A lobectomy is an operation to remove a lobe of your lung. Most often, surgeons do a lobectomy procedure for people with lung cancer. This can cure cancer that’s in an early stage, but may not work as well for larger tumors. It takes at least a month to recover from a lobectomy. A less invasive lobectomy can provide a faster recovery.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
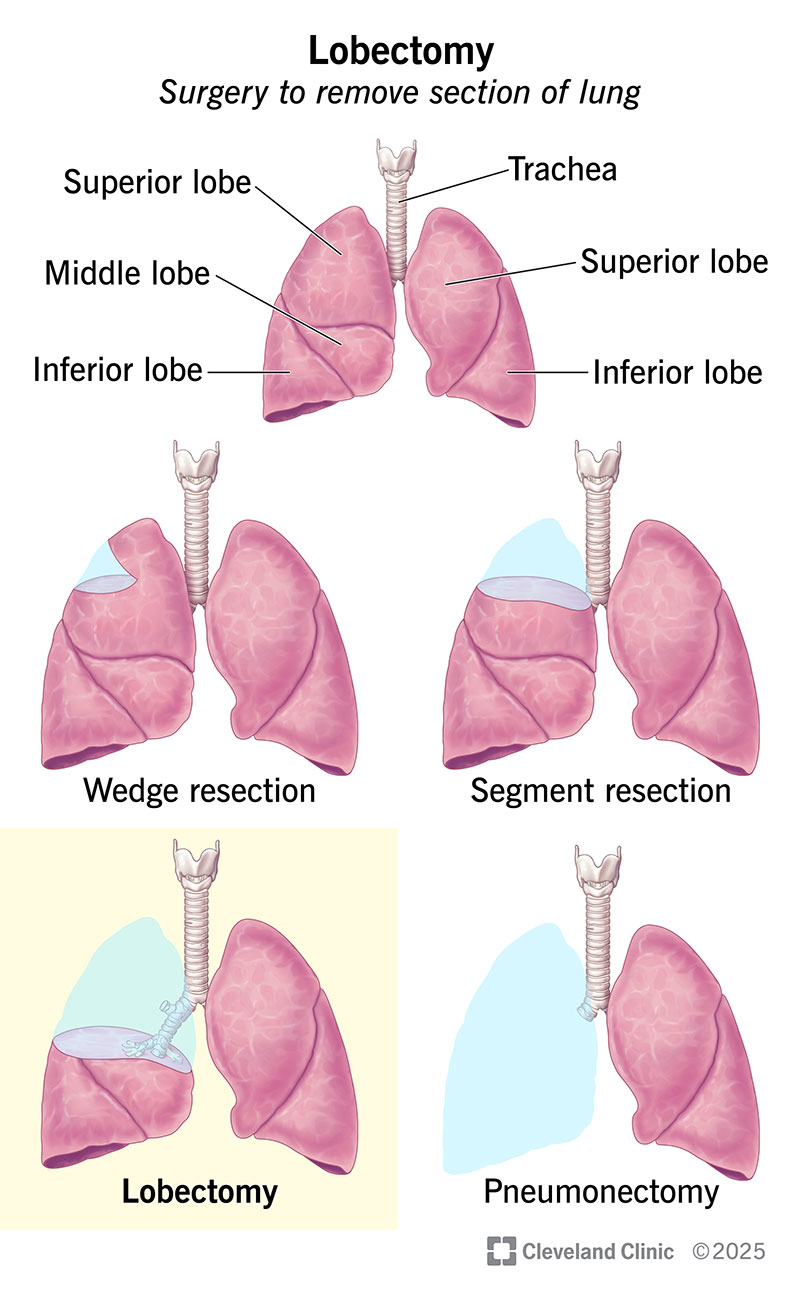
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/17608-lobectomy-illustration)
A lung lobectomy (pulmonary lobectomy) is a surgery to remove a section (lobe) of your lung. This is a common surgery for treating non-small cell lung cancer in its early stages. It also treats lung carcinoid tumors and small cell lung cancer.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
A surgeon may also do a partial lobectomy, a segmentectomy. This means they remove part of a lobe.
Besides lung cancer, other reasons for a lobectomy include:
Surgeons don’t open your chest for most lung resections. Instead, they use a minimally invasive method like video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) or robot-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (RATS). In both types, surgeons use tools they pass between your ribs through small cuts in your chest. This way, they don’t need to break or spread your ribs.
