Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is a mental health condition that causes fear, a constant feeling of being overwhelmed and excessive worry about everyday things. These feelings are hard to manage on your own. It can affect children and adults. Talk therapy and medications can help.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Video content: This video is available to watch online.
View video online (https://cdnapisec.kaltura.com/p/2207941/sp/220794100/playManifest/entryId/1_dgx506xh/flavorId/1_5f3sgelj/format/url/protocol/https/a.mp4)
How to identify signs of generalized anxiety disorder.
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is a mental health condition where you feel excessive worry about everyday situations. It happens often and may be hard to manage. It interferes with your daily activities at home, work or school.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
It’s normal to feel nervous occasionally, especially after a major life stressor. Many people worry about things like health, money or family, for example. But with GAD, those feelings happen more often and more intensely, even when there’s little or no clear reason.
These feelings can lead to physical symptoms like restlessness, headaches or unexplained aches and pains. It can make getting through the day very difficult.
Generalized anxiety disorder is common. It currently affects about 3% of the adult U.S. population and 5% of people at any point during their lives. Only 43% of those affected are receiving treatment.
A healthcare provider can help you manage GAD.
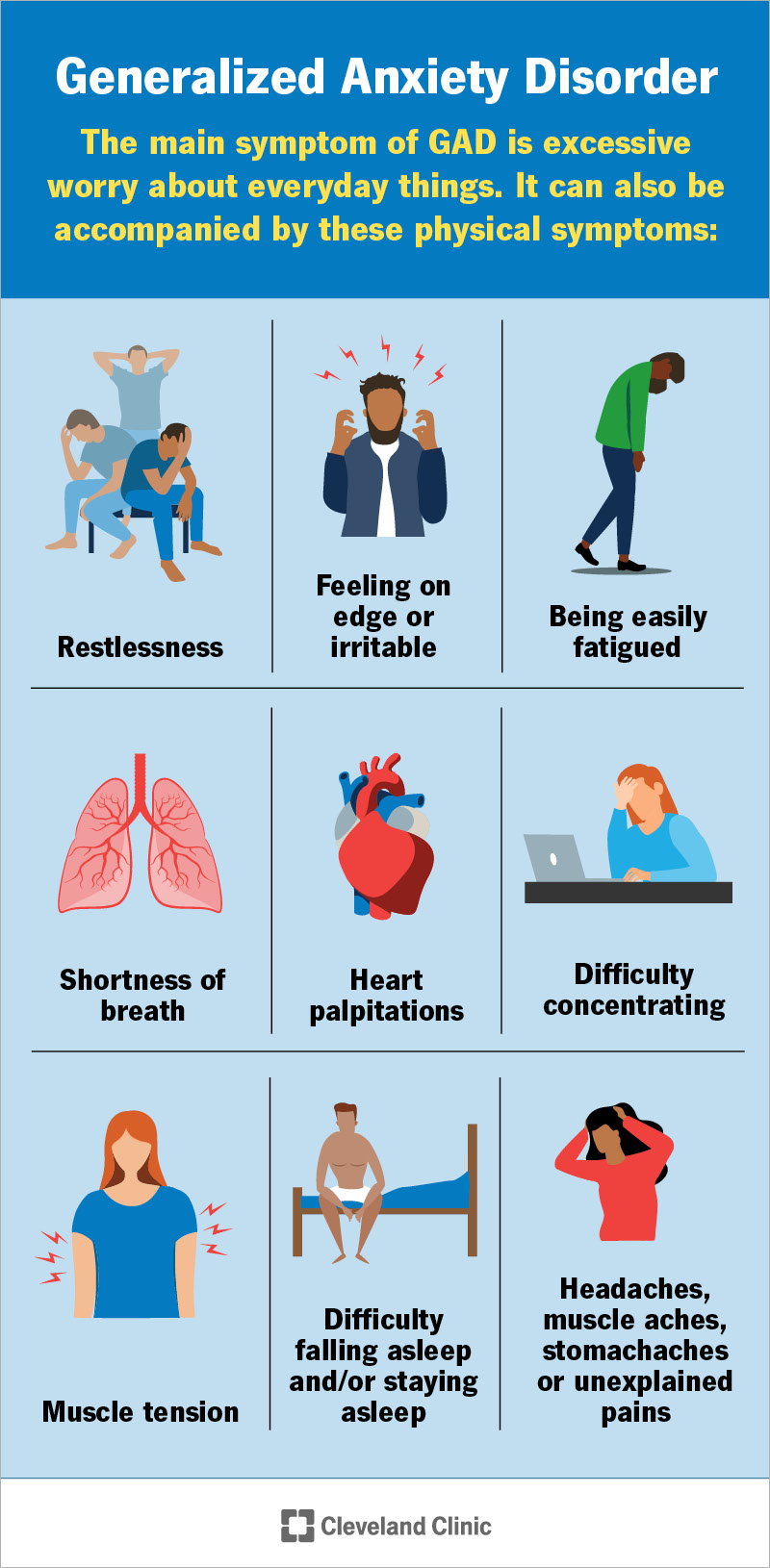
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/23940-generalized-anxiety-disorder)
The symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder may include:
Symptoms may come and go. They’re often worse when you feel stressed.
