Negative pressure wound therapy helps a wound heal faster by removing fluid and bacteria with suction. It also protects your wound from harmful things in the air, creating a good environment for healing. This works for soft tissue wounds on many different areas of your body.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
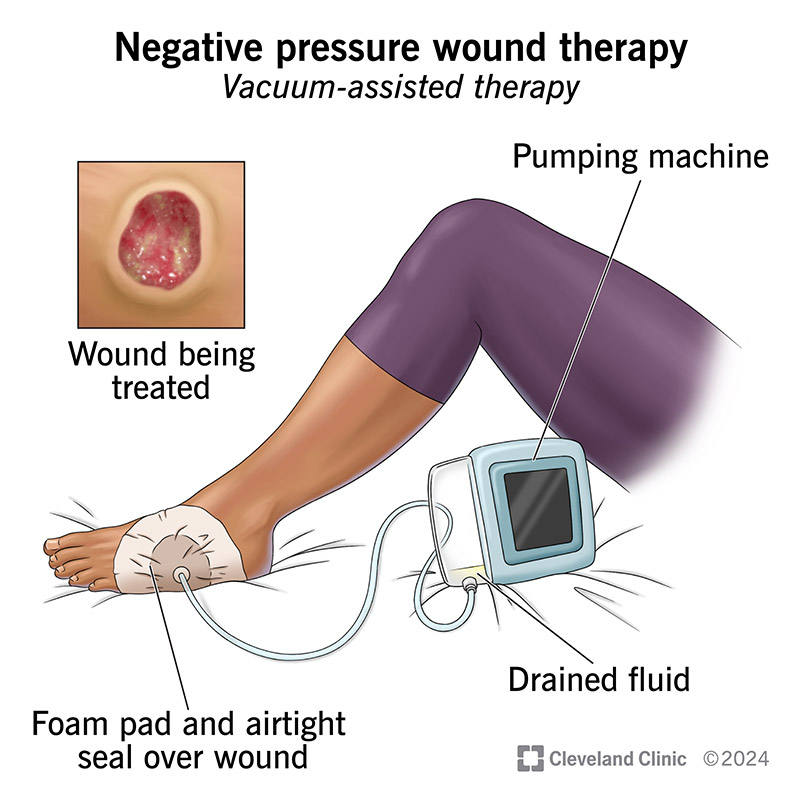
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/17313-negative-pressure-wound-therapy)
Negative pressure wound therapy is a treatment that pulls fluid and bacteria out of a wound to help it heal better. Some healthcare providers call it vacuum-assisted therapy. It works by creating suction. A provider can use this treatment to heal soft tissue on many different parts of your body.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Less fluid leads to less edema (swelling). Negative pressure wound therapy allows the wound to compress down, making it smaller. It also encourages new healthy tissue to form in a clean, moist environment.
A provider may use negative pressure wound therapy in the operating room after cleaning a wound and closing it. After that, a provider can visit your hospital room to change the dressings and ensure a tight seal on your wound. If you use this therapy at home, you can visit a clinic for dressing changes.
Negative pressure wound therapy is a very common treatment providers use for wounds. Millions of people around the world have used it since doctors invented it in the 1990s.
When applying negative pressure wound therapy, a provider will:
A provider may also be able to put saline or antibiotics into a wound using negative pressure wound therapy.
Advertisement
Negative pressure wound therapy devices have a small pump that creates negative pressure or suction. It may use electric or battery power. A provider can program the device to get the pressure setting they want. An alarm goes off if the battery is low or the suction stops working.
Providers can use some devices again and again. They use other devices for one person, disposing of the device when they’re done with it. For either type, they use new tubing and bandaging materials for each person.
Negative pressure wound therapy indications or reasons to use it include:
Examples of uses for negative pressure wound therapy include:
You shouldn’t use negative pressure wound therapy if you have:
Negative pressure wound therapy benefits include:
Possible disadvantages of negative pressure wound therapy include:
The speed of your recovery depends on the kind of wound you have, as well as the size. You may be surprised at how quickly negative pressure wound therapy helps your wound heal. The system creates an ideal environment for wound healing.
Follow your provider’s instructions for taking care of yourself. They may tell you to:
Ask your provider how soon after treatment you can return to normal activities.
If you’re using a negative pressure wound therapy device at home, contact your provider if:
Advertisement
After treatment, you’ll need follow-up appointments with your provider. They’ll want to make sure you’re healing well and are free of infection.
Doctors vary in quality due to differences in training and experience; hospitals differ in the number of services available. The more complex your medical problem, the greater these differences in quality become and the more they matter.
Clearly, the doctor and hospital that you choose for complex, specialized medical care will have a direct impact on how well you do. To help you make this choice, please review our Miller Family Heart and Vascular Institute Outcomes.
Choosing a doctor to treat your vascular disease depends on where you are in your diagnosis and treatment. The following Heart and Vascular Institute Sections and Departments treat patients with all types of vascular disease, including blood clotting disorders:
Section of Vascular Medicine: for evaluation, medical management or interventional procedures to treat vascular disease. In addition, the Non-Invasive Laboratory includes state-of-the art computerized imaging equipment to assist in diagnosing vascular disease, without added discomfort to the patient. Call Vascular Medicine Appointments, toll-free 800-223-2273, extension 44420 or request an appointment online.
Advertisement
Department of Vascular Surgery: surgery evaluation for surgical treatment of vascular disease, including aorta, peripheral artery, and venous disease. Call Vascular Surgery Appointments, toll-free 800-223-2273, extension 44508 or request an appointment online.
IVC Filter Retrieval Clinic - to make an appointment, call Vascular Medicine at 216.444.4420. Ask for Dr. Bartholomew in the Filter Retrieval Clinic. Your appointment will include a consultation with Dr. Bartholomew and the physicians who will perform the IVC filter retrieval procedure.
You may also use our MyConsult second opinion consultation using the Internet.
The Heart and Vascular Institute also has specialized centers and clinics to treat certain populations of patients:
Learn more about experts who specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of vascular and arterial disease.
If you need more information, click here to contact us, or call the Miller Family Heart and Vascular Institute Resource & Information Nurse at 216.445.9288 or toll-free at 866.289.6911. We would be happy to help you.
Advertisement
Diagnostic tests are used to diagnose your abnormal heartbeat and the most effective treatment method.
Our webchats and video chats give patients and visitors another opportunity to ask questions and interact with our physicians.
*A new browser window will open with this link. The inclusion of links to other websites does not imply any endorsement of the material on those websites nor any association with their operators.
Our outcomes speak for themselves. Please review our facts and figures and if you have any questions don’t hesitate to ask.
Maybe you just had surgery. Maybe you have another foot ulcer. Whatever the reason for the wound, it’s not fun. While there’s some inconvenience with negative pressure wound therapy, it’s worth it. This treatment can speed up your healing time by giving your wound what it needs. If the device is causing discomfort, speak up and ask your provider if there’s something they can do to help.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Plaque in your blood vessels can cause tingling, pain and numbness. Cleveland Clinic’s experts treat circulatory problems, including peripheral artery disease.
