Smoking is the practice of inhaling smoke from burning plant material. Nicotine works on your brain to create a relaxing, pleasurable feeling that makes it tough to quit. But smoking tobacco puts you at risk for cancer, stroke, heart attack, lung disease and other health issues. Nicotine replacements and lifestyle changes may help you quit.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
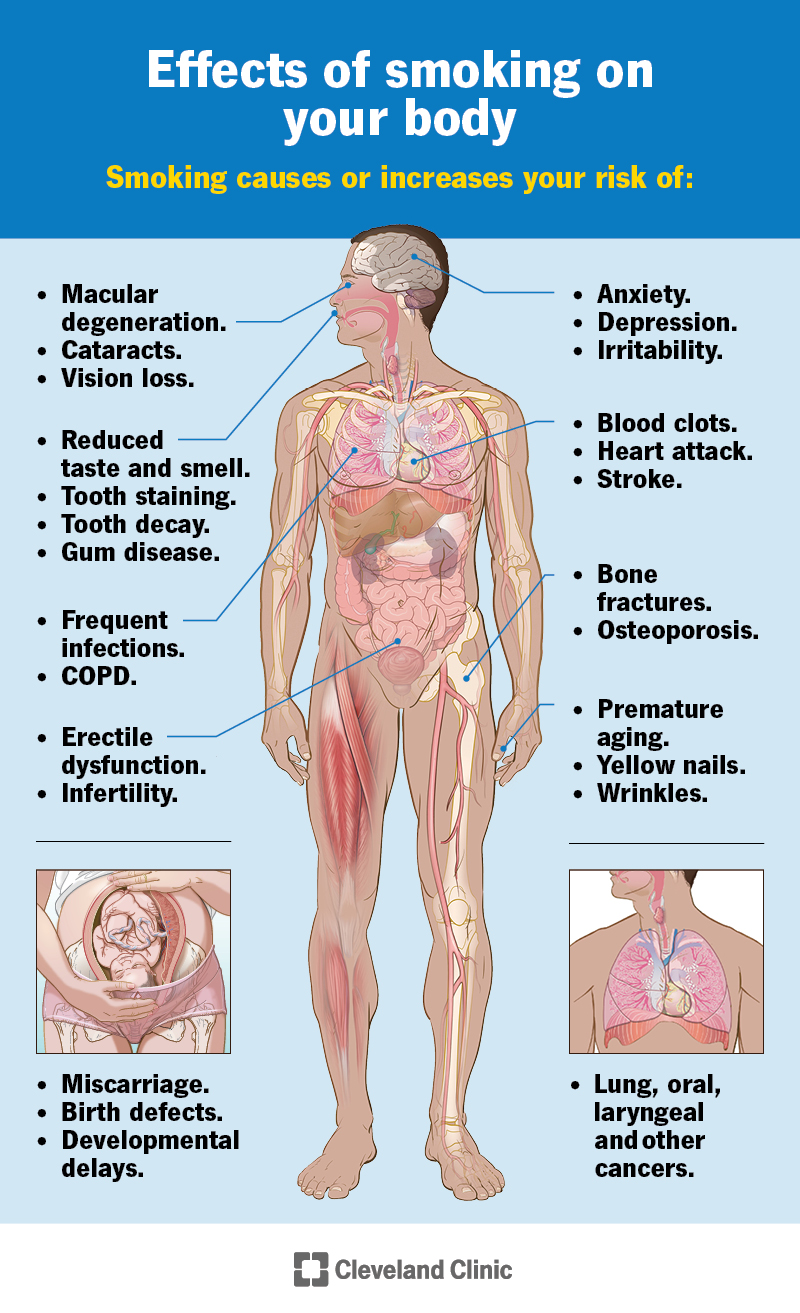
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/smoking)
Smoking is when you inhale and exhale smoke from burning plant material that’s rolled into a wrapper (cigarette). You light the end of the cigarette and pull smoke into your mouth through the other end. It travels down your airways, into your lungs and through your bloodstream to your brain and other organs.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
This piece focuses on smoking tobacco cigarettes, but you can also smoke cigars, pipes, marijuana (weed/pot) or herbal cigarettes.
Commercially produced cigarettes are made up of:
People smoke because they find it enjoyable. And because it’s hard to quit once you start, despite the damaging effects of smoking on your body. This is because of your brain’s cravings for nicotine, which make you feel bad when you don’t get it.
Nicotine releases chemicals in your brain that make you feel good. Smoking might make you feel:
Smoking is also a social activity and a part of people’s routine, just like morning coffee. You might smoke to have fun, to calm yourself before being around a lot of people, or to focus and work. Some people like the taste or just the feeling of holding a cigarette in their hands.
Smoking affects everything from the appearance of your skin and nails to how your tissues, organs and even your DNA work. The effects of smoking on your body start the moment you light up a cigarette. Thousands of chemicals released from burning tobacco start their damaging journey before you’ve even taken a puff.
Advertisement
The heat from burning the cigarette releases nicotine and creates tar (tobacco residue). As you bring the cigarette to your lips, the tar stains your nails. The smoke dries out and inflames your skin, deepening wrinkles. Inhaling smoke through your nose damages nerve endings. Over time, this reduces your sense of smell.
