Breast implants are one of the most popular types of plastic surgery prostheses. Breast implants increase the size of your breasts. Candidates should be in good physical and mental health and have realistic expectations.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
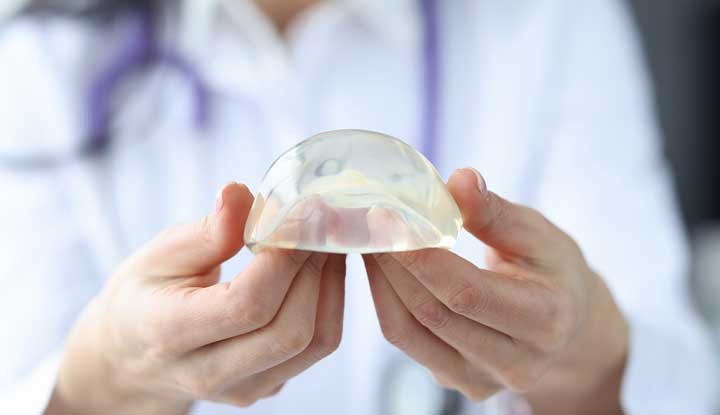
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/21724-breast-implants-1300316377)
Breast implants are artificial devices (prostheses) surgically inserted into your breasts. Breast implants are silicone shells filled with either silicone gel or saline (sterile salt water).
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Doctors called plastic surgeons insert breast implants. You may choose to receive breast implants following the loss of a breast to cancer. You may be a healthy person who wishes to change the shape or size of your breasts. Breast reconstruction is when a patient who has had breast cancer gets breast implants. Breast augmentation is when a healthy person receives breast implants to change the shape or size of their breasts. Breast augmentation is also known as a boob job.
Getting breast implants is a personal decision. Pursuing your wants and desires for your body can be very empowering.
To be considered for breast implants, you should:
Many people who get breast implants wish to make the size of their breasts larger. You may want to enlarge the size of your breasts for many reasons, including:
Advertisement
In the United States, approximately 3.5 million people have breast implants. About 60% of breast implants contain silicone gel. Throughout the world, approximately 35 million people have breast implants.
The terms “breast augmentation” and “breast implants” are often substituted for one another. Breast augmentation is any cosmetic surgical procedure that makes the size of your breasts larger. Breast implants are artificial devices (prostheses) surgically inserted into your breasts. So, breast augmentation refers to a series of procedures that make your breasts larger. Breast implants are silicone shells filled with saline solution or silicone gel that support breast augmentation procedures.
New breast implants typically last about 10 years, but your experience may be different. The older that breast implants get, the more likely they are to rupture (break apart).
Signs of breast implant rupture may include changes in your breast size or shape, firmness or swelling. However, sometimes there is no sign that rupture has occurred.
Breast augmentation and breast implants have made an incredible amount of progress to yield natural-feeling results. Silicone breast implants tend to feel more natural than saline breast implants. However, silicone and saline breast implants can both feel natural, depending on the size of the breast before surgery and the position of their placement.
In submuscular placement, breast implants fit beneath your breast tissue and your chest muscles. As a result, you only feel your natural breast tissue on top of your breast implants.
In subglandular placement, breast implants fit between your breast tissue and chest muscles. If you have a lot of breast tissue, your breast implants will feel natural. However, if you don’t have a lot of breast tissue, your breast implants may not be wholly covered by breast tissue. As a result, your breast implants may not feel or look natural.
The type of shell can also determine how breast implants feel. Breast implant shells are smooth or textured. Smooth shells are thinner than textured shells, so they feel more natural than textured shells. Smooth shell breast implants also move more freely during activity, which is closer to how natural breast tissue moves.
A textured shell is thicker than a smooth shell. Textured breast implants feel coarser to the touch, like the rough side of a sponge. The coarse texture helps the implants stick to the breast tissue, making them less likely to rotate or move. Filled textured shells feel firmer than smooth shells.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved a highly cohesive silicone gel breast implant for use in 2012. These implants are commonly called gummy bear breast implants. When cut in half, they retain their shape, similar to a gummy bear candy.
Advertisement
Breast implants also come in different shapes. Some breast implants may be round, like a doughnut without a hole. Others may look like a natural breast or a teardrop—rounder at the bottom and narrower at the top. As a result, they look more like natural breasts.
Round breast implants may have a smooth or textured shell. However, teardrop-shaped implants usually come with a textured shell only. Textured shells reduce the chance they will rotate and look unnatural.
