A black eye is bruised skin around your eye. A sudden blow to your eye area is a common cause — for example, getting hit with a hard object. The bruising itself should heal within a few weeks. But it’s possible for the trauma that caused the black eye to damage your eye itself or cause other serious issues. See a healthcare provider right away.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
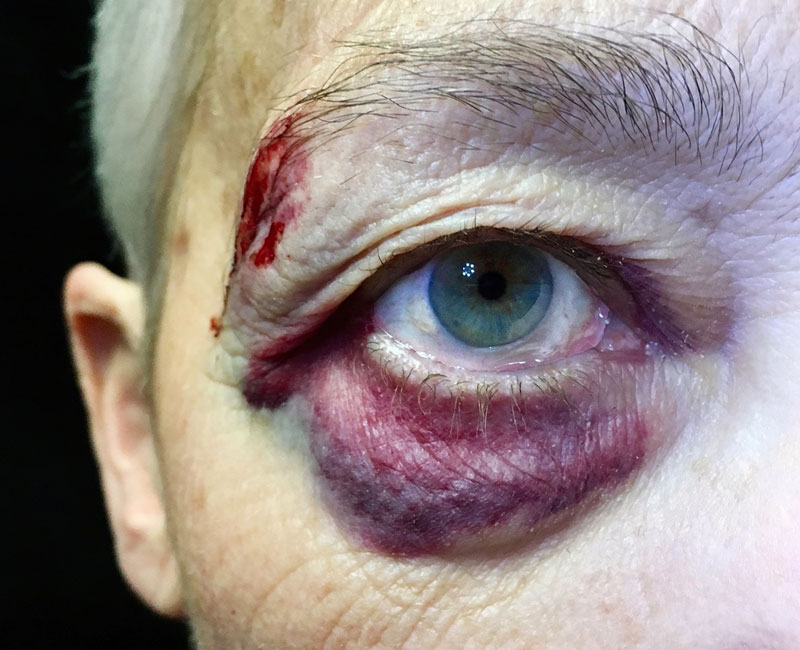
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/black-eye.jpg)
A black eye is bruising around your eye that develops after trauma to your face or head. The bruises form on your upper and lower eyelids and the skin around your eye. These bruises may look purple, blue and/or black in color. Despite its name, a “black eye” doesn’t mean your eye itself is injured. It just refers to the skin around your eye.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
But there’s a catch — sometimes, the trauma that causes a black eye can do further damage. For example, you might have broken bones around your eye or elsewhere in your head. Or there might be damage to your eye itself.
Your eyes are too important to leave to chance. Even if you think you’re fine, don’t just reach for an ice pack and call it a day. See a healthcare provider as soon as possible after getting a black eye (ideally within one to two hours before swelling sets in). They’ll check your eyes and surrounding areas for any further damage. And they’ll make sure you get the care you need.
Symptoms of a black eye include:
A black eye can look different as time goes on. Initially, the skin around your eye might look red. Then, it might change to a deeper red. The redness may then shift to purple, yellow, green or black.
If you have a darker skin tone, the bruising may look purple, dark brown or black.
The most common cause of a black eye is sudden trauma to your eye area. For example, it’s possible to get a black eye if:
Advertisement
This trauma damages tiny blood vessels just beneath your skin. When these vessels get hurt, they start to leak blood. The blood builds up under your skin, causing bruising and swelling.
Not all black eyes happen due to an injury. It’s also possible to develop a black eye after:
You might wonder how surgery in your mouth or somewhere else in your face can cause bruising around your eye. It’s because surgery can cause a bit of blood to leak out. This blood can then move beneath your skin. When it reaches the delicate area around your eyes, it forms a bruise.
Black eyes can also develop as a side effect of a new medication or treatment. If this happens, tell your provider right away. They may want to adjust your treatment plan.
You can also develop bruising or discolored skin due to other medical conditions. Below are some examples.
Although rare, some people develop black eyes out of nowhere — without a history of trauma or facial surgery. Healthcare providers refer to this as spontaneous periocular ecchymosis. Often, both eyes are affected (“raccoon eyes”). The causes are often quite serious and include:
It’s possible to develop dark circles that look like black eyes but aren’t actually bruises. Allergic shiners are discolored circles under your eyes that form due to nasal congestion. Swelling in the inner lining of your nose slows down blood flow in veins near your eyes. When these veins swell, the skin that covers them turns dark and puffy.
A black eye itself doesn’t lead to complications. This is temporary bruising that will heal on its own. But the trauma to your face or head that caused the black eye may lead to other complications, including:
Healthcare providers diagnose a black eye by examining your eye area. They look for the bruising and swelling typical of a black eye. They may also:
Advertisement
If an injury caused your black eye, you can treat it by using cold compresses. These help stop bleeding under your skin and reduce swelling. Here’s what to do:
One method not to try is putting a slab of raw meat on your eye. Raw meat is covered in bacteria that could cause an infection. Plus, there’s no proof it actually does anything to reduce swelling.
If you have a black eye after surgery or for other reasons, ask your provider how best to treat it. They’ll give you advice specific to your situation.
You should always see a healthcare provider if you have a black eye due to trauma to your eye area. Your provider will check for further damage beyond bruising and make sure you get the necessary treatment. They may just tell you to go home and apply ice — but it’s better to know for sure that bruising is the only concern.
Advertisement
It’s especially important to see a provider right away if you have additional symptoms like:
It’s also crucial to see a provider right away if you develop black eyes and can’t identify the cause.
If you develop a black eye after a dental or facial surgery, call the provider who did the surgery. They can explain if this is an expected side effect and what you can do to help with healing.
A black eye usually heals within several weeks. But the total healing time can be longer if you have other injuries besides the bruises around your eye. Your healthcare provider can tell you more about what you can expect.
While your eye heals, avoid activities that could cause further injury to your face or head.
Unfortunately, there’s no fast fix for a black eye, and you can’t heal it overnight. But applying ice every hour or so within the first 24 hours can help stop the bleeding under your skin and reduce swelling.
Advertisement
Using under-eye concealer or foundation can help make the bruising less noticeable while you heal.
Yes. It’s possible to develop black eyes one to two days after a skull fracture. You might not even realize the trauma to your head caused a fracture. So, the black eyes are the first sign of something more serious. See a healthcare provider immediately.
Having a black eye can be very upsetting. It’s a painful injury. Plus, it might make you feel self-conscious about your appearance. But black eyes often heal on their own with time and gentle care. It’s never safe to assume the injury is minor, though. Let a healthcare provider check your eye area to make sure nothing more serious is going on.
It’s also important to see a provider if you develop bruising around your eyes with no known cause. This can be a sign of a serious medical condition that needs treatment.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Need care fast? Cleveland Clinic’s Express Care and Urgent Care locations treat everything from sprains to sinus infections — no appointment needed.
