Serratia marcescens is bacteria that sometimes causes infections, including UTIs and pneumonia. You’re at higher risk for infection if you’re in the hospital or at a long-term care facility, have a weakened immune system or a medical device in your body. S. marcescens can be hard to treat because it’s often resistant to many antibiotics.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
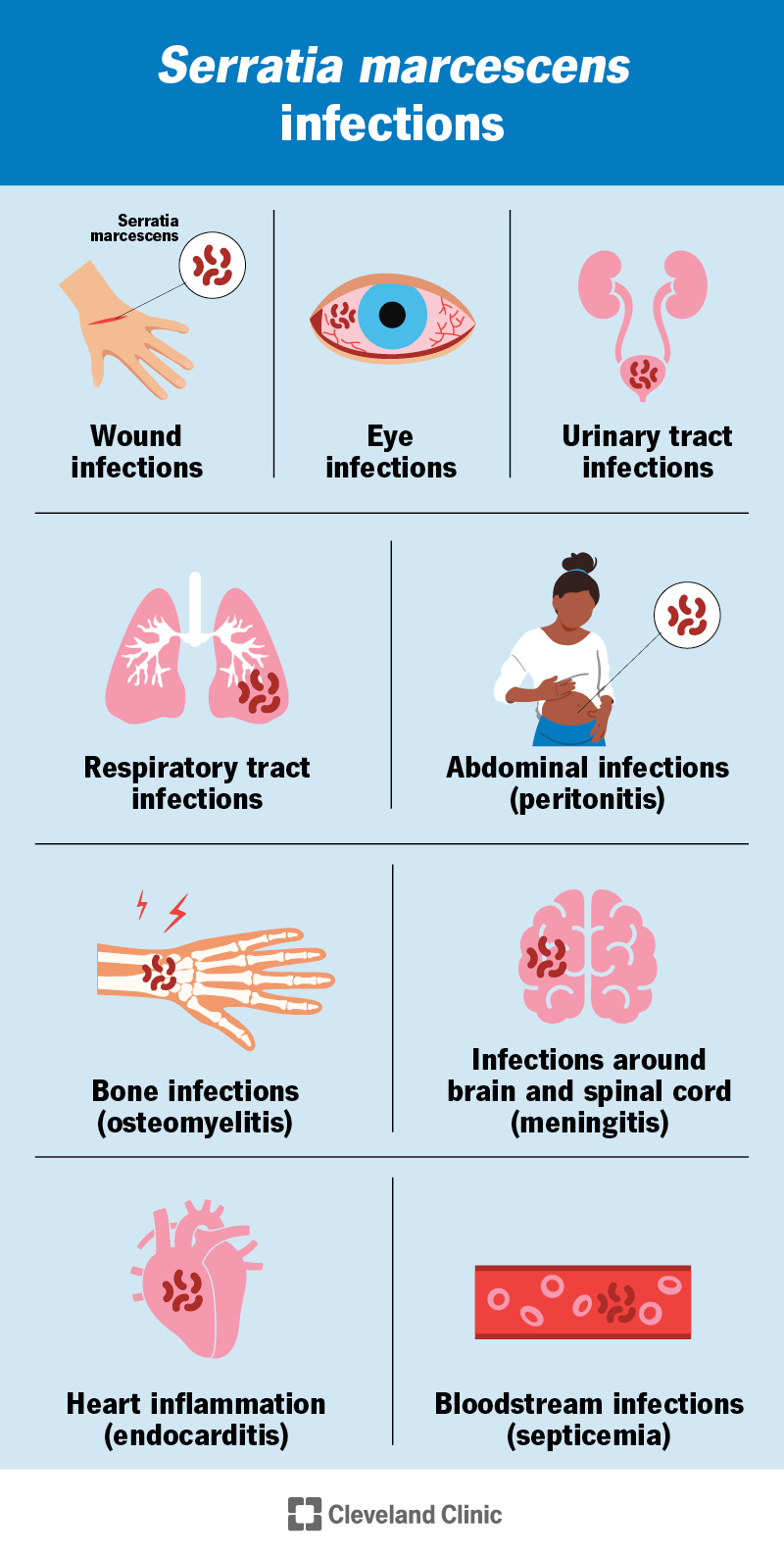
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/serratia-marcescens)
Serratia marcescens (S. marcescens) is a type of bacteria that’s found in the environment and can sometimes cause infections in people. Infections — when they happen — usually only spread in hospitals or long-term care facilities (nosocomial infections). These can be hard to treat because they can develop antibiotic resistance (when antibiotics don’t work to get rid of the infection).
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
S. marcescens can cause:
You may even sometimes see S. marcescens around your house. It looks like a pink film and can grow in moist environments, like showers or toilet bowls. Fortunately, most people don’t get sick from S. marcescens growing in their homes or the environment.
Serratia marcescens is pronounced “sir-AY-shuh maar-SEH-senz.”
Symptoms of an S. marcescens infection depend on where in your body you’re infected. Some symptoms could include:
Examples of specific symptoms based on infection site include:
Most of the time, people get S. marcescens infections in hospitals or long-term health facilities. The bacteria can spread:
Advertisement
Sometimes, people get eye infections from contaminated contact lenses.
You might be at higher risk for an S. marcescens infection if you have:
People who inject drugs into their veins are also at higher risk.
If S. marcescens spreads to your blood, it can cause serious complications, including:
How a healthcare provider diagnoses an S. marcescens infection depends on your symptoms and where you’re infected. They may take samples from your body to try to grow (culture) S. marcescens, including:
Providers treat Serratia marcescens with antibiotics. Because the bacteria can have antibiotic resistance, a lab might test a sample of the bacteria to see which drug is most effective against it. It might take a combination of medications to get rid of the infection.
Even when you’re in the hospital — or if you’ve just gone home — communication with your healthcare team is important. You know when something isn’t right with your body, even if it’s not immediately clear to someone else. Let them know if you’re experiencing symptoms of an infection, like pain, rapid heart rate, weakness or fever.
What to expect with an S. marcescens infection depends a lot on where in your body you’re infected and any existing health conditions (comorbidities). For example, urinary tract infections are often treatable. Bacteria in your bloodstream is more serious.
Make sure to take all of your medication as prescribed, even if you feel better.
Healthcare providers follow safety and sterilization rules to prevent healthcare-acquired infections like S. marcescens. These include:
You can help prevent S. marcescens infections by washing your hands frequently, especially if you’re caring for someone with a weakened immune system or who’s spent a long time in a healthcare facility recently. You can also ask your provider how long you need to use invasive medical devices like catheters.
Advertisement
Healthcare providers work to keep hospitals and long-term care facilities safe. But sometimes, hospital-acquired infections with bacteria like Serratia marcescens still happen. While some infections are easily treatable, others can be serious. Don’t hesitate to speak up to a provider if you’re concerned about S. marcescens for you or a loved one in their care. They can answer any questions you have.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Have a virus, fungus or bacteria? Some of these “bugs” won’t go away on their own. Cleveland Clinic’s infectious disease experts are here to help.
