Vitamin B12 deficiency is a treatable condition that happens if you aren’t consuming enough vitamin B12 in your diet or if your body isn’t absorbing it properly. Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause physical, neurological and psychological symptoms. It can be treated with vitamin B12 medications.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Vitamin B12 deficiency, sometimes called cobalamin deficiency, happens when your body is either not getting enough or not absorbing enough vitamin B12 from the foods you eat. Vitamin B12 is an important nutrient that helps your body make red blood cells and DNA, the genetic material in all of your cells. It’s essential to how your body functions. Without treatment, vitamin B12 deficiency can cause physical, neurological and psychological problems.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Vitamin B12 is an important nutrient that helps your body keep your nerve cells and red blood cells healthy. It also helps your body make DNA.
Your body doesn’t make vitamin B12 on its own. You have to consume food and drinks that have vitamin B12 to get it. Vitamin B12 is found mostly in animal products, like fish, meat, dairy and eggs. It’s also in fortified foods (foods with vitamins and minerals added to them), like cereals, breads, plant-based milks and nutritional yeast.
Adults need around 2.4 micrograms (mcg) of vitamin B12 a day. And women who are pregnant or breastfeeding need more. The amount of B12 babies and children need varies based on age.
Two things need to happen for your body to absorb vitamin B12 from the food you eat:
Your digestive system can then absorb B12.
Vitamin B12 deficiency anemia happens when your body doesn’t have enough healthy red blood cells. As B12 helps make red blood cells, a lack of vitamin B12 can cause anemia. But you can also have a vitamin B12 deficiency without having anemia.
Advertisement
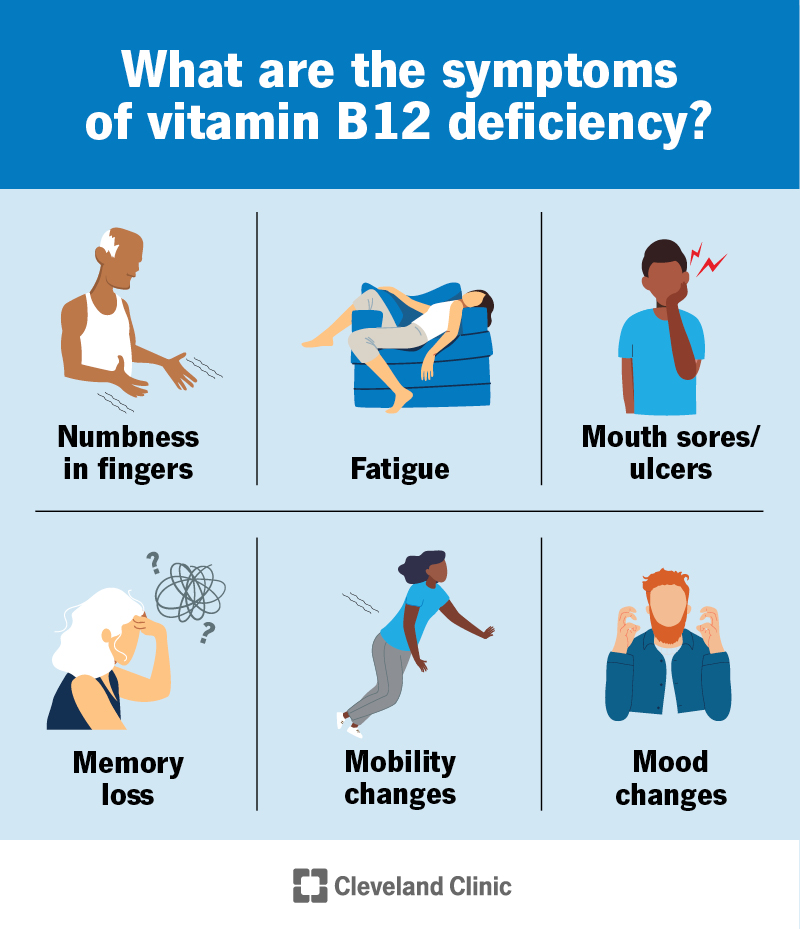
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/22831-vitamin-b12-deficiency-infographic)
The symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency can develop slowly and can get worse over time. You may have no symptoms despite having a low level of vitamin B12 in your body. Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause physical, neurological and psychological symptoms.
Physical symptoms can include:
Neurological symptoms can include:
Psychological symptoms can include:
Vitamin B12 deficiency happens if you aren’t eating enough vitamin B12 or your body isn’t absorbing the vitamin B12 you consume. Situations or conditions that can cause vitamin B12 deficiency include:
You are more likely to develop vitamin B12 deficiency if you have one or more of the following risk factors:
Left untreated, vitamin B12 deficiency can cause lasting side effects that affect your nervous system and brain. More severe side effects include:
Advertisement
It can be difficult to diagnose vitamin B12 deficiency because you may not have symptoms, or symptoms can be like other nutritional deficiencies. Healthcare providers will usually do blood tests to check for B12 deficiency in people who have a high risk of developing it.
Specific tests to help diagnose vitamin B12 deficiency are:
Getting more vitamin B12 treats the deficiency. Providers may prescribe cyanocobalamin, a human-made form of B12. Options for vitamin B12 treatment include:
Depending on the cause of the deficiency, you may only need treatment until your vitamin B12 levels are back to normal, or you may need B12 therapy for the rest of your life.
What you can expect depends on how early the vitamin B12 deficiency is caught and how low your levels are. If your deficit is mild, you may respond quickly to medication and eating more foods containing B12.
Advertisement
If you have chronic low B12 levels or have underlying health conditions that cause the deficiency, you may need to take B12 for the rest of your life (or for as long as you have the underlying condition).
Work with your healthcare provider to find the treatment that works best for you based on your situation.
Most people can prevent vitamin B12 deficiency by eating foods that have vitamin B12.
Options for consuming B12 include:
Other things you can do to help prevent vitamin B12 deficiency include:
Advertisement
Vitamin B12 is an important vitamin that your body needs to be healthy. But it’s one of those things that you probably don’t think about needing until you have symptoms of not having enough of it. Most of us can prevent vitamin B12 deficiency by consuming enough of it in the foods we eat. If you have risk factors for developing vitamin B12 deficiency or are experiencing symptoms, be sure to contact a healthcare provider to get a blood test to check your levels.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Hormonal conditions can be tricky to find and complicated to treat. The experts in endocrinology at Cleveland Clinic are here to provide the best care.
