Your bronchi are the large tubes that carry air from your windpipe to your lungs. Your left main bronchus goes into your left lung, and your right main bronchus goes into your right lung. After the main bronchi, they branch out into smaller segments. Many respiratory conditions, like asthma and bronchitis, can affect your bronchi.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
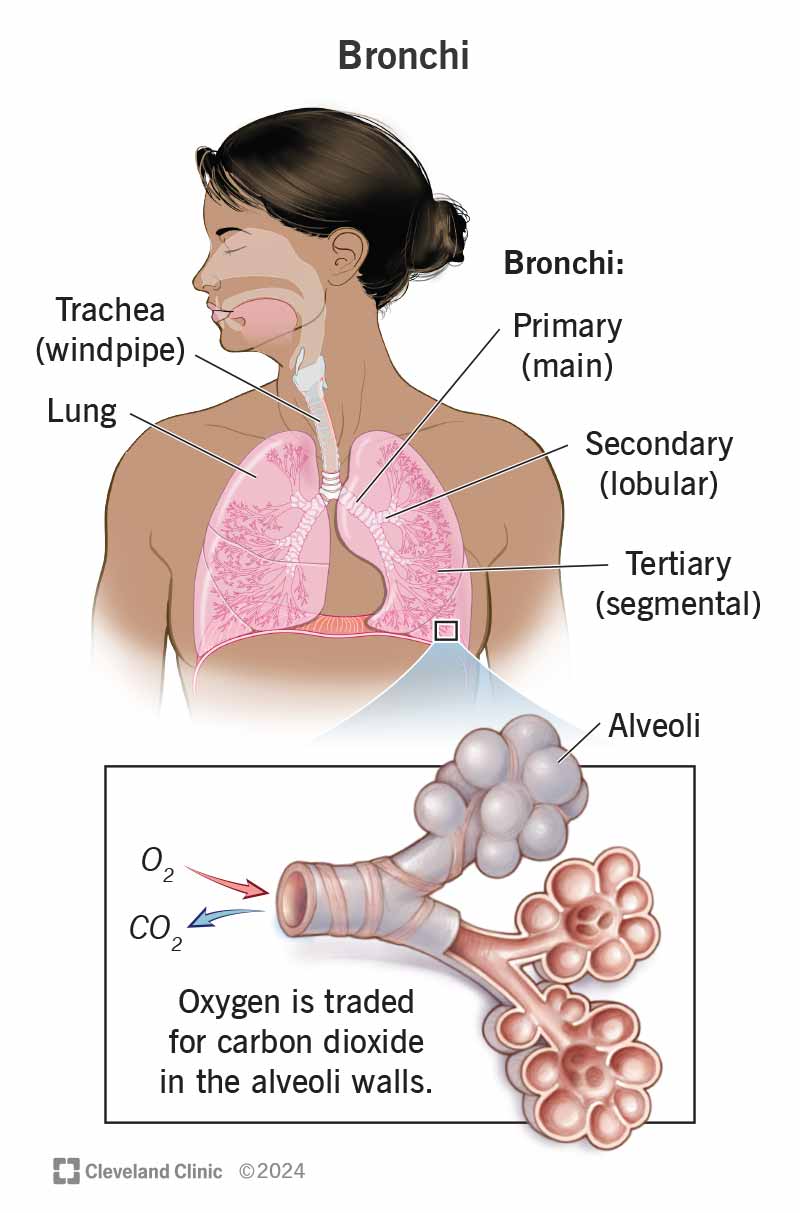
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/bronchi)
Your bronchi (BRON-kai) are large tubes that air travels down to get to your lungs. You have two main bronchi (left and right) that connect to the bottom of your trachea (windpipe) in your chest. Your left bronchus and right bronchus divide into smaller bronchi further into your lungs. (Bronchus is the singular of bronchi.)
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Your bronchi are an essential part of your respiratory system. They’re part of a network of tubes (airways) that bring air in through your nose or mouth and direct it to the air sacs in your lungs (alveoli).
Your bronchi work as passageways that carry air to and from your lungs. As you breathe and your lungs expand, your bronchi distribute the air within your lungs.
Your bronchi are lined with mucus, which moisturizes the air along the way and traps foreign particles, like viruses, bacteria and dust. Cilia (hairlike structures) in your bronchi push trapped germs and other particles out of your body when you cough or sneeze.
Your bronchi are a part of your respiratory system. When you inhale:
Carbon dioxide enters your lungs from your blood as it picks up oxygen. When you exhale, your bronchioles, bronchi and the rest of your airways push carbon dioxide out of your lungs with the air you breathe out.
Your bronchi are located in your lungs, which are inside your rib cage in your chest. They connect to the bottom of your trachea. They start with large tubes and branch off into smaller tubes, eventually leading to your smallest airways (bronchioles).
Advertisement
Your bronchi start off as two large tubes and branch off into segments. The different parts of your bronchi include:
Your bronchi are made up of smooth muscle surrounded by cartilage. This provides support and controls air flow. Your primary bronchi are supported by cartilage rings. Your secondary and tertiary bronchi are smaller and have patches of cartilage instead. Mucus membranes and cilia line your bronchi.
Your bronchi are part of the tracheobronchial tree, which includes your trachea, bronchi and bronchioles. Your tracheobronchial tree looks like an upside-down tree with the trachea as the trunk and the bronchi representing the branches.
Conditions that can affect your bronchi include:
Symptoms of conditions that affect your bronchi include:
Depending on your symptoms, your healthcare provider may use pulmonary function tests to check the health of your bronchi and lungs. One of the most common pulmonary function tests is spirometry, which measures how much air you can hold and how forcefully you can exhale it.
Other common tests include:
Advertisement
Treatments depend on the condition affecting your bronchi. Some common treatments include:
Ways to keep your bronchi and the rest of your airways healthy include:
Advertisement
Contact a healthcare provider if you have a nagging cough or feel like you’re not breathing as well as you could be.
Call 911 or go to your nearest emergency room if you experience any signs of respiratory distress. These include:
Your bronchi have the big job of bringing air into your lungs. Your body uses the air to get the oxygen it needs for energy. Along the way, your bronchi moisturize the air and protect you from germs and other things that might harm you.
Damage and inflammation in your bronchi can lead to conditions like bronchitis and COPD. To keep your bronchi healthy, don’t smoke or vape and avoid breathing in anything that can harm your lungs.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s primary care providers offer lifelong medical care. From sinus infections and high blood pressure to preventive screening, we’re here for you.
