Carotid artery stenosis, also called carotid artery disease, is a condition that can lead to stroke. When you have carotid artery stenosis, a substance called plaque builds up and blocks the normal flow of blood in your artery. One treatment option for carotid artery stenosis is a surgical procedure call endarterectomy.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
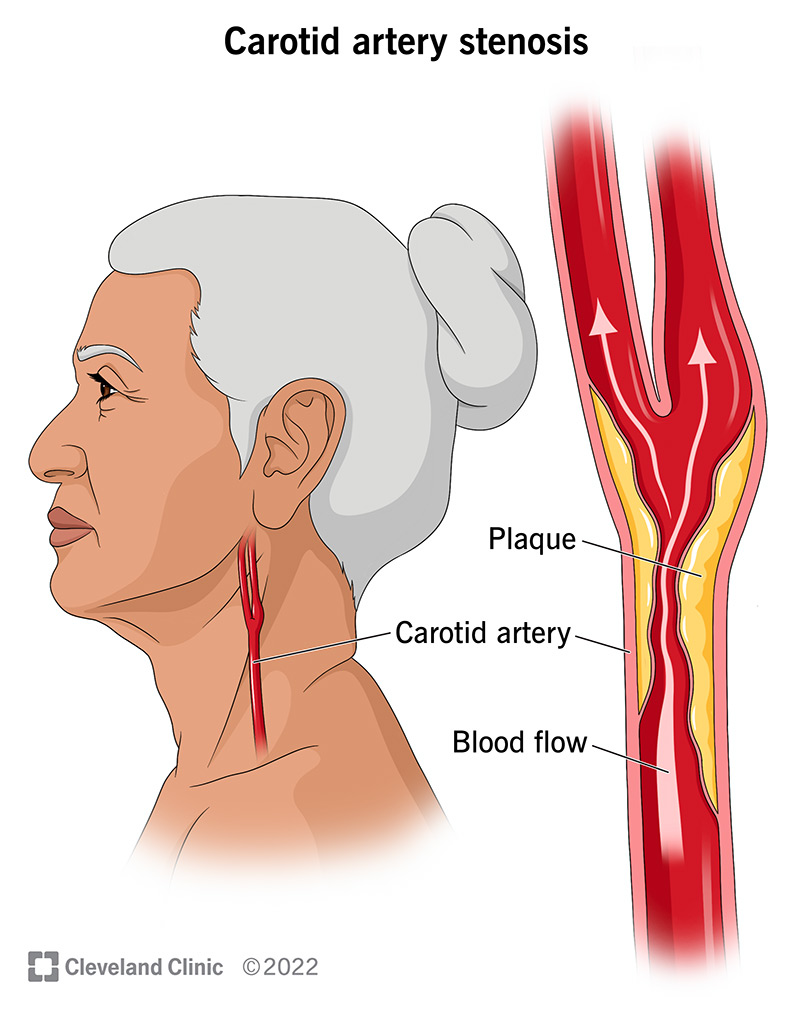
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/16845-carotid-artery-stenosis)
Carotid artery stenosis is a condition that happens when your carotid artery, the large artery on either side of your neck, becomes blocked. The blockage is made up of a substance called plaque (fatty cholesterol deposits). When plaque blocks the normal flow of blood through your carotid artery, you’re at a higher risk of stroke. Plaque build-up is called atherosclerosis.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
You have two carotid arteries — one on each side of your neck. These are large arteries that bring blood to your brain, face and head. When they’re healthy, these arteries are smooth and open, like a clean pipe that allows the free flow of fluid without anything in the way. Your body’s circulatory system is a network of tubes that carry blood (containing nutrients and oxygen) to all the parts of your body.
You can develop carotid artery stenosis in either of the two arteries in your neck or in both. This condition can worsen over time without medical care, leading to stroke with severe complications that can include death.
The prevalence of carotid artery stenosis in the general population is estimated to be as high as 5%. According to the American Stroke Association, stroke ranks fifth on the list of conditions that cause death. Carotid artery stenosis is something that usually happens over time and as you age, the risk for this condition as well as for stroke increases.
There are several factors that can increase your chance of developing this condition over time. Some of these are factors you can change. Some contribute to and compound other factors:
Advertisement
Carotid artery stenosis can cause a stroke. The kind of stroke that usually happens from carotid stenosis is pieces of plaque (or platelets that form on plaque) travel to your brain. Called “ischemic” stroke, it cuts off blood supply to a portion of your brain. When this blockage is permanent, your brain cells or neurons start to die.
A transient ischemic attack (TIA) is a “mini-stroke” that’s only a temporary blockage of a small brain artery from plaque and/or platelets. For many people, a TIA precedes an ischemic stroke. For these conditions, it’s very important to seek treatment as quickly as possible in order to prevent cell death.
The symptoms of a TIA or stroke can include:
If you have carotid artery stenosis that hasn’t caused a stroke, you may not notice any symptoms.
Carotid artery stenosis is often diagnosed after you’ve experienced symptoms of a stroke. The symptoms prompt your healthcare provider to thoroughly check for any type of blockage, which can lead to a discovery of carotid artery stenosis. This condition can also be diagnosed after your provider hears an abnormal sound — called a bruit (whistling sound) or murmur — during an exam of your neck with a stethoscope. There are several tests providers use to confirm a diagnosis of carotid artery stenosis and learn more about the size and location of the blockage. These tests can include:
Advertisement
During the diagnosis process, your healthcare provider will look to see if you have the condition, how large it is, and where it’s located. Carotid artery stenosis is generally divided into three groupings: mild, moderate and severe. A mild blockage is one that’s less than 50%. This means that less than half of your artery is blocked. A moderate blockage is between 50% and 79%. The most severe classification involves having the majority of your artery blocked — from 80% to 99%.
The main goal of carotid artery stenosis treatment is to halt the progression of the disease. This starts with lifestyle modifications including a healthy diet, exercise and stopping smoking. A daily baby dose of aspirin along with medications that lower blood pressure and cholesterol may also be used.
In more severe cases and or cases causing symptoms of TIA or stroke, your provider may use a surgical procedure called carotid endarterectomy to remove the plaque from the carotid artery through an incision. Alternatively, your surgeon may place a stent through a large needle puncture and ultimately through the blocked artery. This will open the artery up to its proper size while trapping the plaque away from the blood flow between the stent and the wall. A vascular surgeon or specialist determines which of these procedures is best for each person who needs treatment for carotid disease.
Advertisement
Not every carotid stenosis needs surgical or interventional treatment as these procedures themselves come with risk. Surgeons only recommend procedures to people when the risks of severe stenosis and/or stroke become higher than the risk of the procedure.
Carotid artery stenosis can be dangerous if it’s not caught and treated quickly. This condition can cause a stroke, which can lead to death or disability. It’s important to know the signs of a stroke and act quickly if you recognize these signs in yourself or someone else. Quick treatment of carotid artery stenosis can be lifesaving. When indicated, the outcomes of surgery and stenting are excellent. Most people recover very quickly with just an overnight hospital stay.
As you age, your risk of developing carotid artery stenosis increases. The main thing you can do to prevent this condition, and a complication like a stroke, is to maintain a healthy lifestyle. Exercising, eating healthy foods and not smoking are all examples of a healthy lifestyle. Make regular follow-up appointments with your primary care provider and vascular specialist. Talk to your healthcare provider about ways to keep your heart and entire circulatory system healthy.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
When the carotid arteries in your neck are blocked, you’re at risk for a stroke. Cleveland Clinic’s experts are world renowned in treating this condition.
