Hypoparathyroidism is a rare but treatable condition that causes low levels of calcium in your blood. Damage to your parathyroid glands during surgery and certain genetic and autoimmune diseases can cause it. Treatment usually involves calcium and vitamin D supplements.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Hypoparathyroidism is a rare, treatable condition that happens when your parathyroid glands don’t produce enough parathyroid hormone (PTH). PTH helps regulate calcium and phosphorus levels in your blood. This condition causes calcium levels in your blood to drop and phosphorus levels to rise. Too much phosphorus in your blood can lower your calcium even more. This can lead to several health problems.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Calcium is one of the most important minerals in your body. Most of your calcium is stored in your bones, but you have it and need it in your blood, too. The calcium in your blood has many important roles, including helping:
Low calcium levels in your blood (hypocalcemia) can affect your how well your body works.
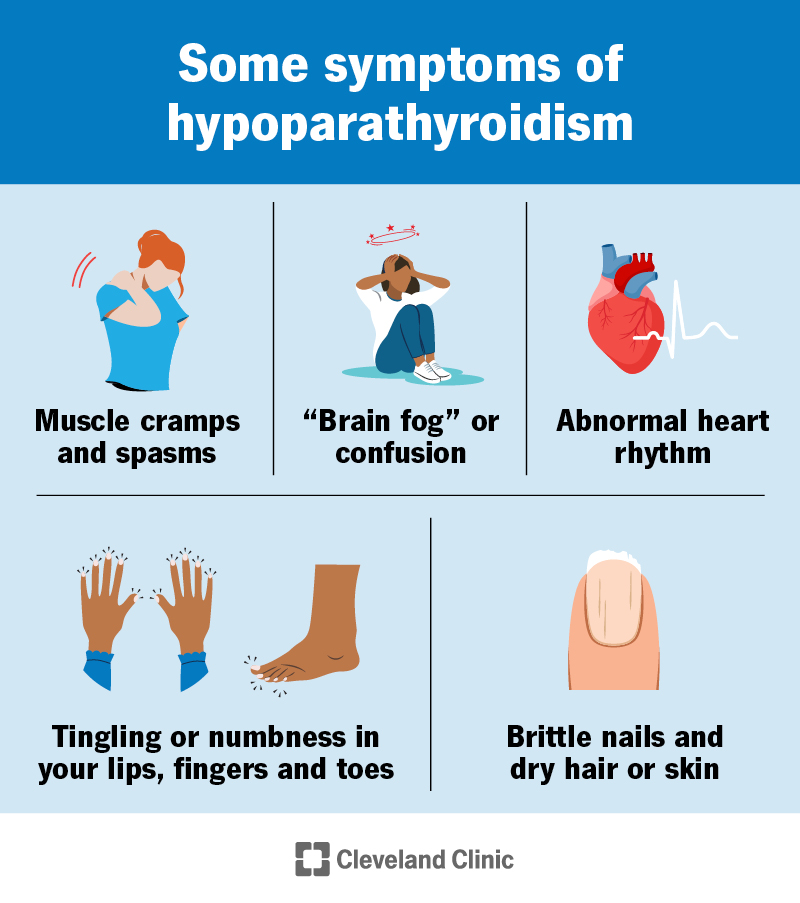
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/22672-hypoparathyroidism)
Signs and symptoms of hypoparathyroidism include:
In most cases, hypoparathyroidism progresses gradually, and symptoms can be mild. Many people have symptoms for years before they get a diagnosis.
Causes of hypoparathyroidism include:
Advertisement
Risk factors for hypoparathyroidism include:
Both adults and children can get hypoparathyroidism. Adults are more likely to get hypoparathyroidism from accidental damage to their parathyroid glands during surgery. Children are more likely to have hypoparathyroidism due to a genetic condition.
Long-term complications of hypoparathyroidism can include:
For children, complications from hypoparathyroidism can include:
Complications of a sudden drop in calcium levels include seizures and larynx spasms. These can be dangerous. If you’re experiencing these symptoms, get to the nearest hospital as soon as possible.
Hypoparathyroidism is generally diagnosed when a person has low levels of calcium and parathyroid hormone in their blood.
Healthcare providers sometimes “accidentally” find hypoparathyroidism when a routine blood screening shows you have low levels of blood calcium.
You have chronic hypoparathyroidism if you have low levels of PTH and calcium at least twice within six months.
If you’re experiencing symptoms of hypoparathyroidism, your healthcare provider will perform a physical exam and ask questions about your symptoms and medical history.
They may order one or more of the following tests to help diagnose hypoparathyroidism:
Your healthcare provider may want to check for more serious side effects of hypoparathyroidism, including:
The goal of treatment for hypoparathyroidism is to get the right amount of calcium and minerals in your body.
Treatment can include:
Advertisement
Contact a healthcare provider if you have symptoms of hypoparathyroidism. If you already have a diagnosis, you should have regular visits with them. They’ll monitor your blood calcium levels to make sure treatment is working.
If you have symptoms of acute hypocalcemia, like painful muscle cramps or seizures, go to the nearest hospital.
The prognosis for hypoparathyroidism is generally good, especially if a healthcare provider catches it early. With treatment, you can feel relief from your symptoms. If calcium levels are hard to manage, you may have long-term issues like kidney problems and muscle changes. Regular check-ups with your provider are important. They’ll perform blood tests to check your calcium and phosphorus levels.
Most cases of hypoparathyroidism are chronic (lifelong), though it can sometimes be temporary.
Hypoparathyroidism is an uncommon condition. The good news is that it’s treatable. Symptoms of hypoparathyroidism can be mild and undetectable, so it’s important to let your healthcare provider know if you have risk factors for hypoparathyroidism, like having a family history of parathyroid disorders or having neck or thyroid surgery. Your provider can run some simple blood tests to make sure your parathyroid hormone and calcium levels are where they should be.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic treats all parathyroid diseases, including cancer, and their side effects. We’ll create a personalized treatment plan that meets your needs.
