Tooth enamel is the hardest substance in your body — even stronger than bones. It shields the inner layers of your tooth (dentin and pulp) from damage. Although enamel is strong, bacteria, plaque and acids in your mouth can damage it. And once it’s gone, it doesn’t grow back. Regular dentist visits and good oral hygiene can protect your enamel.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
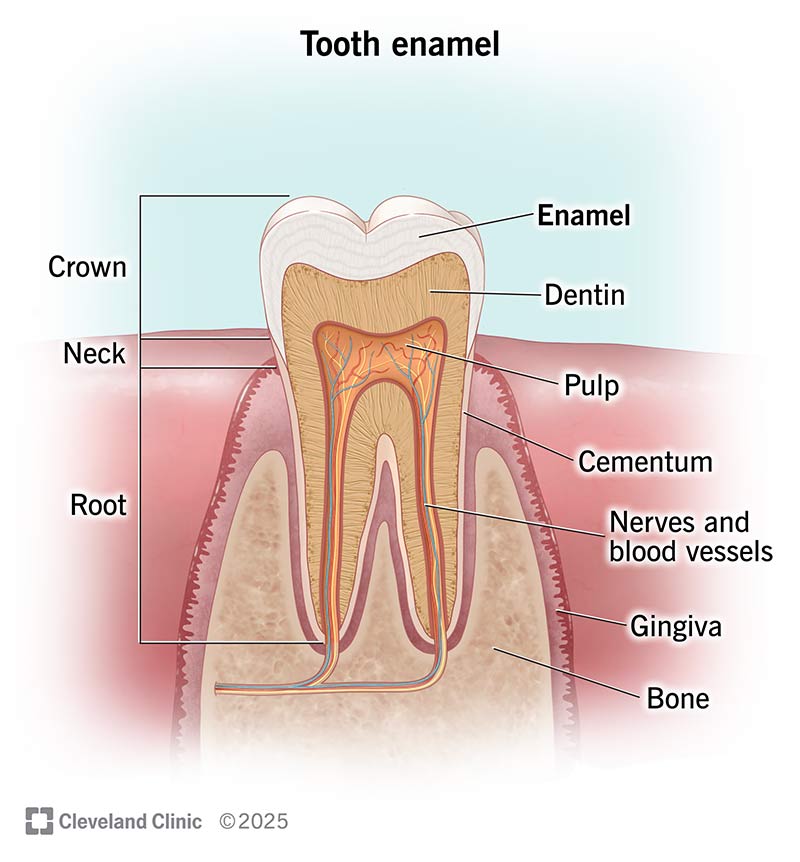
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/Images/org/health/articles/24798-tooth-enamel)
Tooth enamel is the protective outer covering of each of your teeth. It shields your tooth crown (the part you can see above your gums) and the delicate inner layers of your tooth from damage.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Tooth enamel is incredibly durable. In fact, it’s the hardest substance in your body — even harder than your bones.
Even though enamel is strong, it can break down over time. Dental plaque, acids from the foods you eat, and daily wear and tear can all damage your enamel. Once it’s gone, it doesn’t grow back. This is why it’s important to practice good oral hygiene to protect your enamel.
Enamel protects your teeth from damage. Specifically, it protects the innermost layers of your tooth — the dentin and tooth pulp. Damaged enamel can lead to cavities (tooth decay) and infections. It can leave the innermost tissue exposed so that your teeth are more sensitive to hot and cold foods.
Enamel is partially see-through. Dentin (the layer underneath) can vary in color, from grayish-white to light yellow and everything in between. Together, enamel and dentin give your teeth their unique shade.
Tooth enamel is mostly calcium and phosphorus. These minerals, which make up 95% of your enamel, bond together to form ultra-strong crystallites (small crystals).
The rest of your enamel consists of water (4%) and proteins (1%).
Tooth enamel erosion exposes the inner layers of your teeth to open air and the foods and drinks you consume. This makes your teeth more vulnerable to cavities. In addition, tooth enamel loss can make your teeth more sensitive to heat, cold and sweets. They may also stain more easily.
Advertisement
Several things can lead to tooth enamel loss, like:
Keeping your oral hygiene in check is the best way to ensure your enamel stays strong and healthy. Here are some tips:
You can’t regrow enamel that’s gone. But dentists can encourage your body’s ability to repair lightly damaged tooth enamel with fluoride treatments. Fluoride remineralizes and strengthens the outer layers of your teeth.
Your dentist can place a dental crown over your tooth to protect it from further damage.
When used properly, teeth whitening doesn’t damage your enamel. But some whitening products can dry out your teeth. If you’re interested in teeth whitening, talk to a dentist about safe product recommendations.
Enamel is the hardest substance in your body. It protects your teeth from cavities and everyday wear and tear. Although tooth enamel is durable, it’s not indestructible. To keep it healthy, visit your dentist regularly and practice good oral hygiene. Your dentist can also recommend fluoride products and tell you how to strengthen tooth enamel at home.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Dentistry plays an important role in oral health. Cleveland Clinic’s experts can design a personalized plan that will keep you smiling for the long haul.
