SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) are FDA-approved antidepressant medications. They help treat several conditions like depression, anxiety and bulimia. They work by keeping a chemical messenger active in your brain. SSRIs are the most commonly prescribed type of antidepressant.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) are a common type of antidepressant. They work by changing the activity of serotonin, a chemical that affects your mood, as well as many other bodily and mental functions.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
These medications are often used to treat mental health conditions, like depression, anxiety, PTSD and OCD. They can also help manage other conditions and symptoms.
There are several types of antidepressants, but SSRIs are usually the first choice by healthcare providers. That’s because they tend to cause fewer and milder side effects compared to other options.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors that providers currently prescribe in the United States include:
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved SSRIs to treat the following conditions:
Healthcare providers sometimes use SSRIs to help with other conditions, too. This is an off-label use. Examples may include:
Advertisement
Serotonin is a type of neurotransmitter, or chemical messenger. Neurotransmitters are molecules that dictate how different regions of your brain communicate with each other. Normally, after serotonin delivers its message, your brain cells reabsorb it. This is a process called reuptake. SSRIs block this reabsorption, allowing serotonin to remain active in your brain for a longer period of time. Serotonin plays a role in the regulation of:
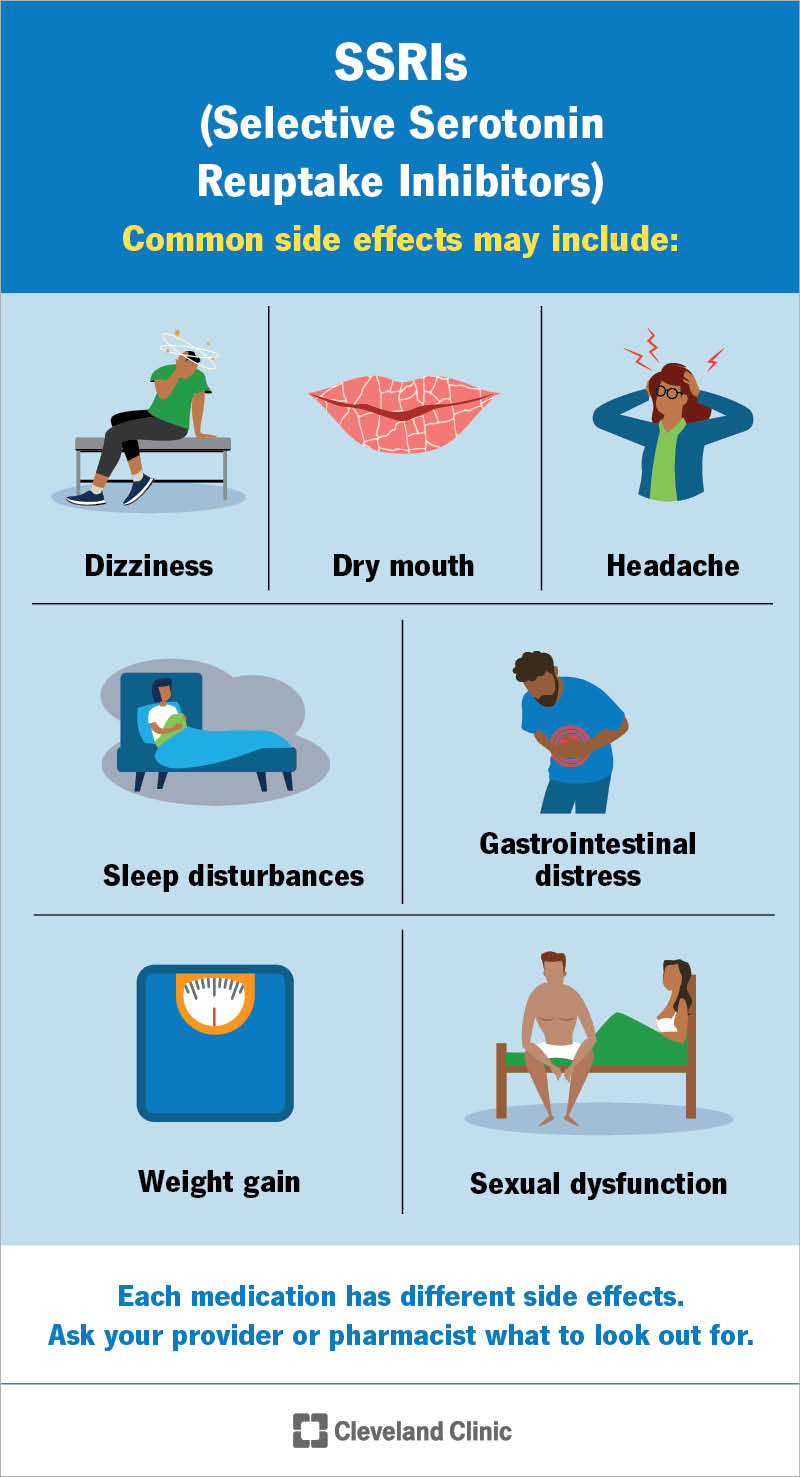
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/selective-serotonin-reuptake-inhibitors)
These medications help manage symptoms of depression and anxiety, as well as many other conditions. These medications often work well when paired with talk therapy, like cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). SSRIs are generally well tolerated, with mild or minimal side effects.
Common side effects may include:
Each medication has different side effects. Ask your provider or pharmacist for more information.
While these medications are generally safe, they may cause rare but serious complications in some cases, such as:
If you’re thinking about suicide, you can reach out for help. Contact your provider. You can also call or text 988 (U.S.) to reach the Suicide and Crisis Lifeline. Someone is available to talk to you 24/7.
Some medications may interact with SSRIs, including:
This isn’t a complete list. Talk to your healthcare provider about all the medications and supplements you currently take. They’ll let you know if an SSRI is the safest option to manage your symptoms.
It’s best to avoid alcohol while taking antidepressants, including SSRIs. Alcohol is a depressant and might interfere with how well the medication works. It can sometimes make depression symptoms worse. If you have concerns about drinking, talk to your provider.
SSRIs have been shown to cause some negative effects in a developing fetus. However, stopping these medications during pregnancy also carries risks. Your depression symptoms may worsen without treatment. If you’re pregnant or planning to become pregnant, talk to your provider. They can explain the risks and benefits in detail and help you decide what’s best.
Advertisement
If you need or want to stop taking an SSRI, your provider will help you gradually reduce your dose. Quitting abruptly can lead to a group of symptoms known as antidepressant discontinuation syndrome. These symptoms typically happen if you’ve been on the medication for six weeks or longer.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors take time to work, usually between four and six weeks after reaching a therapeutic dose. But they can take even longer (between nine and 12 weeks) in certain individuals. If you’re not feeling better by then, check in with your provider, who may recommend an adjustment to your treatment plan.
Taking an antidepressant like an SSRI (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor) isn’t a sign of personal weakness. These medications are widely used and can make a big difference, both mentally and physically. They can manage conditions beyond depression and anxiety to help you get back to feeling like yourself.
It’s normal to have questions when your provider recommends starting an SSRI. Don’t hesitate to speak up. Your provider can guide you through the process and make sure your treatment plan works well for you.
Advertisement
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic's health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability, and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic's health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability, and up-to-date clinical standards.
Anxiety disorders can affect your life in many ways. Cleveland Clinic mental health experts can help you manage anxiety so you’re back in control.
