Your celiac trunk is a major artery that has three branches: splenic, common hepatic and left gastric arteries. These provide many of your digestive system’s organs with blood. Your celiac trunk connects to your abdominal aorta, which carries oxygen-rich blood.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
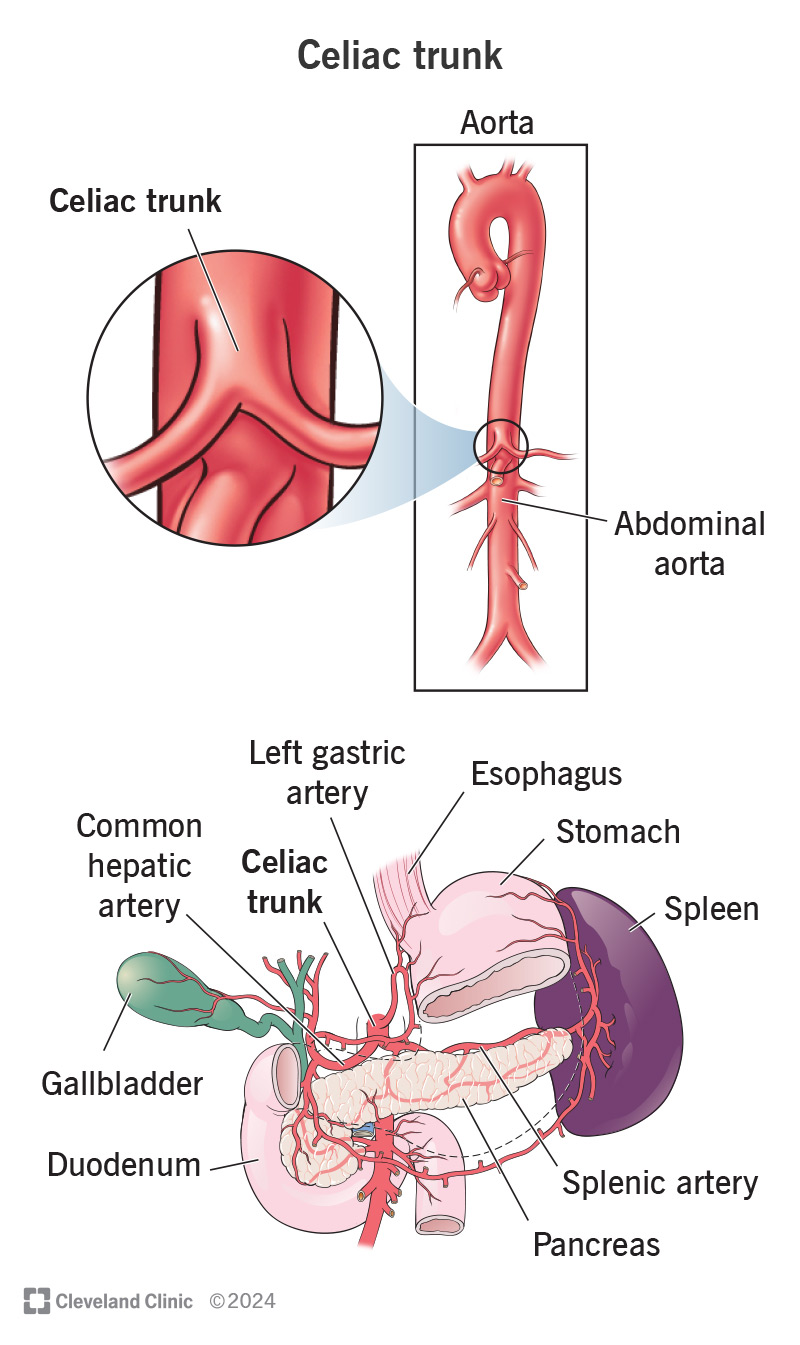
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/celiac-trunk)
Your celiac trunk is an artery that branches off from your abdominal aorta. Because your celiac trunk connects to your aorta (the biggest artery in your body), it handles a lot of blood. Think of your celiac trunk like a large pipe that gets its water supply from a water main in your neighborhood.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
You only have one celiac trunk artery, but it has an important job. It supplies some of your digestive organs with oxygen-rich blood. When you feel sleepy after lunch, think about your celiac trunk sending extra blood to your digestive organs. They’re hard at work getting nutrients from the food you ate.
Celiac comes from a Greek word for abdominal, the same area where people with celiac disease have issues.
Your celiac trunk artery is located below your rib cage, but near your spine. To find your celiac trunk, take your finger and put it below where your breastbone (sternum) ends, then go across your belly, around your side and to your back. Stop at your spine, just above your lower back (lumbar spine). Your celiac trunk is on the other side of your spine.
Your celiac trunk branches include:
Advertisement
Some people have a variation in how other arteries branch off from their celiac trunk. They may not connect to it at all. Examples include a left gastric artery that branches off from an abdominal aorta or splenic artery. It’s also possible for your celiac trunk anatomy to have four, five or six branches instead of the typical three. People who are Black, Japanese or Korean may be more likely to have these variations.
Your celiac trunk is a tube that’s about .59 to .78 inches (1.5 to 2 centimeters) long. That’s smaller than a postage stamp. Your celiac trunk’s average diameter is between .23 to .47 inches (6 and 12 millimeters). That’s roughly the size of a pea.
Like other arteries, your celiac trunk has three layers in its artery wall. These layers contain connective tissue, muscle and elastic fibers. Arteries need to be stretchy to handle the pressure of blood coming from your heart with force.
Multiple conditions can affect your celiac trunk, like:
An issue with your celiac trunk artery may cause pain in your upper abdomen, nausea and vomiting.
Tests to check the health of your celiac trunk and branches may include:
Treatments for conditions that affect your celiac trunk artery include:
Anything that supports good heart health keeps your celiac trunk and branches working well, too. Things you can do include:
Advertisement
Your celiac trunk provides oxygen and nutrients to the organs that digest your food. Taking care of your celiac trunk is like caring for your other blood vessels. That includes eating nutritious foods and staying physically active. Regular checkups can help your provider detect issues with your celiac trunk or other blood vessels. Don’t be afraid to ask about treatments that can help.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
When you come to Cleveland Clinic for aortic disease treatment, you’ll get industry-leading care and support from our heart and vascular specialists.
