Ablation therapy uses extreme heat (radiofrequency ablation) or cold (cryoablation) to destroy diseased tissue. Providers use ablative procedures to treat cancers, arrhythmias, bleeding problems and other issues. This less invasive alternative to major surgery has fewer risks and a faster recovery.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
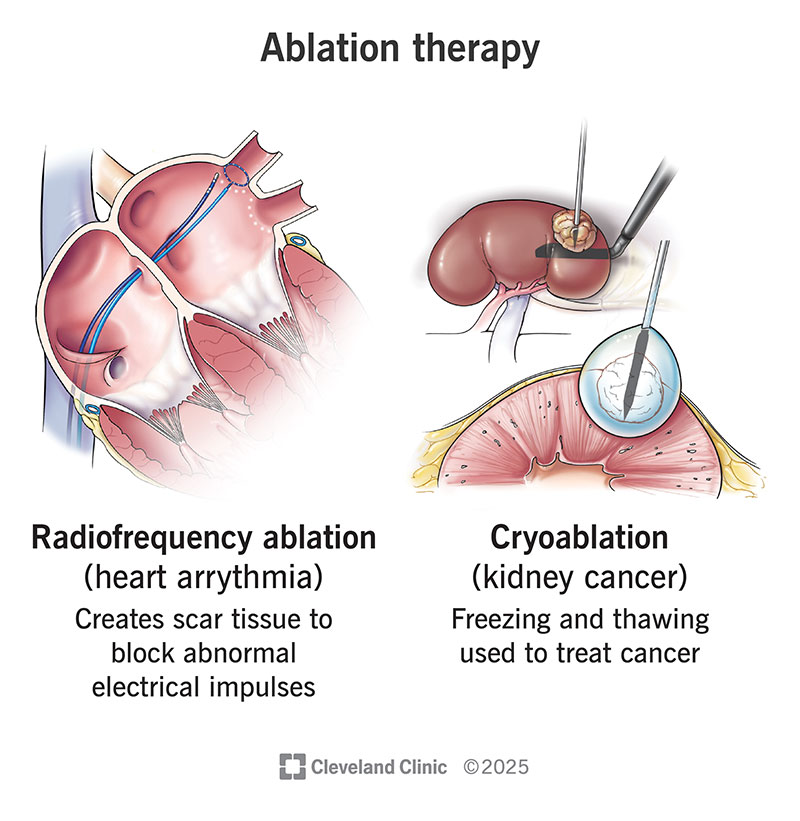
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/17801-ablation-therapy)
Ablation therapy is a treatment that uses extreme cold or heat to destroy (ablate) diseased tissue. Some healthcare providers call it ablative therapy.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Ablation therapy is a minimally invasive procedure. Your provider can use ablation without open, major surgery. It has a faster recovery time than typical surgery.
Ablation therapy destroys cells that cause health conditions or dangerous symptoms.
There are lots of specific kinds of ablation therapy. But they all fit into two main types:
Healthcare providers use ablation therapy to treat many conditions throughout your body, including:
Advertisement
It depends on which type of ablation therapy you need. Your provider will give you specific prep instructions based on your unique situation.
You might have to avoid eating and drinking (fast) for a few hours before your ablation appointment.
Tell your provider which medications and over-the-counter supplements you take. They’ll tell you if you need to stop taking any of them before your procedure.
You probably won’t be able to drive yourself home. Make a plan for someone to pick you up, or arrange transportation ahead of time.
The exact steps of your procedure will depend on where in your body you need ablation and which condition your provider is treating. In general, the steps include:
It depends on which type of procedure you need.
For example, ablation inside an organ like your brain, heart or uterus will take longer than a procedure to remove precancerous skin cells.
Your provider will tell you what to expect ahead of time.
Some types of ablations are outpatient procedures. That means you can go home the same day. More complex ablations are usually inpatient, which means you’ll have to spend at least one night in the hospital.
Either way, you’ll need to spend a few hours in a recovery area after your procedure. Your care team will monitor your vital signs and pain levels.
They’ll tell you when it’s safe for you to go home.
Ablation therapy is less invasive than open, major surgery. If you have cancer, you can continue other treatments like chemotherapy at the same time.
Other benefits include:
Ablation therapy is a safe procedure that has fewer risks than major surgery. However, complications can occur, including:
Advertisement
Each kind of ablation has a slightly different recovery time. Recovery can take anywhere from a few days to a few weeks.
You might have to stay home from work or school for a few days after an ablation to rest.
Your provider will give you a specific recovery timeline, including:
Ablation therapy may sound intimidating. But it’s a safe, effective way for your healthcare provider to treat lots of conditions. They might even be able to use ablation to destroy dangerous cells before they can hurt you.
Ask your provider any questions you have before your procedure. Because ablation can be used in so many ways to treat so many conditions, general information you read ahead of time probably won’t cover every aspect of your exact procedure. Your provider will fill in the gaps and help you understand what they’ll do and how it will help you feel better.
Advertisement
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic's health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability, and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic's health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability, and up-to-date clinical standards.
When you’re diagnosed with cancer, you want expert and compassionate care right away. At Cleveland Clinic we personalize your treatment to match your needs.
