Your rib cage anatomy includes 37 bones and 98 joints that help the structure flex with your movement. Injuries and diseases that affect these bones and joints may cause musculoskeletal chest pain.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
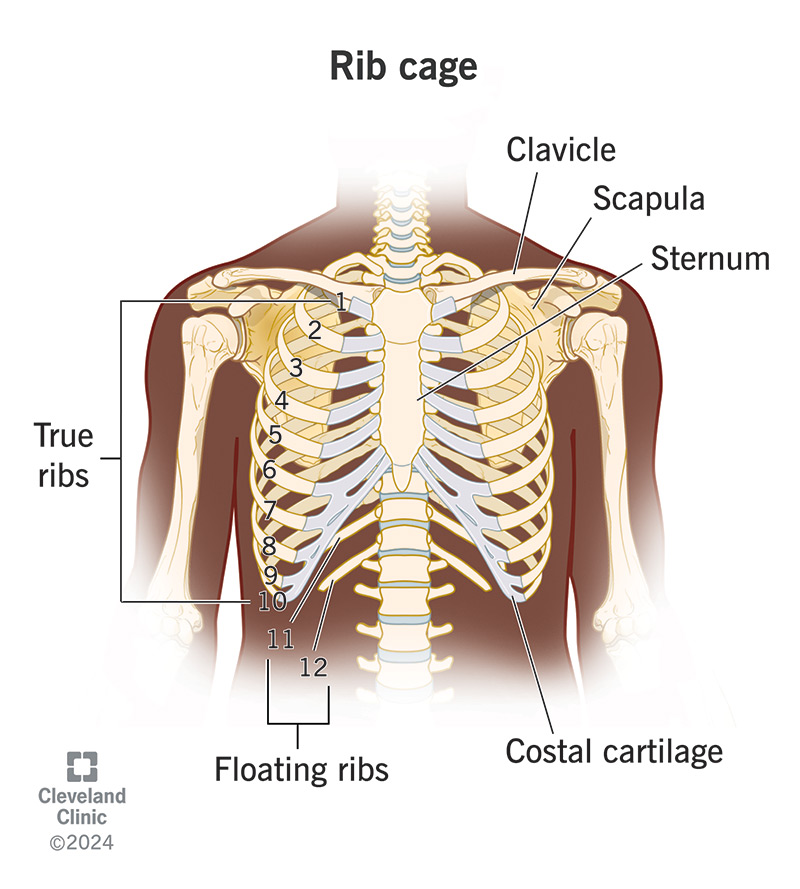
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/rib-cage)
Your rib cage is the cage-like structure of bones that frames your chest cavity (thoracic cavity). It’s also called your thoracic cage. Your 24 ribs (12 on each side) wrap around the sides of your torso from front to back. They connect to your thoracic spine in the back and your sternum (breastbone) in the front.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Your rib cage surrounds and protects the vital organs in your chest cavity, your heart and lungs. It expands with your lungs when you breathe. As part of your axial skeleton, your rib cage helps form the trunk of your body. It also serves as an attachment point for core muscles, like your diaphragm.
As part of your skeletal system, your rib cage is made up of bones and the joints that connect them.
The bones include:
The joints include:
Advertisement
Healthcare providers may use some of these terms when referring to certain ribs.
Musculoskeletal conditions that may affect your rib cage include:
If you have a condition affecting your rib cage, you might have:
Your healthcare provider might order imaging tests of your rib cage, like a:
Treatment for rib cage conditions depends on the type and the cause. Many rib injuries can heal with time, rest and pain relievers, but a visible deformity may require surgery. Arthritis treatments include medications, therapeutic injections and physical therapy. Some severe cases may require surgery.
Advertisement
Your rib cage is both solid and flexible. The many bones frame your chest cavity and protect your heart and lungs. Meanwhile, the many joints make the structure adjustable, moving and expanding with your breath and movement. But diseases and injuries can turn these advantages into disadvantages.
A rib that’s fractured or displaced can injure the soft tissues and endanger the organs in your chest. A joint that’s worn out or inflamed can become sore, stiff and swollen, making movement and breathing difficult. These are the kinds of issues healthcare providers treat when they treat your rib cage.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.