People with bradyarrhythmia have a heart rate that’s slower than typical. When the heart beats too slowly, it doesn’t pump blood and oxygen to your brain as efficiently. This can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, dizziness and shortness of breath.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
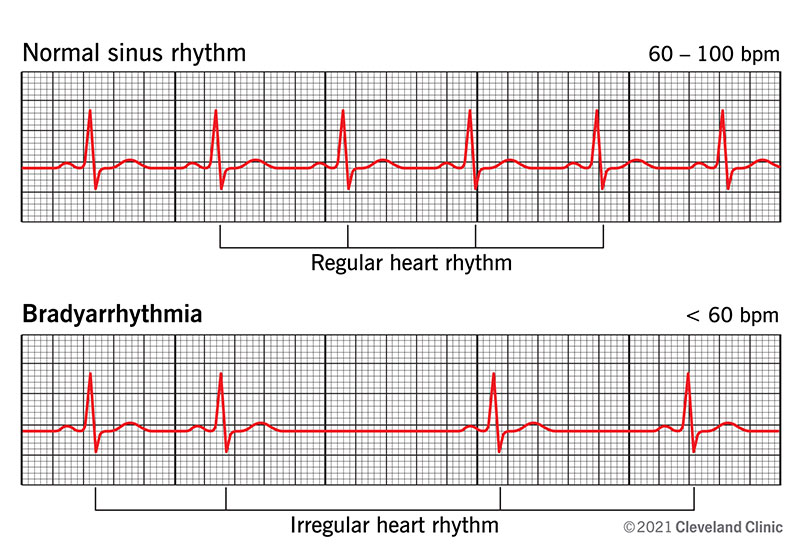
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/Images/org/health/articles/23349-bradyarrhythmia)
A bradyarrhythmia is a heart rate that’s slower than typical because of an irregular heart rhythm. People with bradyarrhythmia have resting heart rates below 60 beats per minute. For most adults, a resting heart rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute is considered normal.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Sometimes, healthy people have naturally slow heart rates. But people with bradyarrhythmia have a heart rate that’s slow because of a medical condition, heart disease or defect that affects the heart’s rhythm.
Both terms mean having a slower than average heart rate. Bradycardia describes a resting heart rate below 60 beats per minute. Bradyarrhythmia describes a slow heart rate caused by an irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia).
Healthy young people and athletes often have resting heart rates below 60 beats per minute. For them, bradycardia doesn’t indicate disease. In fact, the slow heart rate is a sign of their fitness and well-exercised heart. It is also normal for your heart rate to drop below 60 beats per minute when you’re sleeping.
There are several different types of bradyarrhythmias. Each type has its own causes, but they all result in a slower-than-typical heart rate. Types of bradyarrhythmia include:
Advertisement
Most arrhythmias, including bradyarrhythmia, result from heart disease or damage to the heart. Some causes of bradyarrhythmia include:
When the heart pumps too slowly, you may not get enough blood and oxygen to your brain. Symptoms of bradyarrhythmia may include:
Your healthcare provider will perform a thorough physical exam, and ask about any symptoms you are experiencing.
To diagnose a heart arrhythmia accurately, your provider will measure and track your heart rate. Diagnostic tests may include:
In some cases, an underlying medical condition leads to bradyarrhythmia. Treating an underactive thyroid, for example, can help improve your slow heart rate.
When bradyarrhythmia results from changes in the heart’s electrical system, your provider may recommend inserting a pacemaker. This electronic device generates electrical impulses to help you maintain a steady, healthy heart rate.
Left untreated, bradyarrhythmia can lead to serious health problems and can lead to dizziness and syncope. Getting the right treatment can restore your heart’s normal rhythm and reduce your risk of complications.
One preventive step is treating underlying health conditions, like hypothyroidism. You can also lower your risk of bradyarrhythmia by taking good care of your heart.
To keep your heart healthy, you should:
You should call your healthcare provider if you experience:
You may want to ask your healthcare provider:
Advertisement
Bradyarrhythmia is an abnormally slow resting heart rate, typically below 60 beats per minute. A too-slow heart rhythm can result from changes in the heart’s electrical system, a heart defect or other medical conditions. Your healthcare provider can treat bradyarrhythmia with medications or a pacemaker. Restoring a normal heart rhythm helps your heart function properly and reduces your risk of complications.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
When your heart rhythm is out of sync, the experts at Cleveland Clinic can find out why. We offer personalized care for all types of arrhythmias.
