A breast MRI is an imaging test that creates very detailed pictures of your breast tissue. Healthcare providers mainly use it to evaluate known breast cancer. But they also use it with mammography and ultrasound to screen for and diagnose breast cancer and other breast abnormalities.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Breast MRI is a type of imaging test that uses a strong magnet, radio waves and a computer to create detailed images of breast tissue. Your healthcare provider may use a breast MRI along with a mammogram to screen for breast cancer. They may also use it to biopsy breast tissue and check for cancer or see how much cancer has spread.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Your healthcare provider may recommend a breast MRI for several reasons, including to:
Depending on the reason for a breast MRI, the test may require an injection of contrast dye (called gadolinium). For many breast MRIs, a technologist or nurse will place an IV in your arm so they can inject contrast dye. This helps a radiologist see structures in your breast more clearly.
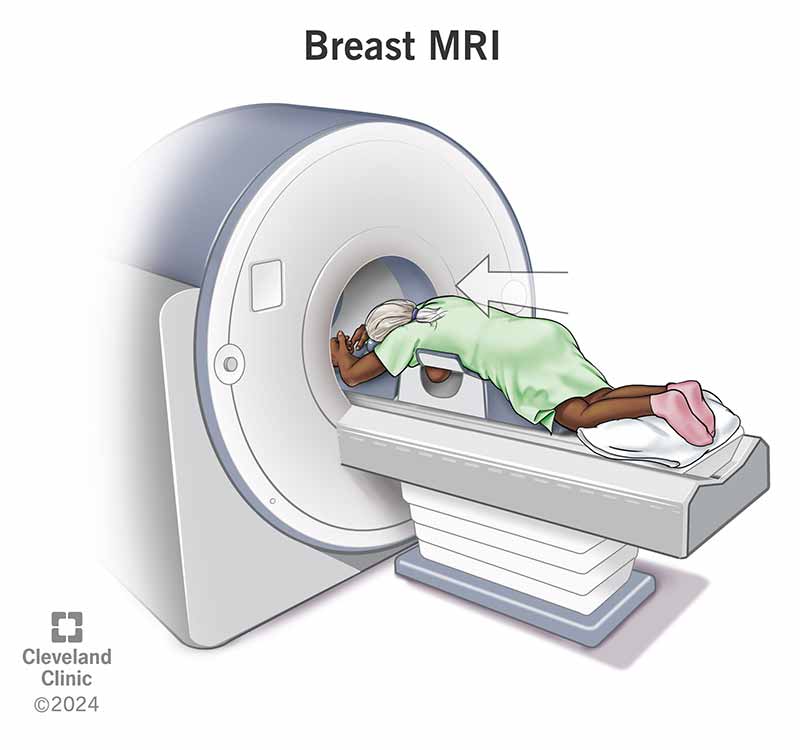
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/8332-breast-MRI)
Before your breast MRI, it’s important to tell your radiologist or radiology technologist if you:
Ask the provider who manages your device what they recommend you do for your MRI.
During a breast MRI, you’ll change into a gown and lie face down on a table with openings for your breasts. If you need contrast dye, your provider will place an IV. The table slides into the MRI machine. The machine can be noisy, so you’ll get earplugs. You’ll need to stay very still while the technologist operates the scan from another room. You can talk to them, and they can talk to you through an intercom. Once the images are complete, they remove the IV (if you had one) and you can go home.
Advertisement
A breast MRI takes about 20 minutes. But facilities plan for up to 60 minutes for preparations like IV placement and getting you in the right position.
There’s very little risk to getting a breast MRI if you and your technologist follow the safety guidelines. The possible risks are:
You can continue your usual activities after a breast MRI. But if your exam was an MRI breast biopsy, follow the at-home instructions your provider gives you. If you took a sedative for your exam, you’ll need someone else to drive you home.
The results of your MRI should be available in your electronic medical records account within a few business days. The provider who ordered the test will discuss the results with you.
Your MRI report may look different depending on why you had a breast MRI. If your results are abnormal, your provider will recommend more imaging tests or a breast biopsy.
All radiologists use the same standardized system to describe screening and diagnostic breast imaging results. This system is called the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS). It categorizes results on a scale of 0 through 6.

Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/bi-rads-chart)
BI-RADS is a reporting tool your provider uses to classify and explain your breast MRI results.
Healthcare providers use mammograms and breast MRIs to help detect breast cancer and other breast abnormalities.
Mammograms are usually the first option for screening and diagnosis of breast cancer.
There are also differences in how the two imaging tests work.
| Mammogram | Breast MRI |
|---|---|
| Uses X-rays | Uses magnets and radio waves (no X-rays) |
| Compresses (squeezes) your breasts | Doesn’t require compression |
| No contrast dye (no IV) | Usually requires contrast dye with an IV |
| Takes two to three minutes | Takes 17 to 20 minutes |
| Mammogram | |
| Uses X-rays | |
| Breast MRI | |
| Uses magnets and radio waves (no X-rays) | |
| Compresses (squeezes) your breasts | |
| Breast MRI | |
| Doesn’t require compression | |
| No contrast dye (no IV) | |
| Breast MRI | |
| Usually requires contrast dye with an IV | |
| Takes two to three minutes | |
| Breast MRI | |
| Takes 17 to 20 minutes |
A breast MRI can help check for breast cancer and other changes in your breast tissue. It’s normal to feel anxious before an MRI. You may have lots of questions or concerns about what the test results show and what they mean for your health. Don’t hesitate to raise your concerns with your healthcare provider.
Advertisement
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic's health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability, and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic's health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability, and up-to-date clinical standards.
When you need a clear picture of what’s happening inside your body, the Cleveland Clinic imaging team is here for you.
