Abnormal uterine bleeding (menometrorrhagia) is bleeding between monthly periods, prolonged bleeding or an extremely heavy period. Possible causes include fibroids, polyps, hormone changes and, in rare cases, cancer. Treatment could involve medication or surgery.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
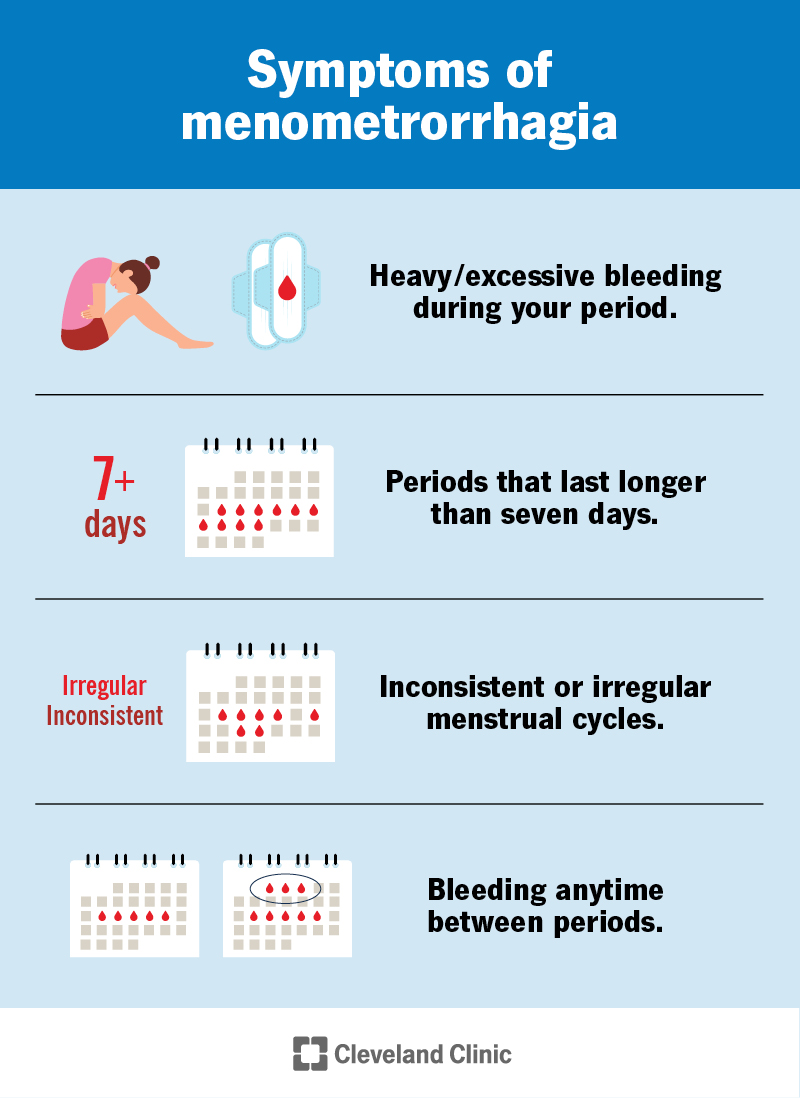
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/menometrorrhagia-abnormal-uterine-bleeding)
Menometrorrhagia (also called abnormal uterine bleeding) is any vaginal bleeding that is heavy, long or irregular. It’s when you bleed from your vagina, but the bleeding doesn’t follow a predictable pattern like a typical menstrual period. A typical period lasts about five days and occurs every 21 to 35 days. Any bleeding that occurs outside of menstruation or a period that is very long or heavy or irregular may be a sign of menometrorrhagia.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Having unpredictable bleeding can be frustrating. Not knowing when you’ll bleed, how much you’ll bleed or how long you’ll bleed can negatively affect your quality of life. It may make you want to stay home or cancel plans you were looking forward to. But it doesn’t have to be this way. Bleeding unexpectedly isn’t something you should just accept.
Your healthcare provider should know about any abnormal bleeding you’re experiencing, especially when it affects your physical and emotional health. What’s causing your bleeding may be harmless. But irregular bleeding could also be a sign of a health condition that could impact your fertility or have other long-term health complications.
Menorrhagia is heavy menstrual bleeding. This means you bleed too much during your period.
Menometrorrhagia is abnormal, unpredictable or irregular uterine bleeding that occurs at any time, not just during menstruation.
Not everyone who experiences abnormal uterine bleeding reports their symptoms. As a result, 10% to 35% of females may have abnormal uterine bleeding. But the numbers may be higher. It’s most common in perimenopause (the years leading up to menopause), but also common when you first begin having a period (around age 12).
Advertisement
The signs of menometrorrhagia vary depending on the cause. Most healthcare providers consider abnormal bleeding to be anything other than bleeding for about five days every 21 to 35 days. If you never know when you’re going to bleed, how much you’ll bleed or for how long, you may have menometrorrhagia.
