Your cerebrum is the largest part of your brain and handles conscious thoughts and actions. Different areas within your cerebrum also have different responsibilities, like language, behavior, sensory processing and more. Areas of your brain also commonly work together on the same tasks, helping you understand what’s happening in the world around you.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
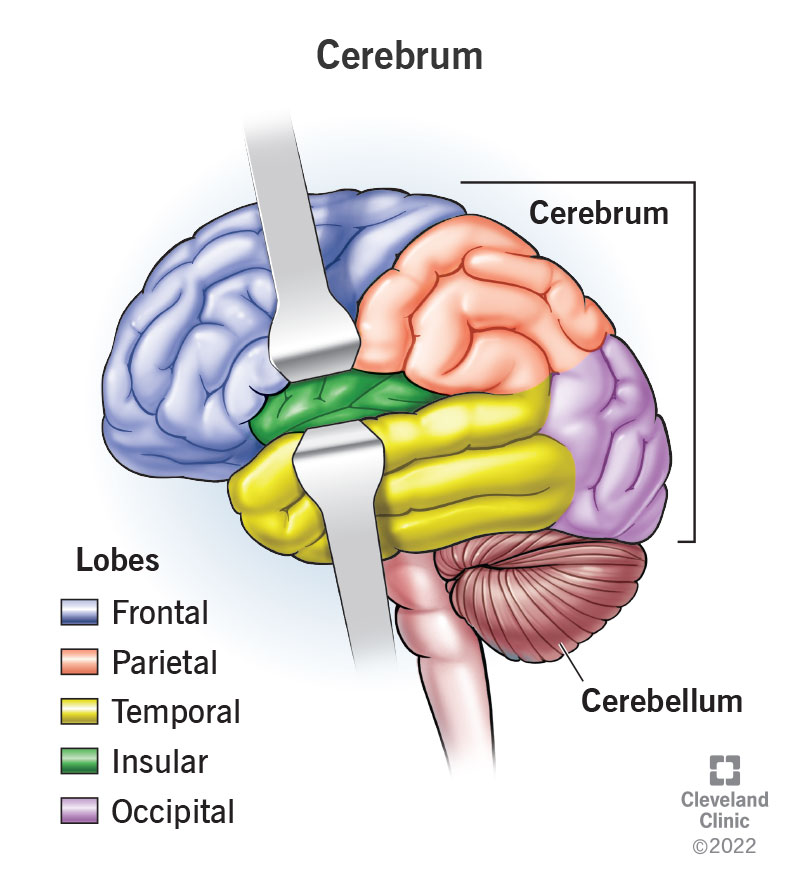
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/23083-cerebrum)
Your cerebrum is the largest part of your brain, and it handles a wide range of responsibilities. Located at the front and top of your skull, it gets its name from the Latin word meaning “brain.”
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Your cerebrum is instrumental in everything you do in day-to-day life, ranging from thoughts to actions. In essence, it’s responsible for the brain functions that allow us to interact with our environment and make us who we are.
Scientists have been studying the brain for years, trying to unlock just how it works and how to diagnose and treat conditions that affect it. While experts know a lot about how the cerebrum functions, there’s still much that’s not fully understood. Fortunately, advances in technology and medical science have helped drive growth in what experts understand about the brain.
Your cerebrum is the largest part of your brain and includes parts above and forward of your cerebellum. Your cerebrum is the part of your brain that starts and manages conscious thoughts; meaning things that you actively think about or do.
Your cerebellum is a small part of your brain located at the bottom of this organ near the back of your head. It processes and regulates signals between other parts of your brain and body, and is involved in coordinating functions of your body (for example, walking).
Your cerebrum handles much of your brain’s “conscious” actions. That means it’s responsible for elements that require thinking, including:
Advertisement
Your cerebrum works together with other parts of your brain, especially your cerebellum, to help you with your daily activities. An example of this is picking up a pencil off a table. Your cerebrum sends the signals to the muscles in your arms, and your cerebellum helps calculate and control your movements, so your hand goes right to the pencil without missing.
Your cerebrum not only manages conscious thoughts, but also planning and actions. That includes when you decide to be physically active, choose what to eat for a meal or set aside time to see a healthcare provider for any reason. Because of this, your cerebrum plays a critical role in the health and well-being of your entire body.
Your cerebrum is inside your skull, at the top and front of your head, and makes up the largest part of your brain.
The outer surface of your cerebrum, your cerebral cortex, is mostly smooth but has many wrinkles, making it look something like a walnut without its shell. It’s divided lengthwise into two halves, the left and right hemispheres, by a deep groove. The two hemispheres connect using a structure called the corpus callosum (pronounced “corp-us” “cal-oh-sum”), a collection of nerve tissue that transmits signals from one side of your brain to the other.
Advertisement
The two hemispheres of your brain also have five main lobes each:
Advertisement
A few structures that are part of your cerebrum stand out because they have very specific purposes. These are:
There’s a reason why different parts of your brain handle the same information as others. That’s because the information is interconnected in many ways. Think of it like when you see an alligator. Your brain has to process an enormous amount of information to help you know what to do around that creature.
Advertisement
The average adult brain is between 3.5 and 4 times the volume of a regulation baseball, and your cerebrum makes up about 80% of your overall brain volume. That means your cerebrum is about 3 to 3.2 times the volume of a baseball.
The average adult brain weighs between 2.6 pounds (lbs.) and 3.1 lbs. Your cerebrum makes up about 2 lbs. to 2.5 lbs. of that total weight.
The tissue of your brain is roughly:
Any condition affecting your brain can affect your cerebrum, including mental health conditions. Some major examples include:
Many symptoms are possible when you have a condition that affects your cerebrum. Some of the most common symptoms include:
Many types of tests can help diagnose conditions that affect your brain, including your cerebrum. Common tests include:
The treatments that affect your cerebrum are as varied as the conditions and symptoms that can affect this part of your brain. They can range from medications of all kinds, from antibiotics for bacterial infections to radiation and chemotherapy for brain tumors. Treatments that help one condition can sometimes make others worse, so there’s no one-size-fits-all for treating problems that affect your cerebellum.
You can do several things to help maintain good brain health, including:
Your cerebrum is one of the most important parts of your brain, helping with literally everything you do in your day-to-day life. While experts know a lot about how it works and its structure, there are still many unanswered questions. Fortunately, technology and advances in medical science are helping answer many of those questions, offering a new look inside the mind’s inner workings. That means healthcare providers can better diagnose and treat any conditions you have and try to prevent issues you could face in the future.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
If you have a neurological condition, you want expert advice. At Cleveland Clinic, we’ll work to create a treatment plan that’s right for you.
