Arthritis in your wrist causes pain, swelling and stiffness that worsens the more you use it. Sometimes, it’s an inflammatory condition (like rheumatoid arthritis), but more often, it’s just old-fashioned wear and tear (osteoarthritis). Many people can manage wrist arthritis with self-care. If you need more, steroid injections or surgery can help.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
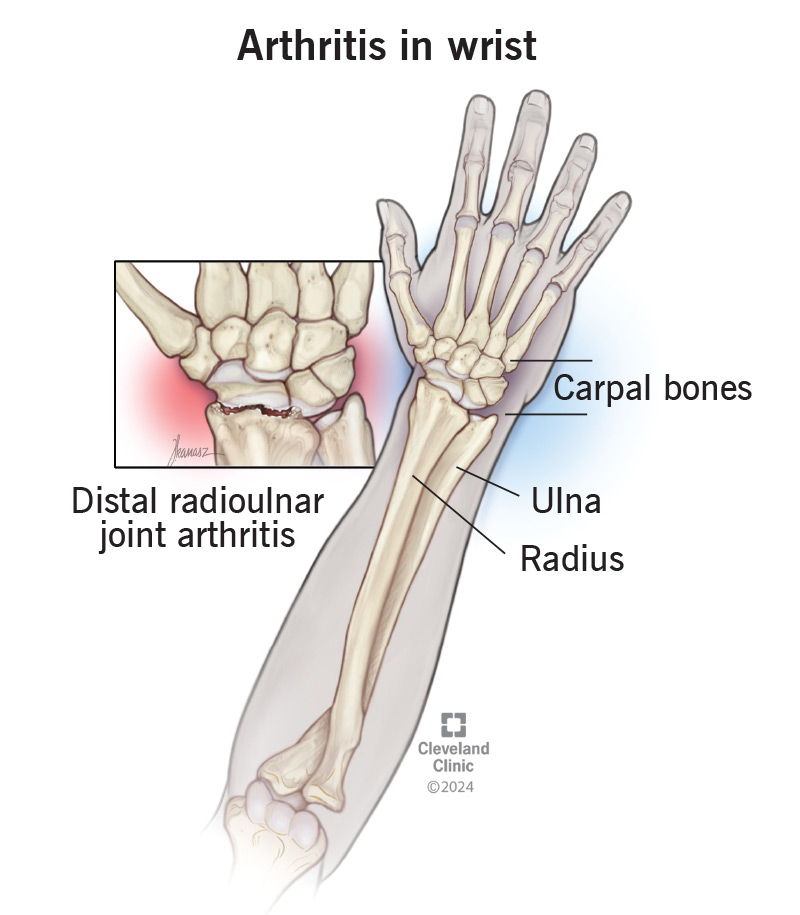
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/arthritis-in-wrist)
Arthritis of the wrist is one of the main causes of chronic wrist pain. It can also cause swelling and stiffness in your wrist. Your wrist is the joint that allows you to bend, straighten and rotate your hand. You use it to accomplish countless tasks throughout the day.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Arthritis is a chronic and progressive (ongoing and worsening) disease that wears away the cartilage in your joints. It especially affects joints that take a lot of stress from weight and/or frequent use. Your wrist doesn’t bear much weight, but you do use it a lot.
Arthritis in your wrist may occur in different places where different bones connect. Your wrist is the most complex joint in your body, with more bones and connection points than any other joint.
Types of wrist arthritis by location include:
In addition, different types of arthritis can affect your wrist. The most common type is osteoarthritis, which is from simple wear and tear. Inflammatory types of arthritis come from inflammatory diseases.
Advertisement
Noninflammatory types of arthritis in your wrist may include:
Types of inflammatory arthritis in your wrist might include:
Different types can cause different symptoms, but the most common symptom is all-over wrist pain. Osteoarthritis may feel like a dull, constant ache. Inflammatory arthritis might feel intense and burning.
You might feel it more when you use your wrist to:
You may also experience:
Osteoarthritis or post-traumatic arthritis may only affect one wrist. Inflammatory types (like rheumatoid arthritis) often affect both wrists and may also affect other joints. With inflammatory types, you may also have:
With all types, severe swelling in your joints can force bones out of their normal positions, causing disfigurement.
Arthritis is gradual, ongoing damage to the cartilage in your joints. That’s the padding between the bones that helps them move smoothly against each other. Inflammatory diseases or common wear and tear can erode this padding, leaving bones to rub against bones. This causes pain, swelling and stiffness. Inflammation itself can also cause these symptoms, even before it starts to wear down the cartilage.
Advertisement
Your healthcare provider will perform a physical exam to assess your range of motion and check for signs of inflammation or disfigurement. Tests to diagnose the type of arthritis in your wrist include:
Treatment for wrist arthritis focuses on relieving your symptoms and slowing or stopping the damage, if possible. Healthcare providers usually start by recommending conservative treatments to relieve pain and reduce stress on your wrist. Depending on your need, they might prescribe medications for pain relief or to reduce inflammation. If these don’t do enough to help, they might recommend surgery.
Conservative recommendations include:
Advertisement
Prescription treatments may include:
Surgical treatments for wrist arthritis include:
Advertisement
Most people with wrist arthritis can manage their pain with conservative treatments. Steroid injections can also help, if needed. If your arthritis is very advanced and you’ve lost a lot of cartilage, it might be harder to manage conservatively. When wrist arthritis begins to seriously affect your life, talk to your healthcare provider. They’ll discuss your surgery options and recommend the best procedure for you.
You might not realize how often you use your wrist throughout the day until using it becomes painful and difficult. If you’ve developed wrist arthritis, you’re not alone — it affects up to 1 in 7 people in the U.S. A healthcare provider can help pinpoint the type of arthritis you have to determine the best treatment plan for you. For many people, self-care and activity adjustments can make a real difference.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
We diagnose and treat conditions that cause wrist pain and elbow pain. Learn how Cleveland Clinic experts use minimally invasive treatments to relieve your discomfort.
