Heel bursitis is a type of bursitis that affects the bursae of your heels. Bursitis is swelling and inflammation in your bursae, the cushioning sacs that surround and protect your bones. Heel bursitis can cause pain that affects your ability to move your foot or ankle. Your healthcare provider can provide treatment options to relieve your symptoms.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
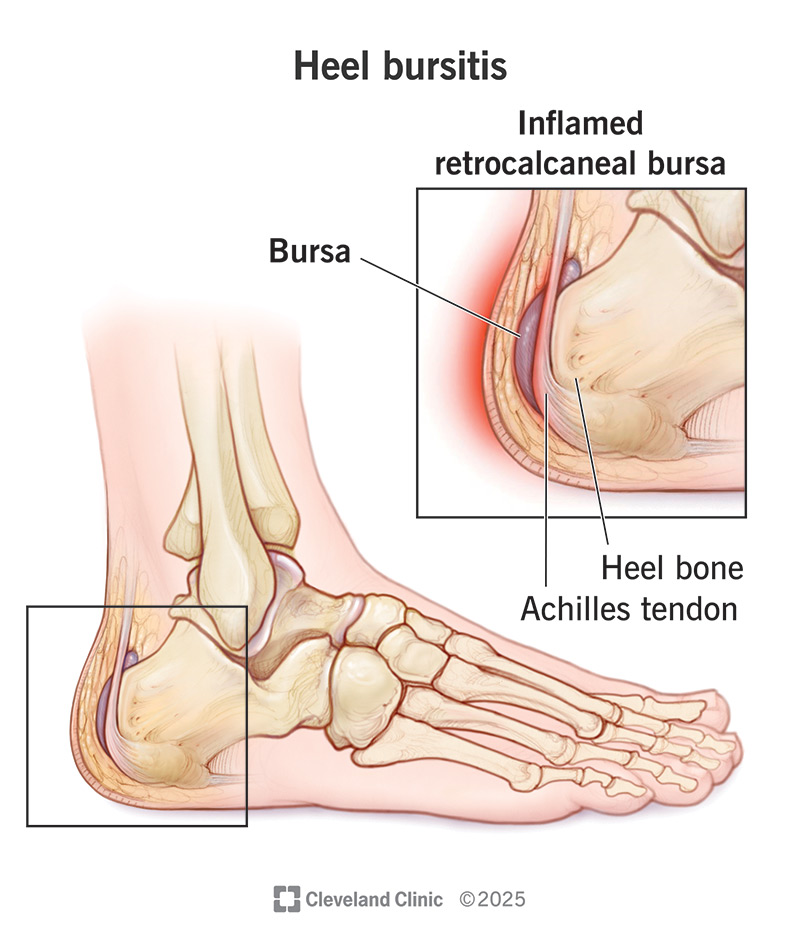
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/heel-bursitis)
Heel bursitis (pronounced “ber-CY-tuss”) is a condition that occurs when a bursa in your heel becomes irritated and inflamed. This inflammation can cause foot, ankle and heel pain.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
A bursa is a small, slippery sac in your body that’s filled with fluid. Bursae (plural form of bursa) act as a cushion and lubricant. They protect bones from rubbing or sliding against tendons, muscles or skin.
Bursitis can affect any of the bursae in your body. There are bursae behind both of your ankles near your heel bone (calcaneus). Fortunately, there are at-home and other nonsurgical options to treat the condition.
There are two main types of heel bursitis:
Heel bursitis symptoms may include:
Heel bursitis has many causes, including:
Advertisement
Heel bursitis most frequently affects people who overuse their ankles without proper conditioning. A sudden increase in walking, running or jumping can cause heel bursitis.
It’s important to wear proper footwear, especially when practicing a sport or exercising. Tight-fitting shoes can cause heel bursitis.
Heel bursitis can also affect those who have other disorders, including:
Before examining your foot, your healthcare provider may ask several questions, including:
Your provider will examine your foot. They’ll:
If your provider suspects that you have a bacterial infection, they may:
Imaging tests can help your healthcare provider confirm heel bursitis. These tests may include:
Heel bursitis treatment depends on what’s causing your pain.
You may be able to relieve pain and inflammation on your own with:
Your healthcare provider may treat heel bursitis with:
Advertisement
Questions you may want to ask your provider about heel bursitis include:
With proper diagnosis and treatment, the outlook for people with heel bursitis is good. Most people feel better after two to three weeks of home treatment. More serious cases may take six to 12 months.
You can reduce your risk of developing heel bursitis by:
Heel bursitis is a common health condition that affects athletes, active people and people who stand a lot. If you develop pain in or around your heel, talk to your healthcare provider. Rest, stretching and strengthening exercises may reduce pain in your ankle and heel. If these methods don’t relieve your symptoms, your provider may recommend other options. While heel bursitis is a frustrating condition, you should be back on your feet again within a few weeks.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Bursitis can make your hobby or your job a real pain. Cleveland Clinic experts can help you find relief and get you back to doing the things you love.
