The corpus cavernosum is one of two chambers in your penis that fill with blood to help create an erection. They run the length of your shaft, on either side of your urethra. Contact a healthcare provider if you have pain, problems peeing or trouble getting or keeping an erection.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
The corpus cavernosum (pronounced “KAWR-puhs” “KAV-er-NO-sem”) is one of two tubelike structures, or chambers, that run the length of the top of your penis.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Along with the corpus spongiosum (pronounced “KAWR-puhs” “SPUHN-jee-OH-sum”), the corpus cavernosum is the erectile tissue of your penis that fills with blood to create an erection. These spongy, tubelike bodies contain blood vessels and sinuses (hollow spaces) that make your penis hard when they fill with blood. They also have nerves that help with these changes.
The main function of the corpus cavernosa (plural form of corpus cavernosum), along with the corpus spongiosum (spongy tissue surrounding the urethra), is to help make an erection.
Sensory stimulations (like something you see, touch or hear) and mental stimulations (like something you imagine or remember) cause your brain to send messages to the blood vessels in your corpus cavernosa. Your arteries relax, which allows more blood to flow into your penis. As the corpora cavernosa fill with blood, they push the veins closed so the blood stays trapped.
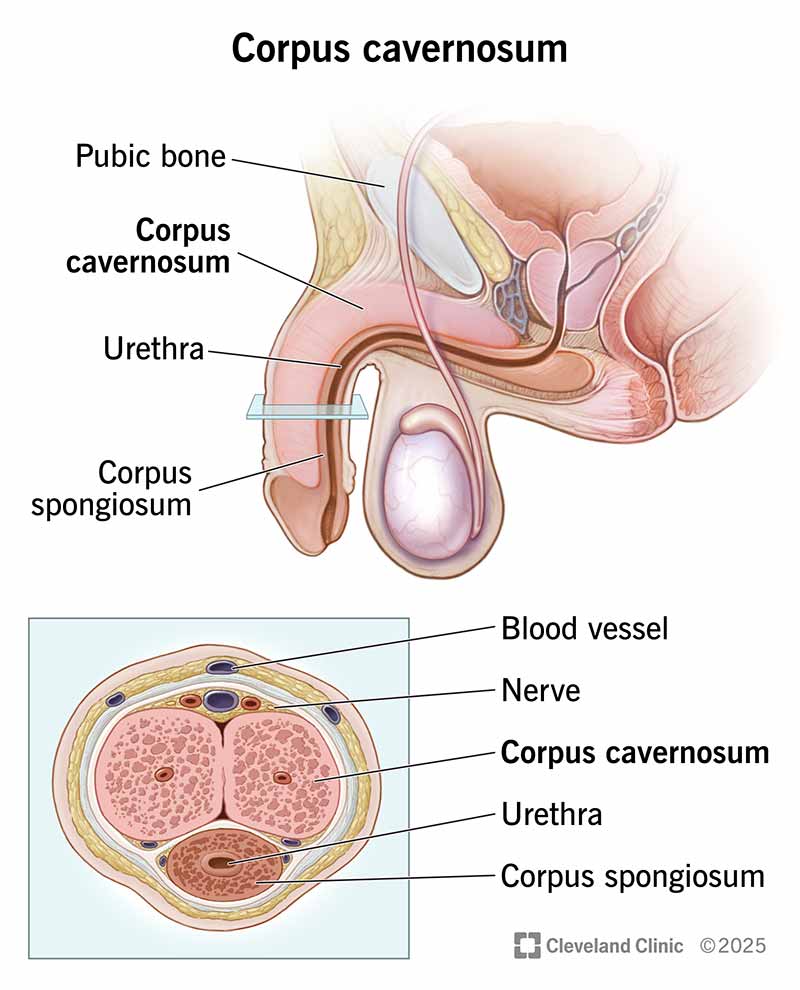
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/corpus-cavernosum)
The corpus cavernosa is in the shaft of your penis, extending from your pubic bone to the head (glans) of your penis.
There’s a corpus cavernosum on either side of your urethra. This is the tube through which urine (pee) leaves your body when you use the bathroom and semen leaves your body when you ejaculate.
Advertisement
The corpus cavernosum mostly consists of connective tissue, including elastin, collagen and smooth muscle. It also has intracavernosal struts (or pillars), which are structures that healthcare providers believe to be important in keeping erectile tissue in place.
Epithelial cells also line hollow spaces in the corpus cavernosa, and endothelial cells line the blood vessels. These cells may be a factor in erectile dysfunction. When an erection occurs, this space fills with blood and becomes rigid.
Some conditions that affect the corpus cavernosum include:
Some signs or symptoms that a condition is affecting your penis and related parts include:
A healthcare provider will review your medical history and perform a physical evaluation. They may also recommend tests, including:
In some cases, they may recommend removing some tissue (biopsy).
Yes. Depending on the condition, different treatments are available. You may need oral, injectable or surgical treatment. A healthcare provider will explain all of the treatment options available to you for your specific condition.
Keeping your penis and corpus cavernosum healthy relates to your overall health. It’s important to manage long-term conditions that can affect blood flow and circulation throughout your body, like diabetes and high blood pressure (hypertension). Healthy blood vessels help create good blood flow, which is essential for creating an erection.
Advertisement
Other tips to promote a healthy penis include:
Odds are, you may not think about your corpus cavernosa too much. In fact, unless you’ve had something wrong with them, you might not know what a corpus cavernosum is at all.
Advertisement
The corpus cavernosa are masses of tissue in your penis that help form an erection when they fill with blood. They’re very important for your sexual function and overall sexual health. Contact a healthcare provider if you notice any changes in your penis, especially if it doesn’t work the way you expect or want it to.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Get the care you need today! At Cleveland Clinic, we offer specialty care that’s focused on you.
