Tonsillitis is a common condition that happens when your tonsils get infected. Symptoms typically include sore throat, fever and swollen lymph nodes. Treatment depends on whether the infection is viral or bacterial, and recovery usually takes about one week.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
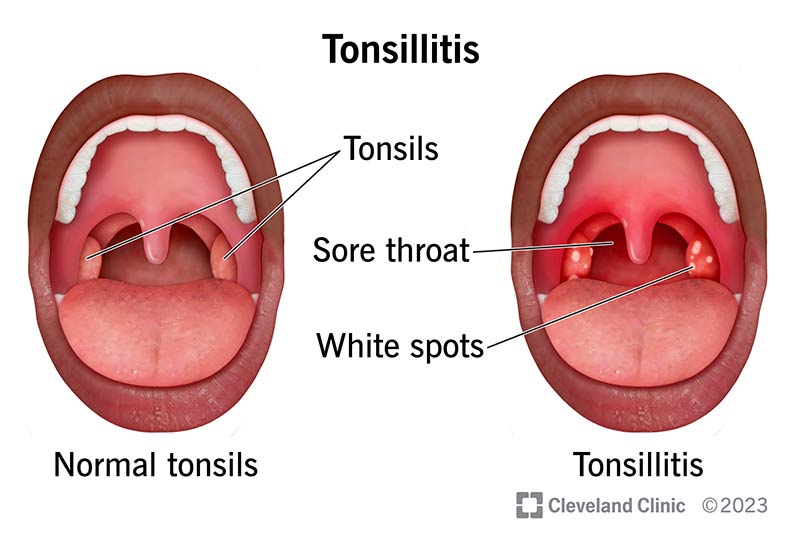
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/Images/org/health/articles/21146-tonsillitis)
Tonsillitis occurs when your tonsils become infected. Tonsils are the two small lumps of soft tissue — one on either side — at the back of your throat. You can see your tonsils in a mirror by opening your mouth and sticking out your tongue.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Your tonsils are part of your immune system, and they help trap germs that make you sick. When your tonsils become infected, they get swollen and sore, and swallowing may hurt. The medical term for tonsillitis is “tonsillopharyngitis”, but most people call it a sore throat because that’s what it feels like.
Tonsillitis is most common in children and adolescents, but it can affect people of all ages. It rarely occurs in children under the age of 3. Most people have tonsillitis at least once in their lifetimes.
Tonsillitis symptoms usually come on suddenly. They may include:
A sore throat is often the first symptom of tonsillitis. If you develop a sudden sore throat, keep an eye on your tonsils to see if they get red or swollen.
Video content: This video is available to watch online.
View video online (https://cdnapisec.kaltura.com/p/2207941/sp/220794100/playManifest/entryId/1_cxajzelr/flavorId/1_5f3sgelj/format/url/protocol/https/a.mp4)
Learn the difference between pharyngitis and tonsillitis.
Viral infections are the most common cause of tonsillitis. But bacterial infections can cause it, too.
Advertisement
The viruses and bacteria that cause tonsillitis are highly contagious. They’re passed along by:
You have an increased risk of getting tonsillitis if you’re:
Tonsillitis can sometimes result in complications like:
People with untreated bacterial tonsillitis have a higher risk of developing:
To diagnose tonsillitis, your healthcare provider will:
After confirming a tonsillitis diagnosis, your provider will need to determine whether the infection is viral or bacterial. To do this, they may request a bacteria culture test.
During this procedure, your provider will swipe the back of your throat with a long cotton swab to gather cells and saliva. Then, they’ll check the sample to see if it tests positive for Group A Streptococcus bacteria. If your results are positive, you have strep throat. If your results are negative, you have viral tonsillitis.
Tonsillitis treatment depends on the cause. While symptoms of viral tonsillitis and bacterial tonsillitis can be similar, their treatments are different. Treatment may include:
Advertisement
In addition to your healthcare provider’s recommendations, you can relieve the symptoms of viral and bacterial tonsillitis by:
Most cases of viral tonsillitis clear up in a few days with fluids and plenty of rest. Antibiotics typically eliminate bacterial tonsillitis in about 10 days. Tonsillitis usually doesn’t cause any serious or lasting health problems.
In most cases, tonsillitis symptoms go away in three to four days. But if symptoms last longer, you should schedule a visit with your healthcare provider to rule out other, more serious issues.
You should stay at home until your fever goes away and you can swallow comfortably again. This usually takes three to four days. If you’re unsure, ask your healthcare provider.
You can’t totally prevent tonsillitis. But you can reduce your risk by practicing good hygiene habits:
The best thing you can do is stay at home, get plenty of rest and drink lots of fluids. Following your healthcare provider’s guidance can ensure a speedy recovery.
Advertisement
You should contact your healthcare provider or an urgent care facility if you have:
Viral tonsillitis typically goes away on its own in about one week. Bacterial tonsillitis takes about 10 days to run its course, but you’ll likely need antibiotics to reduce your risk of complications.
Tonsillitis usually causes visibly red and inflamed tonsils. In some cases, you might have a whitish coating on your throat or white spots on your tonsils.
Strep throat is another common name for bacterial tonsillitis. You can get strep throat even if you don’t have your tonsils anymore.
You know that feeling — that scratchy sensation in the back of your throat. You keep your fingers crossed, hoping it’ll go away. But when you wake up the next morning, it hurts to swallow. If this sounds like you, it could be tonsillitis. And it’s best to make an appointment with your healthcare provider. With some rest and medication, you’ll be feeling like yourself again in a few days.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Not just kids need a tonsillectomy. Adults who have frequent sore throats or snore a lot get them, too. Cleveland Clinic is here to help.
