Melatonin is a natural hormone that’s mainly produced by your pineal gland in your brain. It plays a role in managing your sleep-wake cycle and circadian rhythm. Scientists still have a lot to learn about all of its effects on the human body. Synthetic melatonin supplements aren’t approved to treat or manage any conditions or symptoms.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
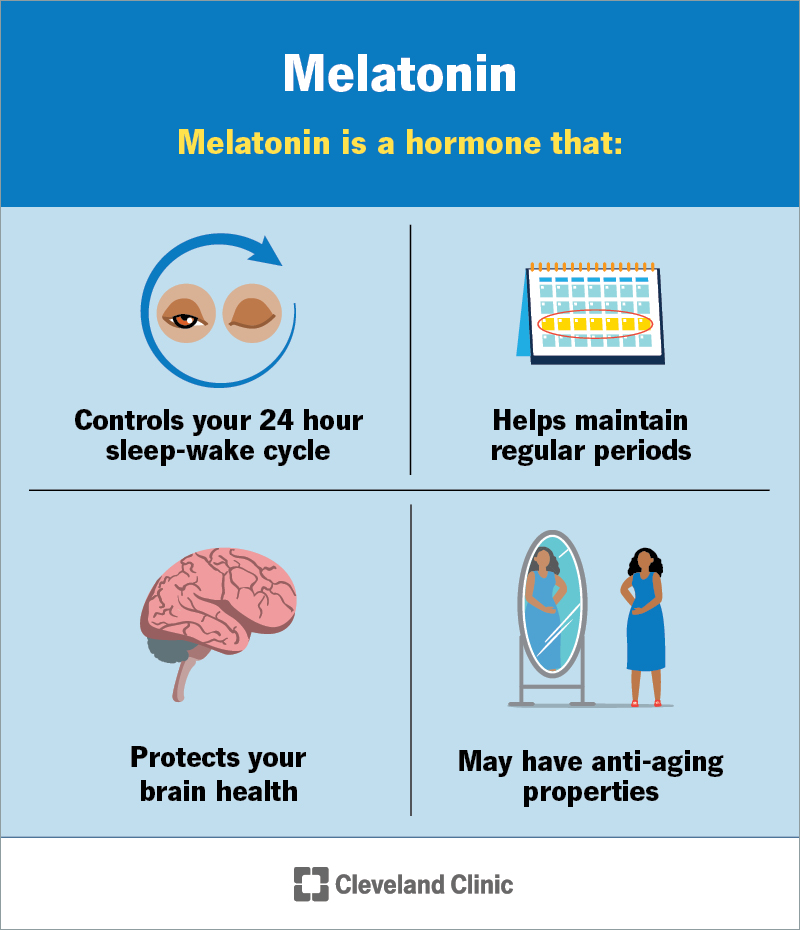
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/melatonin)
Melatonin is a hormone that’s an important part of your ability to sleep. The pineal gland produces it. Natural melatonin your body makes is also known as endogenous melatonin. It helps regulate your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle, which makes you feel tired at the end of the day and wake up after resting.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Melatonin can also be made synthetically in a lab and sold as a dietary supplement. It’s called exogenous melatonin.
Melatonin helps control your circadian rhythm. This is your sleep-wake cycle that happens automatically about every 24 hours.
Melatonin helps your body get ready to fall asleep. It’s not a magic potion that makes you sleepy, but it’s an important chemical change in your body that happens each day.
Your pineal gland releases the most melatonin when there’s darkness and decreases melatonin production when you’re exposed to light. In other words, you have high melatonin levels at night when you’re sleeping and less in your blood during the daylight hours.
The longer the night, the longer your pineal gland secretes melatonin. That’s why some people feel sleepy earlier or more often in winter months. In winter, there’s less sunlight in the day and it stays dark longer, so your body naturally releases more melatonin in response.
Melatonin is a chemical messenger that tells your body it’s time to relax and get ready to rest. Your pineal gland automatically releases extra melatonin around the same time every day. This usually happens when the sun goes down.
Melatonin affects cells in your brain’s hypothalamus. It tells your hypothalamus it’s time to slow activity down for the day. Once it gets the message, your hypothalamus dials back the functions it controls — like your body temperature, blood pressure and mood — to get you ready for sleep.
Advertisement
In your eyes, melatonin changes your retinas to get ready for rest and being less active. Melatonin helps your retinas become less responsive to light, which helps you wind down and feel less alert. When there’s more natural light the next morning, your retinas automatically become more active and your body stops releasing as much melatonin.
Melatonin plays an important role in making sure you get enough sleep. Your body needs that natural, chemical reminder to feel tired each night. Getting enough sleep is important for every part of your health and body, including your:
Melatonin’s biggest job is regulating your sleep-wake cycle. But it works in other areas of your body, too:
Your natural melatonin level can vary depending on your age and sex recorded at birth. Females typically have higher melatonin levels than males.
The level of melatonin your body produces changes throughout your life.
Newborn babies don’t produce their own melatonin. Before birth, they receive melatonin from the placenta. After birth, they can receive it through breast milk or formula. Babies develop a melatonin cycle when they’re 3 to 4 months old.
Melatonin levels are highest in kids and teens right before starting puberty. After puberty, there’s a steady decrease in melatonin levels until it evens out in your late teens. The level is stable until around age 40, followed by a natural decline for the rest of your life.
You may never know your melatonin level if you don’t experience any symptoms or need tests to measure it. If you do need a melatonin test, your healthcare provider will let you know if your levels are within normal ranges.
The two main conditions that involve melatonin issues are hypomelatoninemia (lower-than-usual levels of melatonin) and hypermelatoninemia (higher-than-usual levels of melatonin).
Hypomelatoninemia happens when you have lower-than-normal nighttime melatonin levels. It can also happen if your body produces a total amount of melatonin that’s less than expected for your age.
Hypomelatoninemia can play a role in circadian rhythm sleep disorders. These sleep disorders disrupt your natural sleep-wake cycle. These can affect:
Advertisement
Hypermelatoninemia is when there’s too much melatonin in your blood. Taking too much synthetic melatonin from supplements is the most common cause. It can also happen if your pineal gland produces excess melatonin (but this is rare).
Having hypermelatoninemia can increase your risk of some health conditions, including:
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) doesn’t regulate supplements. Researchers are studying the potential benefits of synthetic melatonin.
It’s important to know that a melatonin supplement isn’t a “magic pill” that can solve sleep issues. It’s not FDA-approved to treat health conditions, manage symptoms or give any proven health benefits.
Advertisement
It’s always a good idea to see a healthcare provider before starting any new supplements, especially if you’re taking other medications. Talk to a provider about any sleep issues you’re experiencing. They’ll help you figure out what’s causing them and how you can get good, refreshing rest.
Melatonin is an important part of your daily routine, even if you don’t know it. It helps your body get ready to sleep at night and wake you up in the morning. If something throws your melatonin out of whack, you might notice symptoms of a sleep disorder. Talk to your healthcare provider if you’re having trouble sleeping (or waking up).
Synthetic melatonin supplements are available over the counter, but they’re not guaranteed to help your health. Talk to your provider before starting a new supplement. They’ll help you make the best choices for you and your health.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
When you can’t fall or stay asleep or drift off during the day, you want answers. Cleveland Clinic’s sleep disorders experts can help you get them.
