Intubation can help save your life when you can’t breathe. A healthcare provider uses a laryngoscope to guide an endotracheal tube into your mouth or nose, voice box and then trachea. The tube keeps your airway open so you can get air into your lungs. Providers usually perform intubation in a hospital during an emergency or before surgery.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
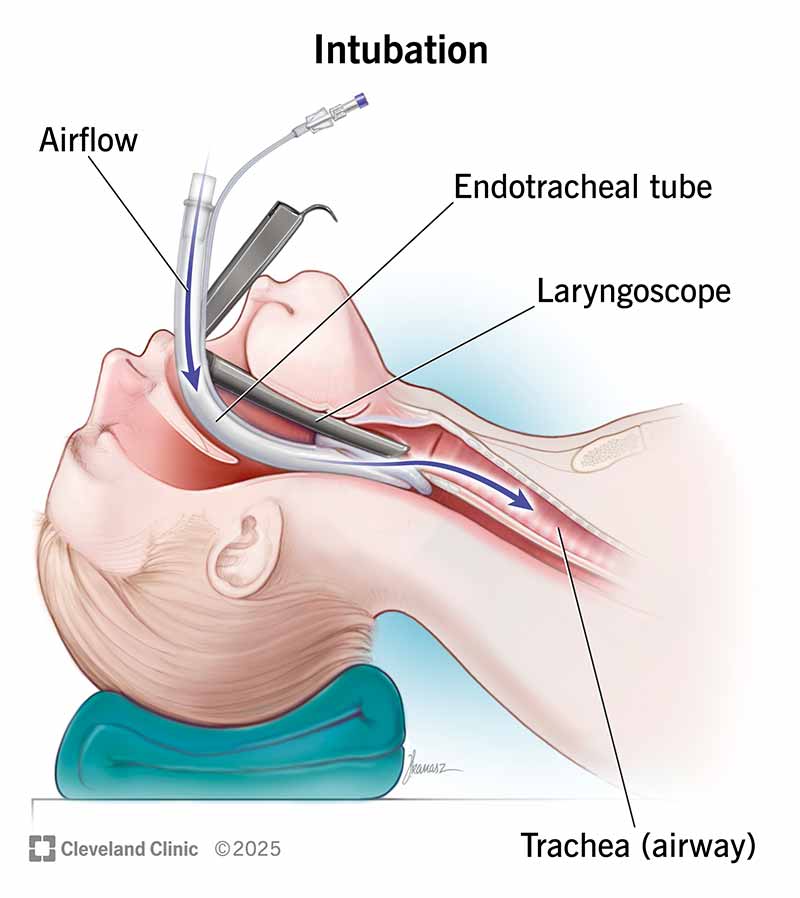
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/intubation)
Intubation (in-too-BEY-shuhn) is a process in which a healthcare provider inserts a breathing tube through your mouth or nose, then down into your windpipe (trachea). The tube keeps your trachea open so air can get through. The tube can connect to a machine that delivers air or oxygen with pressure (mechanical ventilation).
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Other names for intubation include:
A healthcare provider may need to intubate you when a blockage or damage to your airways keeps you from breathing. Some conditions that can lead to intubation include:
Intubation is a very common lifesaving procedure. Each year in the U.S., healthcare providers perform intubation approximately:
Most intubation procedures happen in the hospital. Sometimes, emergency medical services (EMS) personnel intubate people outside of a hospital setting.
Advertisement
During endotracheal intubation, healthcare providers will:
In an emergency, a healthcare provider can complete intubation in less than a minute.
No. The endotracheal tube passes through your vocal cords, so you won’t be able to speak.
You also can’t swallow while intubated, so you can’t eat or drink. Depending on how long you’ll need intubation, healthcare providers may give you a peripheral IV to provide liquid nutrition (enteral nutrition) or IV fluids. They may also deliver them through a separate slim tube that they insert in your mouth or nose, which ends in your stomach or small intestine (small bowel).
When healthcare providers decide it’s safe, they’ll remove the tube (extubation). They’ll:
Your throat (pharynx) may be sore for a few days after extubation. You also may have trouble speaking.
Intubation is a common and generally safe procedure that can help save your life. The benefits of intubation far outweigh any possible risks.
The intubation survival rate varies according to many factors, including the reason for intubation, your age and your overall health. But according to one study, a little less than 7 out of every 10 people survive intubation in an emergency department setting.
Advertisement
Though intubation is generally safe, risks may include:
Advertisement
In some cases, healthcare providers may decide that it’s not safe to intubate. This may happen if there’s severe trauma to the airway or an obstruction prevents providers from safely placing the tube.
In these cases, providers may decide to surgically open your airway through your throat at the bottom of your neck (tracheostomy). A tracheostomy is often necessary when you have an endotracheal tube in place for more than a few days or when you’re expected to have it for weeks.
Most people recover from intubation in a few hours or days. Reach out to a healthcare provider if you still have problems with coughing, swallowing or talking a few weeks after intubation. They may refer you to a head and neck specialist (otolaryngologist).
Immediately contact a healthcare provider if you experience any of the following symptoms after intubation:
It depends on why you need intubation. Healthcare providers sometimes use intubation during scheduled surgeries. But in emergency situations, intubation acts as a form of life support when you can’t breathe on your own.
Advertisement
Intubation and mechanical ventilation relate to each other. But they’re not exactly the same.
Intubation is the process of inserting an endotracheal tube into the airway. A healthcare provider then hooks the tube up to a device that delivers air. The device can be a bag that the provider squeezes to push air into your body, or it can be a ventilator. A ventilator is a machine that blows oxygen into your airway and lungs. Sometimes, a ventilator delivers air through a mask, not a tube.
Nasotracheal intubation is when healthcare providers insert a tube through your nose. Providers commonly use it if you need surgery in your head, mouth or neck. You may also need nasotracheal intubation to help prevent additional trauma to your neck or windpipe.
The thought of a healthcare provider inserting a tube down your throat can be frightening. But intubation is a common medical procedure in operating rooms and emergency departments that can help save your life if you can’t breathe. Most people have a sore throat or difficulty talking after the procedure. But these side effects typically go away within a week.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Sometimes you have surgery planned. Other times, it’s an emergency. No matter how you end up in the OR, Cleveland Clinic’s general surgery team is here for you.