Some specific signs that your bleeding may be abnormal include:
Hormonal issues, noncancerous growths, cancer, infections, other medical conditions and medications can cause abnormal uterine bleeding. Only your healthcare provider can determine what’s causing you to bleed irregularly. There are many possible causes, so it’s best to talk to a provider about your symptoms so they can figure out what’s going on.
Hormone imbalances are often to blame for abnormal uterine bleeding. They’re most common if your periods are just beginning or if your periods are about to stop because of menopause. Your hormones are responsible for your menstrual cycle. Like a symphony orchestra, your hormones need to play in perfect harmony for menstruation to occur exactly how it should. Any disruption to the balance of your hormones can cause abnormal uterine bleeding. Some of these disruptions include:
Benign (noncancerous) growths in your uterus can create blockages or bleed themselves, depending on what kind of growth it is. Some examples are:
Rarely, certain cancers are the cause of menometrorrhagia. These include:
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and infections you don’t get through sex can cause irregular bleeding. The following may be the cause of menometrorrhagia:
Advertisement
Other medical conditions or events can be a factor in abnormal uterine bleeding. Some examples of health conditions that could cause menometrorrhagia are:
Always contact your provider if you bleed during pregnancy. It could be a sign of a pregnancy complication.
Certain medications can cause irregular uterine bleeding. (Ironically, some of these medications can also help treat irregular bleeding.) Always tell your provider what medications you take so they can rule out medication being a cause.
The term “abnormal uterine bleeding” describes bleeding in nonpregnant women in their reproductive years. But this doesn’t mean that irregular bleeding won’t affect you if you’re post-menopausal or pregnant. Almost anyone with a uterus can experience abnormal bleeding. In fact, the chances are high that you’ll experience it at some point in your life. Even so, most cases of irregular bleeding aren’t serious and get better with the right treatment.
Advertisement
If you’re bleeding and have transitioned to menopause, contact a healthcare provider. Bleeding after menopause is never normal. Blood may be red, pink, brown or even rust-like in appearance.
You should also contact your provider if you’re bleeding during pregnancy. Some causes are harmless, but others require medical attention.
Abnormal uterine bleeding isn’t life-threatening, but it can lead to anemia. Anemia happens when your blood doesn’t have enough healthy red blood cells. It can leave you feeling weak and sluggish.
Irregular bleeding can also be a sign of certain cancers and other medical conditions. Because you don’t know what’s causing irregular uterine bleeding, you should seek care from a healthcare provider to avoid these and other complications.
Your healthcare provider will ask you several questions when working to diagnose abnormal uterine bleeding. These questions may include:
It may help to keep track of your bleeding for several weeks leading up to your appointment. Note when you bleed, how long it lasts, the type (spotting, medium, heavy) and if you have other symptoms with it.
Advertisement
Your healthcare provider will also perform a physical exam, including:
The most common steps your provider will do to diagnose the condition are:
Based on those results, your provider may do the following tests:
Your treatment depends on what’s causing your bleeding. Medications and surgical options are available to manage your bleeding or treat what’s causing it.
Medication is often the first treatment your healthcare provider will consider. Your provider may recommend the following medications for abnormal uterine bleeding:
There are several procedures available to treat abnormal uterine bleeding. Some options your provider may offer include:
Ask your provider about the risks and benefits of surgical procedures. Make sure you know exactly what to expect with each treatment option.
Getting to the root cause of your irregular bleeding is key to your prognosis. Diagnosing and treating the underlying cause may be a process that takes several weeks, or it could be relatively easy for your provider to diagnose. Either way, your provider will consider multiple factors, including your age, symptoms and risk factors for certain conditions that cause abnormal bleeding.
The good news is that most cases of irregular bleeding are treatable. Follow your provider’s advice and recommendations and be sure to check in with them if a treatment option isn’t working for you. They’re there to help you and get you back to living a life without bothersome or random vaginal bleeding.
You can’t prevent many causes of abnormal uterine bleeding. But you can reduce your risk of certain conditions that lead to abnormal bleeding. For instance, maintaining a healthy weight plays a potential role in keeping your hormones in sync. Practicing safer sex (like wearing a condom) can reduce your risk of certain sexually transmitted infections (STIs) that can cause irregular uterine bleeding.
Schedule an appointment with your provider if you notice abnormal uterine bleeding so they can address the underlying cause.
Symptoms to watch out for include:
If abnormal bleeding interferes with your quality of life, see a healthcare provider. You shouldn’t have to double up on menstrual products to manage your period. You shouldn’t have to skip activities you enjoy or avoid going to work and school because of unpredictable bleeding.
Some questions you may want to ask your provider are:
You’re the best judge of what’s normal for you — how long your periods usually last and how heavy your bleeding is. If your periods are especially heavy or lasting longer than usual or if you’re bleeding outside your menstrual cycle, speak to a healthcare provider. Don’t just chalk it up to a fluke or something that you just need to deal with. Having irregular bleeding shouldn’t define you or make you want to hide. Seek treatment when it begins affecting your mental well-being. Many noninvasive treatment options are available so you can get back to enjoying your best life.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
When your periods aren’t acting the way they typically do, the experts at Cleveland Clinic can help craft a treatment plan that works for you.