For a more complex lung surgery, a surgeon uses a thoracotomy. This involves making a larger cut and spreading your ribs apart to reach your lung.
Before lobectomy surgery, you’ll have tests, like:
Advertisement
If you have lung cancer, your provider will want to know if cancer cells have spread to other parts of your body. This is staging, and it helps your team plan your treatment. In some cases, a provider may do a CT scan or MRI of your head. This can show if cancer has spread to your brain.
A heart expert (cardiologist) may evaluate you if you’ve had heart issues. This helps with estimating risk and planning your surgery. Also, you’ll meet with an anesthesiologist who will discuss pain control during and after your surgery.
Avoiding the use of tobacco products before surgery can make you less likely to have complications.
A provider will tell you in advance what time to stop eating and drinking the night before your surgery.
During your lobectomy surgery, you’ll be asleep and won’t feel any pain. This is because of the anesthesia you’ll receive. A ventilator will manage your breathing through a tube in your throat. You’ll have an IV in your arm so you can receive medicine through it.
Your surgeon will follow these steps:
The median time for a pulmonary lobectomy is about two hours. That means half of the surgeries take less than that, and half of them take longer.
A lung surgery offers the best chance of a cure for people with early-stage lung cancer. A segmentectomy or lobectomy can cure cancer in people with stage I to III non-small cell lung cancer. Results of a less invasive lobectomy are as good as (or better than) those of an open procedure.
The most common complication is an irregular heart rhythm, atrial fibrillation.
Other possible risks of a pulmonary lobectomy may include:
After your lobectomy surgery, here’s what happens:
Advertisement
With a VATS or RATS lobectomy, your hospital stay is typically two to three days. Recovery tends to be faster due to less pain and bleeding with VATS or RATS compared to an open-chest procedure. This means a faster return to work and regular activities.
Lobectomy recovery after an open-chest surgery typically requires three to four days in the hospital.
When you go home after VATS or RATS, you’ll have a one-week supply of strong pain medication. Most people don’t need a refill. When you leave the hospital, you should be able to care for yourself. But it’s good to have someone nearby who can help you if you need it as you recover.
You may receive oxygen therapy after your hospital stay. Most people will need this for a brief time while they recover from surgery.
After a VATS or RATS, you can drive again once you stop taking strong pain medicine. In general, you may be able to return to work at a desk around two weeks after going home. You should take four weeks to recover for jobs that require lifting.
Contact your provider if you have signs of infection, like a fever, chills and fatigue.
You’ll have a follow-up visit seven to 21 days after your surgery. Your provider can talk with you about your test results then. You’ll have a chest X-ray, and your surgeon will assess your wounds and your recovery. Also, they’ll give you more guidelines about your activities, return to work and what to eat.
Advertisement
Depending on the cancer stage, your provider may refer you to an oncologist. For any stage, you can expect to have CT scans for the next five years. You may worry about lung cancer coming back. This is why your provider will schedule a CT scan every six months after your surgery.
Yes, a lobectomy is a major surgery. Some side effects can be serious. Your lungs contain large and fragile blood vessels that can bleed.
It can be. Death after lung surgery is quite rare. In most cases, a problem with your lungs or airways is the cause. These risks are lower in some healthcare facilities than others. This is why it’s better to choose one that performs a lot of lobectomies. It’s important to ask about these risks during your preoperative visits.
Long-term survival after a lobectomy for lung cancer depends on the stage of the tumor. The stage is in the surgical pathology report.
It’s possible to have a lung cancer recurrence after a lobectomy. This means the cancer comes back. If it happens, it’s usually in the first five years after surgery. Your provider considers you cured of cancer if you have no evidence of it five years later.
You may feel like people are judging you because you had a type of cancer typical for people who smoke. It’s ok to own these feelings, but try not to dwell on them. Instead, put your energy into getting well.
Advertisement
A lung cancer diagnosis can bring uncertainty and stress, but lung surgery is the best treatment due to a long history of safety. Ask questions if there’s anything you don’t understand about your operation. This is a major surgery, so give yourself time to recover. Ask friends and family to help you with grocery shopping or housework while you recover. Also, you can cook meals and freeze them so they’re ready to reheat with little effort during your recovery.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic's health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability, and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic's health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability, and up-to-date clinical standards.
If you have lung cancer, you might feel alone and afraid. You don’t have to be. Cleveland Clinic is here to help find and treat your cancer at any stage.