Breasts continue to develop in women into their late teenage years or early 20s. As a result, you have to be at least 18 years old to get saline-filled breast implants. The FDA recommends that you are at least 22 years old to get silicone-filled breast implants.
Your healthcare provider will assess many factors, including your mental health and any social conditions. Your healthcare provider may ask the following questions:
Your physical health and body type are also important. Your healthcare provider will examine your body to help you choose the right implant. They will measure your height and weight, and they will also study your overall body structure. For example, larger implants are often necessary for patients with broader shoulders or wider hips. If you have a smaller body structure, larger breast implants may cause health issues, including back, neck and shoulder pain.
Advertisement
When you are determining breast implant sizes, it is important to consider how you will look. Think about shopping for clothes. You may like how a shirt looks on a hanger, but you should try it on in a changing room. Once you examine yourself from different angles in front of full-length mirrors, you may not like how the shirt looks or feels on your body. You may wish to ask your healthcare provider if they have sample breast implants that you can place under your shirt or sweater so you can look at yourself in a mirror (preoperative sizing). Preoperative sizing allows you to try different sizes and shell types to pick the best breast implants for you. Ultimately, when it comes to choosing the right size, the input of an experienced plastic surgeon is invaluable.
You and your healthcare provider will also consider whether saline or silicone breast implants are best for you. You’ll also consider breast implant shape (round or teardrop-shaped), shell texture and placement.
There are typically two locations where your healthcare provider will place your breast implants. In submuscular placement, the breast implants fit beneath your chest muscles. In subglandular placement, the breast implants fit between the chest muscles and the breast tissue (glandular breast parenchyma). Be sure to talk to your healthcare provider about the advantages and disadvantages of each type of breast implant placement.
Advertisement
During a breast implant procedure, you are sedated (put under) so that you aren’t awake and won’t feel any pain.
Once you are asleep, an incision (cut) is made in one of four discreet areas of your body so that breast implant scars aren’t very noticeable. The types of incisions include:
There are advantages and disadvantages to each type of incision. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best type of incision for you.
Your breast implants are then inserted through the incision and placed either under your breast tissue and chest muscles or between your chest muscles and breast tissue.
After the breast implant procedure is complete, your healthcare provider will wrap your breasts in a special supportive bra or compression band. Your anesthesiologist will stop putting anesthesia into your body to keep you asleep. You’ll move to a recovery room, where healthcare providers wait for you to wake up and monitor your overall health.
Once you wake up, you may feel dazed, your breasts may feel sore and your chest may feel tight. Your healthcare providers will continue to monitor your overall health for up to several hours. Once they determine that you no longer need monitoring, they will discharge you (let you go home). You must have a family member or friend drive you home and take care of you for the first 24 hours after your breast implant procedure.
On average, your body should fully recover between six and eight weeks after your breast implant procedure.
There are many advantages to breast implants:
Getting breast implants poses some risks, including:
The first several days after your breast implant procedure are often the most painful.
After five to seven days, your pain and discomfort should decrease. To manage pain, some people take either a prescribed pain medication or over-the-counter acetaminophen. As always, discuss your allergies and complete medical history with your provider. After one to two weeks, you should be able to return to light daily activities, including desk work. However, you should avoid physical activity, including running, lifting heavy objects or moving your arms above your head.
After several weeks, you may continue to experience some soreness and swelling, but it should be mild. You may still have some bruising. At this point, you may be able to participate in light exercises. However, you should still avoid lifting heavy objects or any other strenuous activities.
Your body should fully recover between six and eight weeks after your breast implant procedure.
It is important to remember that your body is unique, so recovery times may vary. Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions on how to manage your pain and discomfort throughout your recovery.
Depending on your job, you should be able to go back to work between two and six weeks after your breast implant procedure. If you have a less physically demanding job, you may be able to return to work sooner. If you have a more physically demanding job, you should schedule at least six weeks to recover before returning to work.
Schedule regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider.
After one to two weeks, your healthcare provider will remove your bandages and possibly stitches. They will also check your incisions.
You should then see your healthcare provider four to six weeks, three months and six months after your breast implant procedure.
Getting breast implants is a personal decision. If you wish to increase the size of your breasts, you can see a plastic surgeon to discuss your options. Breast implants can boost your self-confidence, but you should be aware that breast implants last on average 10 years. You may need to get new breast implants several times throughout your life. Talk to your healthcare provider about your questions and concerns, and learn more about outcomes and risks.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic's health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability, and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic's health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability, and up-to-date clinical standards.
Whether you need cosmetic or reconstructive plastic surgery, you’ll need skilled, detailed and compassionate providers. At Cleveland Clinic, we’re here to help.
