Tonsil cancer is a type of oropharyngeal cancer. Symptoms include persistent sore throat and swollen tonsils. The condition is commonly linked to human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, though heavy alcohol and tobacco use may also increase tonsil cancer risk. Tonsil cancer treatments include surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
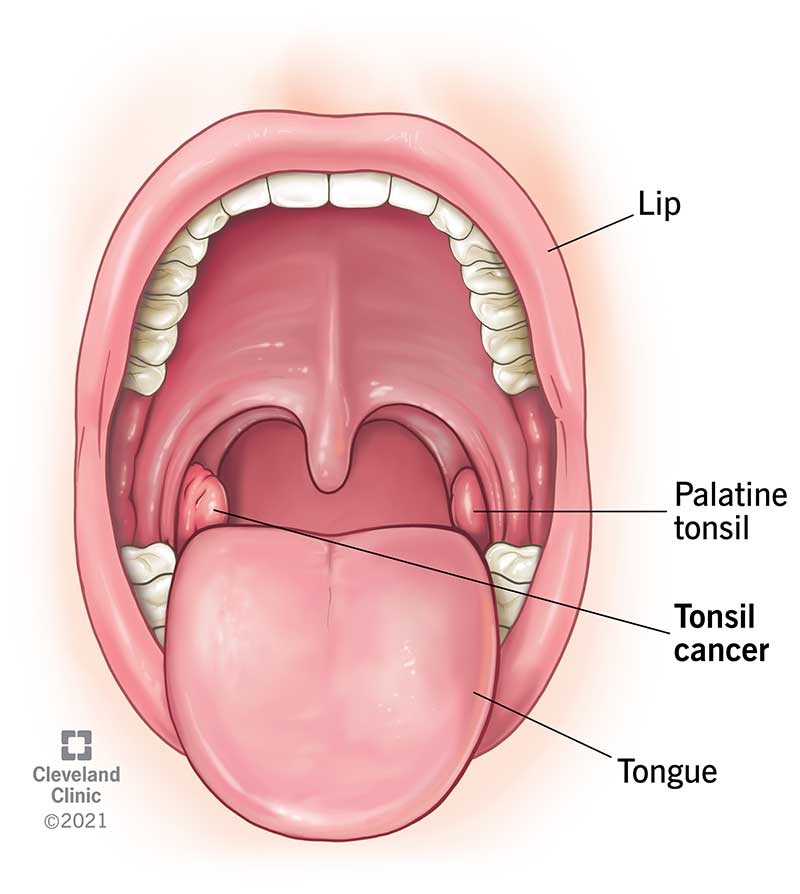
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/Images/org/health/articles/21931-tonsil-cancer)
Tonsil cancer is a cancerous tumor on your tonsils, which are in the back of your throat (pharynx). Tonsil cancer is the most common form of oropharyngeal cancer. A sore throat that doesn’t go away is a common early symptom. Often, healthcare providers can successfully treat tonsil cancer if they detect it before it spreads.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
It’s not common. The American Cancer Society (ACS) estimates that in 2024, more than 21,000 people in the U.S. will develop a type of oropharyngeal cancer, including tonsil cancer. For comparison, the ACS estimates more than 2 million people in the U.S. will develop some type of cancer.
The most common symptom of tonsil cancer is a sore throat that won’t go away. Another symptom is when one tonsil is swollen and larger than the other tonsil. Other common symptoms are:
Having these symptoms doesn’t mean you have tonsil cancer. But you should talk to a healthcare provider if your symptoms last longer than a few days.
Tonsil cancer symptoms can look and feel like other less serious conditions. For example, viral and bacterial infections can cause tonsillitis. Tonsillitis symptoms include a sudden sore throat and tonsils that look swollen, red and/or have white spots.
Experts know that tonsil cancer develops when healthy cells mutate (change) and become cancerous cells. They don’t know exactly why this happens. But recent research shows that having the human papillomavirus (HPV) increases your risk of developing tonsil cancer. Other risk factors are:
Advertisement
Tonsil cancer can be aggressive, meaning it can spread (metastasize) very quickly from your tonsils to other areas of your body.
