Candidiasis is a yeast infection that occurs when a type of yeast called Candida albicans grows out of control. It commonly affects your mouth, skin and vagina. Candidiasis isn’t a serious infection, but you still want to seek treatment right away. Antifungal medications can effectively treat and clear up the infection within two days to two weeks.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Candidiasis is a fungal infection caused by an overgrowth of a type of yeast that lives on your body called Candida albicans. A candidiasis infection often appears where Candida naturally lives in small amounts, like your skin, mouth or vagina.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Normally, healthy bacteria on your body prevent yeast overgrowth. Imagine you have a two-armed scale with healthy bacteria on one side and yeast on the other. The scale stays balanced until something disrupts it, like:
When something disrupts your scale, a candidiasis infection can occur.
Candidiasis causes discomfort, itching and irritation until you find treatment, but it isn’t a major threat to your overall health. Like any other infection, you should treat it right away to relieve your symptoms. Left untreated, severe infections could spread to other parts of your body, including your blood, heart and brain.
Since yeast naturally lives on your body, there are different types of candidiasis based on the location of the infection. Types of candidiasis include:
Advertisement
A serious type of candidiasis is called invasive candidiasis. Invasive candidiasis is a life-threatening infection that occurs when Candida gets into your bloodstream and spreads to your internal organs. It most often affects people in hospitals and people with weakened immune systems.
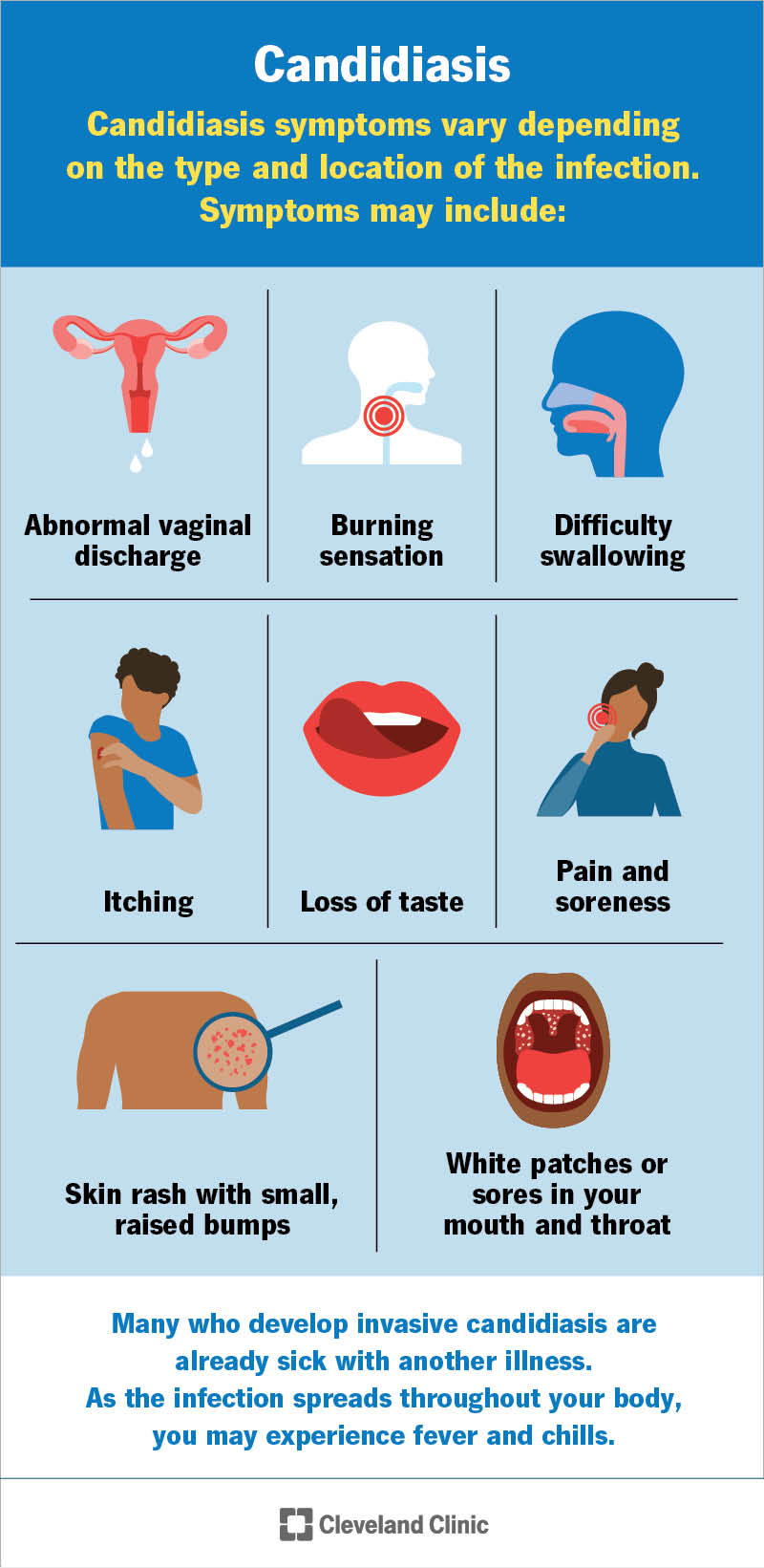
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/23198-candidiasis.jpg)
Candidiasis symptoms vary depending on the type and location of the infection. Symptoms of candidiasis may include:
Many people who develop invasive candidiasis are already ill. So, it can be difficult to determine which symptoms are from their original conditions and which are from the infection. But as the infection spreads throughout your body, you may experience fever and chills.
An overgrowth of Candida yeast causes candidiasis infections. This occurs when there’s an imbalance between healthy bacteria and Candida yeast on your body. Triggers that can disrupt this balance include:
Candidiasis can affect anyone because yeast naturally lives on your body, and it’s easy to upset the balance of healthy bacteria and yeast. But there are certain groups of people who are more likely to develop an infection. Candidiasis most often affects:
Your healthcare provider will perform a physical examination of the affected area and ask you about your medical history. They’ll also ask you questions about your symptoms, including their severity and how long you’ve had them.
