Osteoblastoma is a type of bone tumor. It’s not cancerous, but it can grow large and may cause pain or swelling. It also weakens your bone and increases your risk of fractures. Orthopaedists treat osteoblastoma with surgery to remove it. This usually cures it, but sometimes, it comes back.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
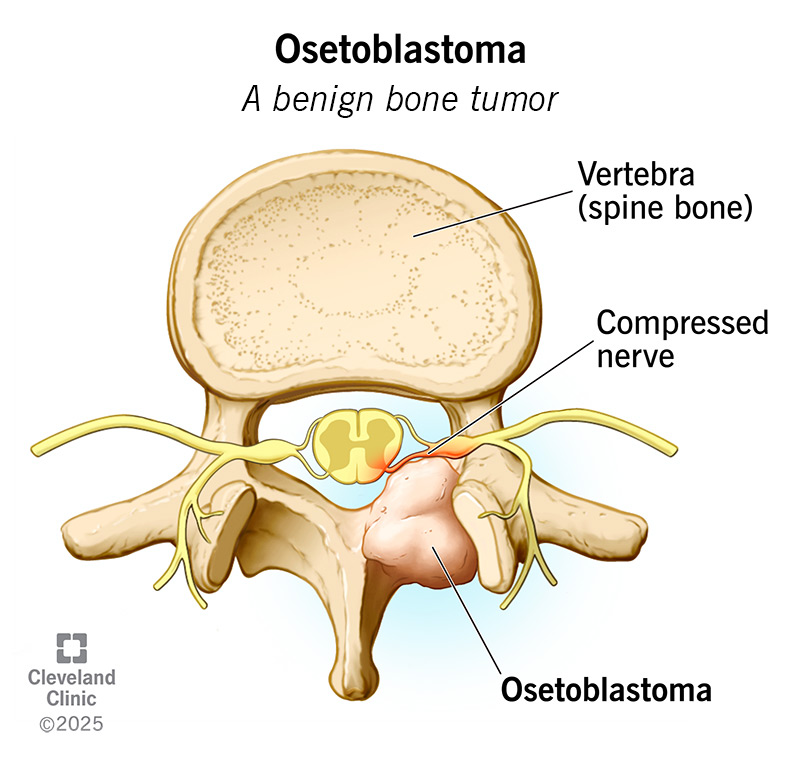
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/osteoblastoma)
Osteoblastoma is a type of benign bone tumor. It’s not cancerous, but it can cause changes in your bones. The tumor attacks your healthy bone tissue and creates a new kind of tissue called osteoid. Osteoid is weaker than healthy bone tissue, so it weakens your bones and makes them more prone to fractures. Osteoblastomas may also cause symptoms as they grow bigger, like pain or swelling.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Osteoblastoma can grow in any bone, but it's most common in your spine. Up to 40% occur there.
It may also occur in your:
The most common symptom of osteoblastoma is bone pain — a dull, aching type of pain that seems to come from deep in your body. You might also see a lump or swelling under your skin that’s tender to touch. An osteoblastoma in one of your legs or feet might cause a limp or change the way you walk.
As the tumor grows bigger, it might cause additional symptoms. The average size of an osteoblastoma is 4 centimeters (cm), which is about the size of a cherry tomato. But some have been known to grow twice or even three times as big. A larger tumor might compress a nearby nerve, causing nerve-related symptoms, like:
An osteoblastoma that grows too much may cause complications, including:
Advertisement
Other rare complications of osteoblastoma might include:
Healthcare providers don’t know what causes osteoblastoma. But they have observed that it tends to occur in younger adults (under age 30). It’s also twice as common in males as it is in females.
A healthcare provider will start by discussing your symptoms and health history. Then, they’ll physically examine the sore or swollen spot. They’ll follow up with imaging tests, starting with X-rays. Depending on what the X-rays show, they might want to order more detailed imaging tests, like a CT scan or MRI. These can help locate the tumor and show how it’s affecting your surrounding tissues.
Your provider will often recognize osteoblastoma by its appearance on imaging tests. But they may need to take a tissue sample (biopsy) to confirm it. Once they’ve located the tumor, they can take the sample with a biopsy needle or with a small incision. They’ll send it to a pathology lab to analyze. A process called immunostaining helps pathologists distinguish between osteoblastoma and osteosarcoma.
Treatment for osteoblastoma usually means surgery to remove the tumor. The only exception is if the tumor is located in a tricky place on your spine that’s too risky to operate on. In this case, your orthopaedic surgeon will use other methods to try to destroy the tumor and stop it from growing.
Procedures to treat osteoblastoma may include:
Advertisement
Osteoblastoma usually has a good outlook. Most people are cured after surgery to remove the tumor. Most bones will repair themselves from the damage. But sometimes, the tumors can grow back again. This is more common after curettage than after resection. It might be because some tumor cells were left behind. If your tumor comes back after curettage, your surgeon might do a resection next time.
Osteoblastoma isn’t cancerous or life-threatening, but it’s fast-growing and can be destructive. This means it’s best to treat it sooner than later. Many people don’t take their bone pain seriously enough to seek a diagnosis until after they’ve lived with it for several years. But it’s always worth finding out what’s causing your pain. Osteoblastoma is very treatable, and treating it can prevent it from worsening.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
From sudden injuries to chronic conditions, Cleveland Clinic’s orthopaedic providers can guide you through testing, treatment and beyond.
