Cystic kidney disease causes cysts to form in or around your kidneys. There are different types of cystic kidney disease. Some are the result of abnormal genes. Others start during fetal development or due to kidney failure. Symptoms commonly affect how you pee. Treatment often includes medication, dialysis or a kidney transplant.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
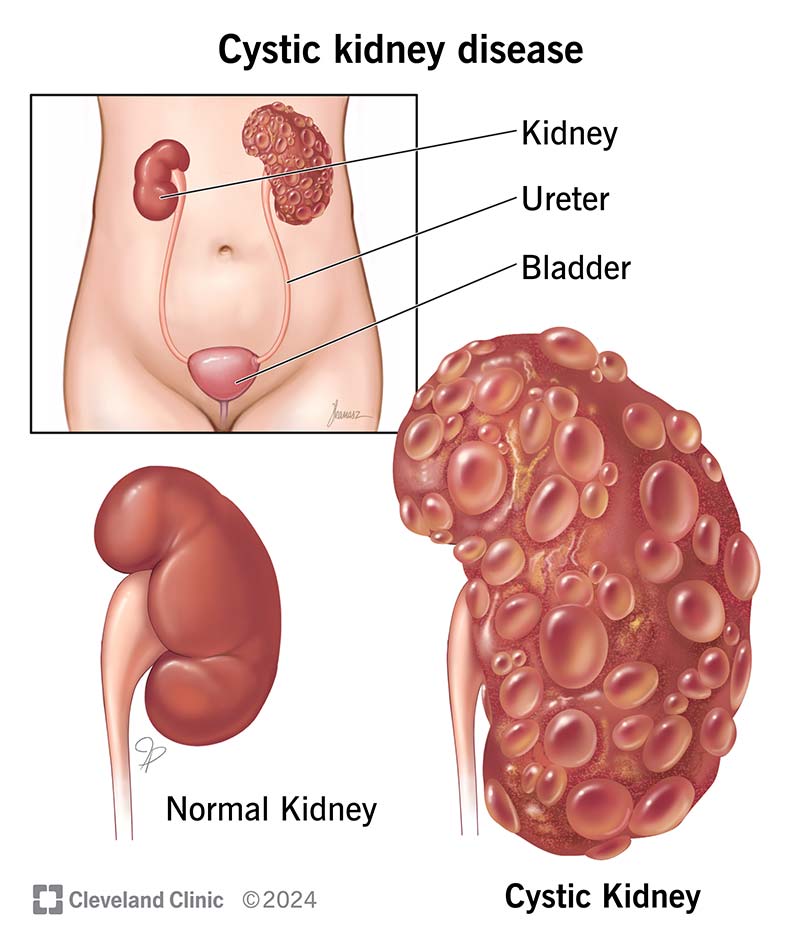
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/cystic-kidney-disease)
Cystic kidney disease describes a group of conditions that cause fluid-filled sacs (cysts) to form in or around your kidneys. Kidney cysts can prevent your kidneys from filtering wastes and excess water out of your blood. Cystic kidney disease can lead to kidney failure.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Another name for cystic kidney disease is renal cystic disease.
It depends. Some cystic kidney diseases are very common. For example, simple kidney cysts occur in about 1 out of every 10 people. But other forms of cystic kidney disease are rare.
The various cystic kidney diseases have different symptoms. But some of the most common symptoms include:
Cystic kidney diseases have different causes. Some may result from genetic variations. Others might develop over time due to diseases, birth defects or age.
Cysts occur when renal tubule pieces detach from a larger parent tube. Your kidneys have thousands of tiny tubes that clean your blood and release pee into your bladder.
Risk factors for cystic kidney disease vary widely across the different types. But in general, you’re more likely to get cystic kidney disease if you’re:
Some of the more common complications of the various cystic kidney diseases include:
Advertisement
A healthcare provider will ask you about your symptoms and review your medical history. They’ll also order one or more of the following imaging tests to check for kidney cysts:
A provider will also likely order blood tests and a pee test (urinalysis) to see how well your kidneys are filtering your blood.
Simple kidney cysts that don’t cause any symptoms may not need treatment. A healthcare provider may monitor the cysts and perform annual ultrasounds to make sure they don’t grow. If the cysts are painful or cause other symptoms, they may perform fine-needle aspiration to drain the cyst or laparoscopic surgery to cut or burn away the cyst tissue.
If you develop kidney failure from cystic kidney disease, a provider may recommend:
It depends. Unless you’re in a lot of pain or have other symptoms, healthcare providers usually don’t recommend removing your kidneys, even if they stop filtering wastes. They may still filter excess water from your body. But a provider may recommend a nephrectomy to remove your damaged kidneys if they cause a lot of pain or other symptoms.
There’s no cure for cystic kidney disease. But there are many treatment options to slow the progression of polycystic kidney disease. You may need dialysis or a kidney transplant.
This can vary. It depends on the specific genetic variation. But it often has a similar pattern in a given family. PKD (polycystic kidney disease) involves two major genes — PKD1 and PKD2. People with the PKD1 gene variation tend to go on to kidney failure sooner (around mid-50s) than people with the PKD2 gene variation (early 70s).
Your healthcare team will give you a better idea of what to expect according to your unique situation.
Nearly 80% of people with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease have preserved kidney function at 50. Over 50% have preserved kidney function into their early 70s.
About one-third of babies who have autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease at birth don’t survive. Babies who do survive need treatment for the rest of their lives.
Advertisement
There’s no way to prevent cystic kidney disease. But talking to a healthcare provider when you first notice symptoms and working with a nephrologist may help slow the progression of some forms of cystic kidney disease.
You may need to work with a renal dietitian to develop kidney-friendly eating patterns if you have chronic kidney disease or reduced kidney function due to cystic kidney disease. This may include:
Call a healthcare provider or get to the nearest emergency room if you have the following signs of sudden kidney failure, including:
You may want to ask your provider:
Advertisement
It depends. Simple kidney cysts don’t make your kidneys larger, replace kidney tissue or affect how well your kidneys work. They usually don’t develop into a serious problem.
Complex kidney cysts can affect the size, structure and function of your kidneys. They can also be a sign of kidney cancer.
If you have a kidney cyst, healthcare providers will monitor it for changes and recommend treatment, if necessary.
Yes, there are several types of cystic kidney disease. Some types are genetic. That means they develop because of variations in certain genes in your body. If you have a genetic kidney disease, you usually inherit the gene variations from one or both of your biological parents. A genetic variation can also start with you. Other types of cystic kidney disease may develop during your lifetime (acquired).
Some genetic cystic kidney diseases include:
Advertisement
Cystic kidney disease describes a group of disorders that cause cysts to form in or around your kidneys. Some cases are mild, and you may not experience any symptoms or need any treatment. But others can have a greater effect on your kidneys and prevent them from working. Managing cystic kidney disease is possible, and many people can live for years with proper treatment. Trusted family members and friends can help you cope with your feelings and overcome difficulties. Support groups are also available to help you safely and confidentially share your feelings and experiences.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
You can’t reverse chronic kidney disease (CKD), but you can manage it. Cleveland Clinic healthcare providers are here to help you keep your CKD under control.