You may feel physical symptoms with ongoing worry, too, like:
Researchers don’t know the exact cause of GAD, but it likely involves a mix of factors:
Advertisement
GAD can affect children and adults. The condition usually begins in childhood or adolescence but may start at any age.
You may be more at risk of developing GAD if you:
GAD may happen alongside other mental health conditions like substance use disorder and depression. It’s common to feel significant mood swings or changes in your behavior and energy level.
This condition can also raise your risk of thinking about suicide or wanting to hurt yourself. If you’re ever in a difficult spot, don’t hesitate to reach out for help when you need it. Call or text 988. This is the Suicide & Crisis Lifeline (U.S.). Someone is available to talk to you 24/7.
A healthcare provider, like your primary care physician, may refer you to a mental health specialist, like a psychologist or psychiatrist. They’ll ask questions about your mental health and medical history to better understand what you’re experiencing.
It’s OK to feel nervous or unsure, but try to be as open as you can. Your honesty helps your provider truly understand what you’re going through so they can offer the right care to help you feel better.
Your provider may do a physical exam, have you complete a mood questionnaire, like the GAD-7, make observations about your facial expressions and speech, and run tests to see if something else is causing your symptoms. These tests may include:
Providers use the criteria in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5-TR). To be diagnosed with GAD, you must feel worried most days for at least six months. The worry is hard to manage.
In addition to feeling anxious, adults typically experience at least three of the following symptoms (children only need one):
Advertisement
These symptoms interfere with your daily life. They may affect your work, relationships and overall health.
Your provider will check that GAD isn’t caused by drugs or medicine you take. They’ll also make sure symptoms can’t be better explained by another mental health disorder. These may include panic disorder, social anxiety, obsessive-compulsive disorder or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), among others.
GAD is usually treated with psychotherapy, medications or a combination of both. Research shows that the largest improvement happens with combined treatment (medications plus therapy). Your provider will work with you to find the right treatment plan based on your symptoms, needs and overall health.
Psychotherapy, also known as talk therapy, is a treatment that helps you explore and better understand your thoughts, emotions and behaviors. It involves working with a licensed mental health professional in a safe, supportive setting.
Therapy can also provide tools and strategies to improve your well-being and how you function day to day.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is one of the most effective approaches for treating GAD. It helps you notice and change negative thoughts that make your anxiety worse and make you behave in a certain way. Over time, CBT may help reduce excessive worry and build healthier coping skills.
Advertisement
Medication may also be part of your GAD treatment plan. Common options may include:
If you don’t respond to those medications, your provider may consider the following:
If you’re taking medication for generalized anxiety disorder, it’s important to see your provider regularly. They’ll check how well the medication works and adjust the dose if needed. Let them know if you have any side effects or new symptoms.
If you’re in therapy, try to attend all of your sessions, and reschedule if you need to miss one. It can take time to feel the full benefits of treatment. But sticking with it is an important part of your treatment.
If at any time you feel overwhelmed or at risk of harming yourself, tell your provider. If you’re in immediate danger, contact 911 or your local emergency services number.
The outlook can vary from person to person. For some, GAD may be a long-term condition that requires ongoing management. Some days, your anxiety may feel stronger. This is especially true when you’re stressed. Other days, it may feel easier to manage.
Advertisement
Treatment may make a meaningful difference. The right mix of therapy, medication and coping strategies can help you manage symptoms and feel more in control. Your care team will work closely with you to find what works best for your body, your lifestyle and your goals. And if your needs change over time, your treatment plan can change with you.
If you have GAD, there are steps you can take, alongside medical treatment, to help manage your symptoms:
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) can make everyday tasks feel overwhelming. Simple activities, like cooking or leaving your house, may trigger anxiety. By the end of the day, the constant stress can leave you feeling drained.
But you don’t have to manage these symptoms on your own. A healthcare provider can help you explore coping strategies and find a treatment plan that fits your needs. Therapy, medication or a combination of both may offer relief.
Progress takes time. You’ll need to be patient with yourself. You might not feel different right away, but with help, you can start to feel more like yourself.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Your mental well-being is just as important as your physical well-being. Cleveland Clinic’s mental health experts can help you live life to the fullest.