Your provider may be able to diagnose oral candidiasis by the appearance of your mouth or throat. For other types of candidiasis, they’ll likely request testing to confirm a diagnosis.
The No. 1 treatment option for a candidiasis yeast infection is an antifungal medication. Depending on the type and severity of the infection, your healthcare provider may prescribe an antifungal that’s topical (cream or ointment) or oral (pill, lozenge or liquid). For severe infections, you may need to receive an antifungal intravenously (through a vein).
Invasive candidiasis will require more intensive treatment. Your provider will likely start with an intravenous antifungal like echinocandin.
Advertisement
Yes, you can take an over-the-counter (OTC) antifungal medication. But the success of OTC medicine is dependent on knowing which type of yeast you’re trying to treat. This can be difficult to identify without visiting your healthcare provider. They can perform a culture test of the infection and give you a specific plan to treat your infection.
Most mild to moderate cases of candidiasis will clear up in two to three days after you complete treatment. More severe cases may take a couple of weeks to clear up completely after treatment.
You should contact your healthcare provider when you notice any symptoms of candidiasis, including:
Untreated candidiasis symptoms could become worse over time. So, it’s best to visit your provider at the first sign of infection to start treatment.
Treatment for candidiasis is extremely effective. Symptoms are bothersome but should start to fade after treatment begins. Infections usually clear up completely between two days and two weeks, depending on the type and severity.
If left untreated, symptoms of candidiasis can cause irritation and discomfort and could increase in severity over time. Sometimes, candidiasis returns after treatment, so it’s best to work with your healthcare provider on a treatment plan. They can target the specific type of yeast that caused the overgrowth on your body.
Advertisement
You may be able to prevent candidiasis by:
Although candidiasis can cause uncomfortable symptoms like itching and soreness, you can rest easy knowing that it’s not usually a serious infection. Treatment with an antifungal medication should clear up your symptoms quickly. Each antifungal has specific instructions, so make sure you ask your healthcare provider to explain how to apply or take the medication and how long you should take it.
Even if your symptoms stop, continue taking the antifungal as advised by your provider. This will completely clear the infection and prevent it from coming back.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Need care fast? Cleveland Clinic’s Express Care and Urgent Care locations treat everything from sprains to sinus infections — no appointment needed.
