Genetic mutations are changes to your DNA sequence that happen during cell division when your cells make copies of themselves. Your DNA tells your body how to form and function. Genetic mutations could lead to genetic conditions like cancer, or they could help humans better adapt to their environment over time.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
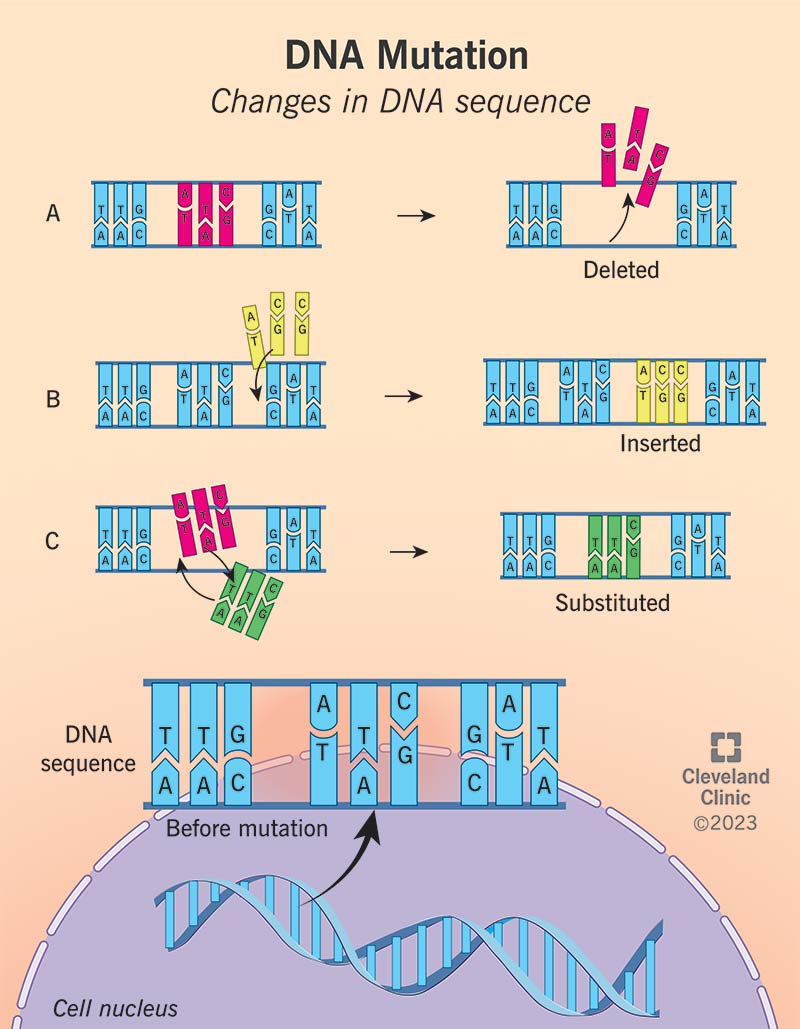
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/23095-genetic-mutations)
A genetic mutation is a change in a sequence of your DNA. Your DNA sequence gives your cells the information they need to perform their functions. If part of your DNA sequence is in the wrong place, isn’t complete or is damaged, you might experience symptoms of a genetic condition.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Genetic mutations occur during cell division when your cells divide and replicate. There are two types of cell division:
Genetic mutations occur during cell division. When your cells divide, they handwrite your body’s instruction manual by copying the original document word for word. There’s a lot of room for error during cell division because your cells might substitute (replace), delete (remove) or insert (add) letters while they’re copying. If you have an error (genetic mutation), your genetic instruction manual for your cells may not be readable by the cells, or may have missing parts or unnecessary parts added. All of this can mean that your cells can’t function as they normally should.
A genetic mutation changes the information your cells need to form and function. Your genes are responsible for making proteins that tell your body what physical characteristics you should have. If you have a genetic mutation, you could experience symptoms of a genetic condition because your cells are doing a different job than they should be.
Advertisement
Symptoms of genetic conditions depend on which gene has a mutation. There are many different diseases and conditions caused by mutations. The signs and symptoms you experience could include:
Not all genetic mutations lead to genetic disorders. Some genetic mutations don’t have any effect on your health and well-being. This is because the change in the DNA sequence doesn’t change how your cell functions.
Your body also has enzymes, which are a substance that creates chemical reactions in our body. These enzymes help your body protect itself from disease. Enzymes can repair a variety of genetic mutations before they affect how a cell functions.
Some genetic mutations even have a positive effect on humans. Changes in how cells work can sometimes improve the proteins that your cells produce and allow them to adapt to changes in your environment. An example of a positive genetic mutation is one that can protect a person from acquiring heart disease or diabetes, even with a history of smoking or being overweight.
A genetic mutation is a change to a gene’s DNA sequence to produce something different. It creates a permanent change to that gene’s DNA sequence.
Genetic variations are important for humans to evolve, which is the process of change over generations. A sporadic genetic mutation occurs in one person. That person passes their genetic mutation onto their children (hereditary), and it continues for generations. If the mutation improves that person’s chance of survival, or freedom from disease, then it begins being passed through generations and spread through the population. As the mutation passes from generation to generation, it becomes a normal part of the human genome and evolves from a gene variant into a normal gene.
Genes reside on threadlike structures in your body called chromosomes. Chromosomes are in each cell in your body. There are trillions of cells in your body that make you who you are.
There are different types of genetic mutations based on where they form. Types of genetic mutations include:
Advertisement
Yes, you can inherit germline genetic mutations, while somatic mutations occur with no previous history of the mutation in your family. There are several patterns that genetic mutations can pass from the parent to a child (hereditary), like:
Advertisement
A genetic disorder is a condition caused by changes in your genome, or the genetic material present in a human. It includes your DNA, genes and chromosomes. Several factors cause genetic conditions, including:
You can inherit the genetic condition from your parents (if it’s germ cell DNA in the sperm or egg) or the genetic condition can happen randomly, without having a history of the genetic condition in your family.
There are thousands of genetic conditions that exist. Some of the most common genetic conditions are:
If your healthcare provider suspects that you have a genetic condition or you’re at risk of having a child with a genetic condition, they may offer a genetic test. There are many genetic tests that require a sample of your blood, skin, hair, amniotic fluid or tissues to identify changes to your genes, chromosomes or proteins. Genetic testing can locate mutated genes or chromosomes that cause genetic conditions. These tests can also let you know if you’re at risk of having a child with a genetic condition, if you plan on fathering a child or becoming pregnant.
Advertisement
Some genetic mutations happen randomly and you can’t prevent them from occurring. Other genetic mutations can be the result of changes in your environment. You can take steps to prevent some genetic mutations by:
While some genetic mutations can lead to genetic conditions, most mutations don’t cause symptoms in humans. It’s difficult to prevent mutations from happening, especially as genetic mutations can occur randomly — some without being present in your family history. If you plan on having biological children and want to understand your risk of passing a genetic mutation on to your child, talk with your healthcare provider about genetic testing.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Do certain health conditions seem to run in your family? Are you ready to find out if you’re at risk? Cleveland Clinic’s genetics team can help.