When you take a puff from the cigarette, it goes through a filter. This mostly keeps you from breathing in large particles, but tar, nicotine and other chemicals still get through. The tar stains your teeth and coats your gums and tongue. It damages your tooth enamel, puts you at risk for tooth decay and gum disease, and reduces your ability to taste foods you love.
The tar coats your throat and vocal cords as it moves toward your lungs. This might make you cough. Traveling through your airways, tar and hydrogen cyanide (a poisonous gas) paralyze your cilia. Like bristles on a broom, cilia are hair-like strands whose job is to trap and sweep germs and other harmful particles out of your lungs. When they’re damaged, you’re more likely to get sick with respiratory infections.
When the smoke reaches your lungs, it travels to the small air sacs (alveoli) and damages them. This can lead to emphysema, a form of COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease). From your alveoli, carbon monoxide in the smoke moves into your blood. It bumps oxygen out of your red blood cells, starving your cells and tissues. The lack of oxygen can make you feel short of breath. Your cells sound the alarm to let your body know you need more oxygen, but this causes inflammation and mucus to form, making it even harder to breathe.
While traveling through your bloodstream, nicotine damages the lining of your blood vessels. This thickens and narrows them, and causes blood cells to stick to them, putting you at risk for blood clots, heart attack and stroke. For men, decreased circulation can make it difficult to get an erection (erectile dysfunction).
Once in your blood, chemicals from cigarette smoke travel throughout your body. This damages your:
From your blood, nicotine heads to your brain. There, it activates receptors that release dopamine, adrenaline, endorphins, serotonin and other “feel-good” signals in your brain. This is where a nicotine “buzz” comes from. It’s like nicotine pushing buttons to make you more relaxed, content or energized. It’s only been seconds since you inhaled that first puff of smoke.
Advertisement
Your liver processes nicotine and you pee it out within a few hours of smoking a cigarette. Your body misses the buzz and craves more, encouraging you to have another one. If you don’t, you experience symptoms of withdrawal, like anxiety, depression, restlessness, anger and insomnia. Your body will develop a tolerance to nicotine and eventually need more and more to make you feel good, leading to nicotine dependence.
Narrowed blood vessels in the placenta and umbilical cord restrict blood flow to the fetus. The blood that does flow through carries carbon monoxide, nicotine and other harmful chemicals. This can prevent the fetus from getting enough oxygen and damage its DNA. Women who smoke while they’re pregnant are more likely to have a miscarriage. Babies born to someone who smokes can have low birth weight, heart and lung issues, and developmental delays.
People most commonly associate smoking with causing lung cancer, but smoking can cause or increase your risk for many health conditions in almost every part of your body. These include:
Advertisement
Secondhand smoke, or smoke you breathe in from someone smoking nearby, also has significant health risks.
Smoking causes or increases your risk for many types of cancer. There’s also evidence that people who smoke while getting cancer treatment have a worse outcome (prognosis), are less likely to respond to treatment and are more likely to have the cancer come back (recur). Smoking can cause or increase your risk for:
Yes, your lungs and airways can start to heal if you quit smoking. Inflammation and mucus production calm down in the weeks after quitting and cilia regenerate in a few months. In fact, many of your body systems begin to heal after you quit smoking.
How long this takes depends on how long you smoked before quitting and how much damage it did to your lungs. Some issues, like infertility, can start improving quickly. And some damage may never heal — conditions like COPD and pulmonary fibrosis are irreversible. But if you can stop smoking for several years, your risk of cancer and other health conditions reduces or even returns to the same level as someone who doesn’t smoke.
Advertisement
There are many tools to help you quit smoking. You might need a combination of different approaches before you find a solution that works for you. Or you might need to change your approach when one stops working. Some options include:
It’s no secret that the best way to take care of yourself if you smoke is to quit. But while you’re in the process of quitting, you can help your body heal with exercise, and by eating nutritious foods and drinking plenty of water. Whether you currently smoke or no longer do, talk to your healthcare provider about getting a routine lung cancer screening. It could catch cancer early and save your life.
People have been smoking for social and cultural reasons for centuries. Today, the reasons for smoking aren’t all that different: Having a cigarette might be a routine part of your day — or a way to take a break from it.
But now we know how harmful smoking is for your health — and for the health of your loved ones around you. Unfortunately, because of nicotine’s relationship with your brain, knowing that cigarettes are dangerous doesn’t make kicking the habit any easier. It can be helpful to understand this relationship and know why it’s hard to quit. And remember to be kind to yourself while you do so. Going from smoker to former smoker is a process, and a commitment you make to yourself every day.
In addition to smoking cessation tools, it can be helpful to keep in mind how much better you’ll feel in the long run. You may be able to return to activities you used to enjoy, taste and smell foods properly again, protect the health of your loved ones and probably even save some money. Ask for support from friends, family and your healthcare providers — let them know about the change you’re making and how they can help.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s primary care providers offer lifelong medical care. From sinus infections and high blood pressure to preventive screening, we’re here for you.
