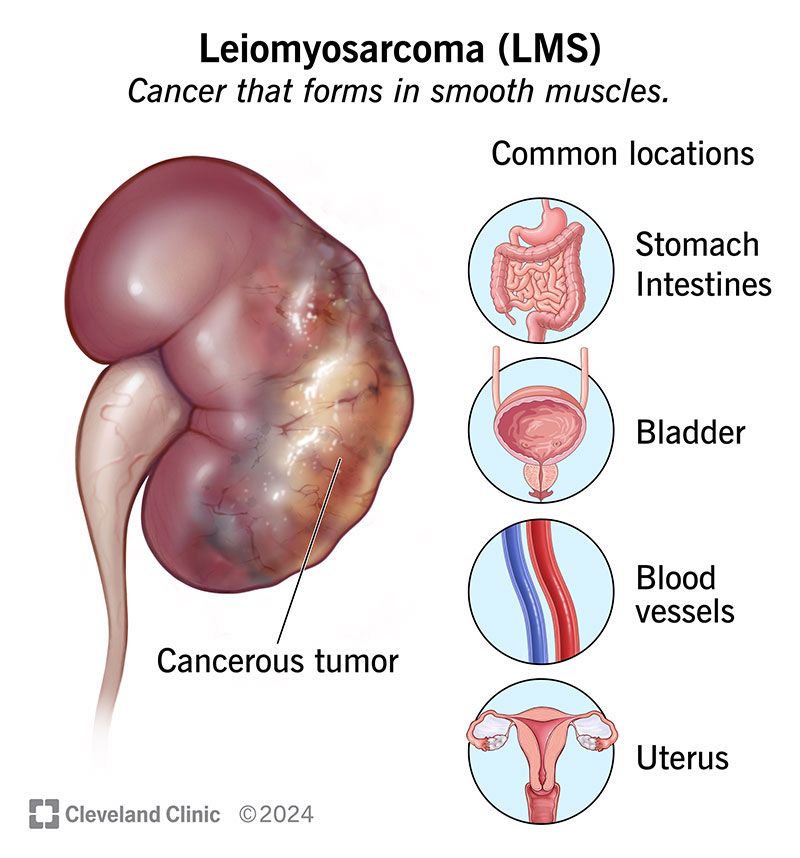
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/Images/org/health/articles/leiomyosarcoma)
Leiomyosarcoma (LMS) is a rare, aggressive cancer that forms in smooth muscles. Smooth muscles are involuntary muscles located in various parts of your body. You have smooth muscles in your hollow organs, including your:
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
LMS cancer is a type of soft tissue sarcoma. It grows quickly and can double in size in as little as one month. The cancer cells travel through your bloodstream and can spread to any soft tissue in your body.
Some people don’t develop LMS symptoms until the disease reaches an advanced stage. In these cases, leiomyosarcoma is life-threatening. But when it’s detected and treated early, recovery is possible.
A cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming. Lean on your healthcare team. They can recommend resources and support groups that may help you on your journey.
There are three subtypes of leiomyosarcoma:
In the United States, about 15,000 people receive a soft tissue sarcoma diagnosis every year. Leiomyosarcoma accounts for 10% to 20% of those cases. About 1 in every 100,000 people in the U.S. develops LMS cancer.
Advertisement
Leiomyosarcoma can affect anyone. But it’s most common in females over age 5.
Leiomyosarcoma symptoms vary depending on the size and location of the tumor. Some people don’t experience symptoms early on, but may notice certain signs as the tumor grows, like:
Leiomyosarcoma in your digestive system may cause:
Uterine leiomyosarcoma can cause:
Experts aren’t exactly sure what causes leiomyosarcoma. It could be hereditary (meaning you inherited altered genes from your parents), or it could be because your own genes changed, causing normal cells to grow out of control and become cancer cells.
Researchers have found links between LMS and these genetic conditions:
A healthcare provider will do a physical examination and ask you about your symptoms. They’ll also review your medical history, including any past or current health conditions.
Your provider will take imaging tests to see inside your body and determine the size and location of the tumor. These imaging tests may include:
Your provider will likely need to do a biopsy, too. When testing for LMS, providers try to take small samples from several parts of the cancer. Once they have the tissue samples, they’ll send them to a pathologist for testing.
Leiomyosarcoma treatment depends on the location and size of the tumor. Options include:
Recovery times can vary drastically depending on several factors, including:
Advertisement
It could take several weeks or months to fully recover. Even after you’re feeling better, you’ll still need regular checkups to monitor your health and reduce the risk of cancer recurrence (return).
The outlook for leiomyosarcoma varies significantly depending on the stage, size and location of the tumor. In some cases, LMS is curable, especially when detected and treated early.
Treatment is more complicated when it’s discovered in the later stages. Advanced, Stage 4 leiomyosarcoma can be managed with treatment, but not cured.
Leiomyosarcoma survival rates depend on several factors like:
The following shows five-year survival rates for three different stages of LMS (localized, regional and distant):
| Cancer stage | Description | Five-year survival rate | What this means |
|---|---|---|---|
| Localized | Cancer hasn’t spread beyond where it started. | 63% | Sixty-three of 100 people with localized LMS will still be alive five years after their diagnosis. |
| Regional | Cancer has spread to surrounding tissues and possibly to nearby lymph nodes. | 36% | Thirty-six out of 100 people with regional LMS will still be alive five years after their diagnosis. |
| Distant | Cancer has spread to distant areas of your body. | 14% | Fourteen out of 100 people with distant LMS will still be alive five years after their diagnosis. |
| Cancer stage | |||
| Localized | |||
| Description | |||
| Cancer hasn’t spread beyond where it started. | |||
| Five-year survival rate | |||
| 63% | |||
| What this means | |||
| Sixty-three of 100 people with localized LMS will still be alive five years after their diagnosis. | |||
| Regional | |||
| Description | |||
| Cancer has spread to surrounding tissues and possibly to nearby lymph nodes. | |||
| Five-year survival rate | |||
| 36% | |||
| What this means | |||
| Thirty-six out of 100 people with regional LMS will still be alive five years after their diagnosis. | |||
| Distant | |||
| Description | |||
| Cancer has spread to distant areas of your body. | |||
| Five-year survival rate | |||
| 14% | |||
| What this means | |||
| Fourteen out of 100 people with distant LMS will still be alive five years after their diagnosis. |
Survival rates are only estimates. Researchers base them on the experiences of people who had LMS in the past. Survival rates can’t tell you how long you’ll live or how well you’ll respond to treatment.
To learn more about survival rates and what they mean for you, talk to your healthcare provider.
Advertisement
Currently, there’s no known way to prevent leiomyosarcoma. But you can reduce your risk by avoiding risk factors whenever possible. Known leiomyosarcoma risk factors include:
If you’re undergoing treatment for leiomyosarcoma, call your healthcare provider whenever you notice new or worsening symptoms. For example, if you notice any changes to your tumor — or if you develop severe pain, sudden weight changes or other symptoms — seek prompt medical care.
If you have leiomyosarcoma, talking with your healthcare provider can inform, empower and help you take control of your health. Here are some questions you may want to ask:
A cancer diagnosis of any kind can turn your world upside down. When it’s a rare disease like leiomyosarcoma, it can feel especially isolating. You might feel like no one really understands what you’re going through. Joining a local or online support group can help you feel less alone and meet others who are going through similar challenges. Your healthcare team is here to help. Talk to them any time you have questions or need a listening ear.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Sarcomas are a rare form of cancer affecting your bones and soft tissues. Our specialists use the latest treatments to care for these types of tumors.
