Sperm are male sex cells with three main parts: a head, midpiece and tail. Males start to produce sperm around puberty. Your body releases tens of millions of sperm when you ejaculate. But it only takes one sperm to fertilize an egg cell.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
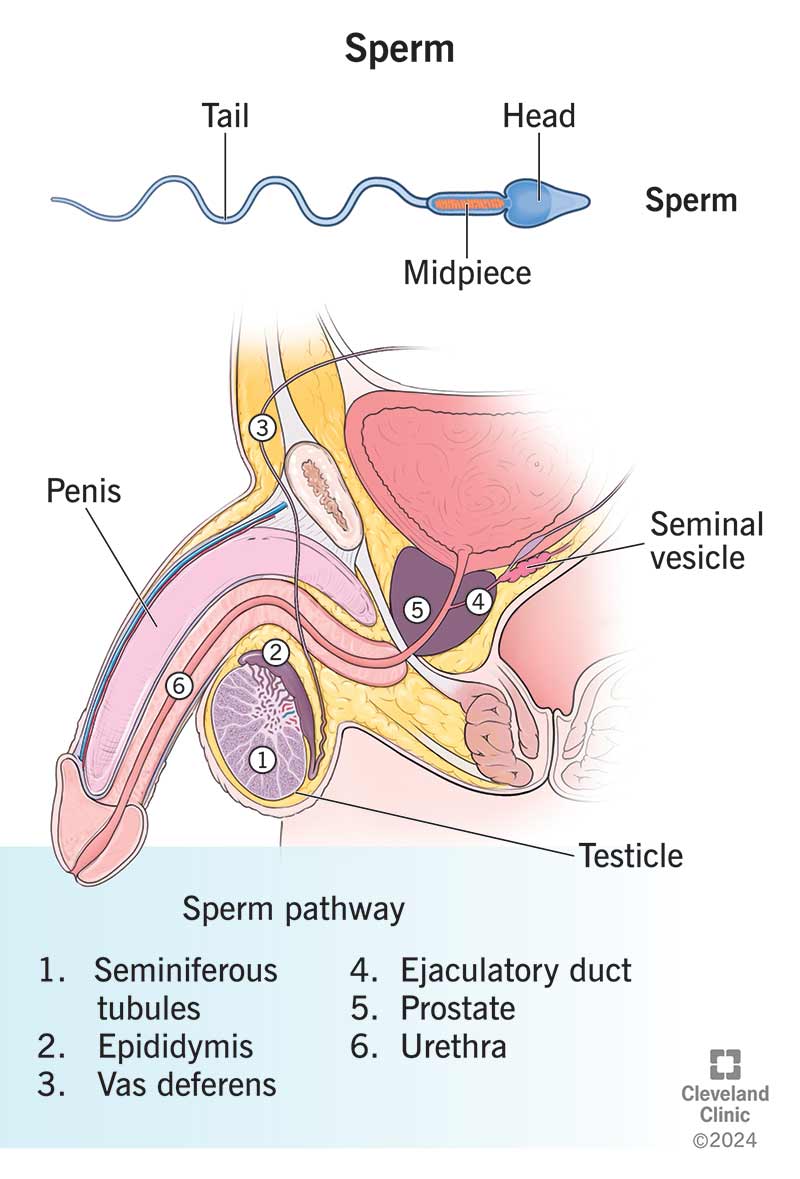
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/sperm)
Sperm are tadpole-shaped microscopic male sex cells. In humans, when a sperm cell joins with (conception or fertilization) a female sex cell (ovum or egg cell), the fetal development process begins. This often happens after vaginal intercourse. But it can also occur through assisted reproductive technologies, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Males start producing sperm around puberty — usually between 10 and 12 years old. They can produce sperm throughout their lives.
Other names for sperm include:
Sperm’s only function is to fertilize female sex cells.
Not ejaculating or releasing semen (the sticky liquid that contains sperm cells) won’t hurt you or cause any problems. Your body absorbs any sperm you don’t release.
A typical sperm count may range from 15 million to more than 200 million per milliliter of semen (about 0.2 teaspoons).
A low sperm count (oligospermia) is less than 15 million sperm per milliliter of semen.
After unprotected vaginal intercourse, sperm cells travel through the vagina, cervix, uterus and eventually fallopian tubes. The immune system recognizes sperm as foreign invaders and mobilizes to kill the sperm. If any surviving sperm make it to the fallopian tubes, they’ll try to penetrate the egg cell.
Sperm can stay alive within the female reproductive system for up to five days.
Unejaculated sperm can stay alive in your testicles for about 2.5 months. Around this time, sperm cells die, and your body reabsorbs them.
It depends. Sperm can live up to an hour outside your body in a room temperature environment — 68 degrees Fahrenheit (20 degrees Celsius). Exposure to different temperatures can kill sperm quickly.
Advertisement
If you bank your sperm, it can survive for decades as long as the freezing conditions remain the same.
Tiny tubes in your testicles (seminiferous tubes) produce sperm. During ejaculation, sperm:
The three main parts of a sperm cell include:
Sperm morphology is the shape of sperm. Specifically, it refers to:
Healthy morphology allows sperm to swim strongly in a straight line.
Examples of abnormal sperm morphology include:
Sperm problems can cause male infertility. Many things can affect your sperm’s health or their ability to travel. But you may not be aware that something is affecting your sperm unless you and your partner are having difficulty getting pregnant. Conditions that may affect your sperm health include:
Varicoceles are swollen veins in your scrotum. Blood builds up in the veins and increases the temperature inside your scrotum, which may affect sperm growth.
Testicular trauma can damage your testicles and affect their ability to produce sperm.
Some sexually transmitted infections (STIs), including chlamydia and gonorrhea, can harm your sperm.
Certain medications may have side effects that affect your sperm quality. These include:
Advertisement
Testosterone replacement therapy also causes your body to stop producing sperm. It comes in many forms, including:
Drinking alcohol and smoking or vaping tobacco or marijuana can affect sperm count and quality.
Long-lasting heat exposure can also damage your sperm. This may include spending time in saunas or bathtubs. Sitting down in a chair or wheelchair for long periods can also increase the temperature of your testicles.
Your immune system mistakenly identifies sperm as a foreign invader and sends antibodies to kill it.
Sperm disorders can affect the quality and amount of sperm you produce. They include:
A semen analysis is the best way for a healthcare provider to analyze your:
You may produce a semen sample at a fertility clinic, lab or at home. If you produce your sample at home, you must bring your sample to a clinic or lab quickly — usually within an hour.
Advertisement
The following tips may help you improve your sperm quality:
It only takes one sperm cell to get pregnant. But tens to hundreds of millions of sperm release during ejaculation.
Sperm have one goal: fertilize an egg cell to pass on your DNA. You may not think too much about your sperm unless you have difficulties getting pregnant. But if you and your partner have infertility problems, a healthcare provider will order tests to analyze your sperm and determine how many you have, as well as their shape and activity levels. You can help promote sperm health by quitting smoking, drinking alcohol in moderation, being physically active and protecting yourself from STIs.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
If you have a condition that’s affecting your urinary system, you want expert advice. At Cleveland Clinic, we’ll work to create a treatment plan that’s right for you.