A healthcare provider will do a physical examination, focusing on your throat and tonsils. They may do a throat culture to rule out infections as a possible cause. They’ll look for changes in your tonsils like sores that could be cancer.
If they suspect tonsil cancer, they’ll refer you to an otolaryngologist (an ear, nose and throat specialist or ENT). This is a healthcare provider who specializes in conditions that affect your ear, nose and throat. They may order tests, including biopsies and imaging tests.
Your provider may do a biopsy to obtain cells and tissue. A medical pathologist will examine the cells and tissue for signs of tonsil cancer. Possible types of biopsy are:
If biopsy results show signs of tonsil cancer, your oncologist may order imaging tests to see if the cancer is spreading to other areas of your body. Tests may include:
Your provider will use test results to set the tonsil cancer stage. Healthcare providers use cancer staging systems to develop treatment plans. They base tonsil cancer stages on factors like the tumor location and size, whether cancerous cells are in nearby lymph nodes and if the tumor in your tonsils is spreading to another part of your body.
For example, an early-stage tonsil cancer is one that’s only on your tonsils. Advanced or late-stage tonsil cancer means there’s tonsil cancer in lymph nodes and other areas of your body.
There are a few different options. Treatment depends on the size and location of the tumor and whether it has spread to other parts of your body. Possible treatments for tonsil cancer include surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
Your otolaryngologist may do surgery to remove small tumors or affected lymph nodes, including:
Advertisement
You may receive radiation therapy or chemotherapy as an alternative to surgery or after surgery for tonsil cancer. Your healthcare provider will base your treatment plan on factors like treatment response rate and treatment side effects.
For example, your provider may recommend radiation therapy as an alternative to surgery to cure tonsil cancer tumors, or after surgery to eliminate any potential remaining cancerous cells. Radiation may be given simultaneously with chemotherapy to enhance its effects, depending on the cancer stage.
They may recommend chemotherapy when surgery or radiation therapy isn’t an option for tonsil cancer. Chemotherapy can slow down tonsil cancer growth and ease its symptoms.
Side effects and complications will be different depending on the treatment type. For example, TORS and lymphadenectomy surgery have different side effects. Radiation therapy and chemotherapy often cause similar side effects.
TORS may cause the following side effects or complications:
Advertisement
Possible lymphadenectomy side effects are:
Common chemotherapy and radiation therapy side effects include:
Overall, 85% of people with tonsil cancer and HPV were alive five years after their diagnosis. Tonsil cancer survival rates may vary based on several factors, including whether the tonsil cancer is HPV-positive or negative or if the tumor is spreading.
When you think about cancer survival rates, it’s also important to remember:
Survival rate data can be complicated and confusing. If you have tonsil cancer, ask your oncologist about survival rate estimates and how they apply to your situation.
Statistically, tonsil cancer isn't likely to be fatal. As with most cancers, treatment is most successful when the condition is detected and treated in the early stages.
Advertisement
You may not be able to prevent tonsil cancer, but you can reduce your risk with these precautions:
It can be challenging to manage tonsil cancer symptoms and treatment. Here are some suggestions:
If you had tonsil cancer surgery, contact your surgeon right away if:
If you didn’t have surgery, contact a provider if you have symptoms like:
Tonsil cancer isn’t common, but it can cause common symptoms like a painful sore throat or swollen lymph nodes in your neck. Caught early, healthcare providers can cure tonsil cancer. That’s why it’s important to keep an eye on your overall health and pay attention to everyday symptoms that don’t go away. In some cases, these symptoms are signs of serious illness, and that’s the case with tonsil cancer. Contact a healthcare provider if you notice changes in your throat that last for more than a few days.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
When you learn you may have oral cancer, you’ll want the best care. Cleveland Clinic’s head and neck cancer experts offer personalized treatment and support.
