See your healthcare provider if you have any signs or symptoms of a staph infection. On your skin, these include red, inflamed and painful sores that may contain pus.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
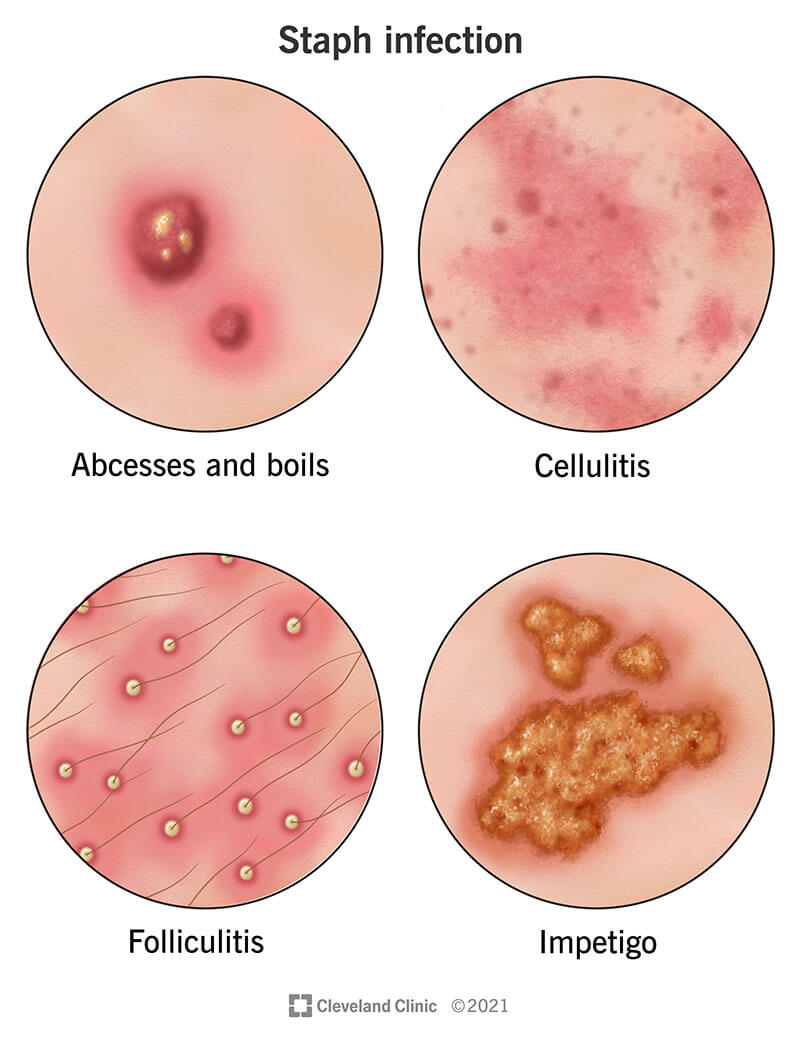
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/21165-staph-infection)
Staphylococcal infections, commonly called staph infections, are caused by a genus of bacteria called Staphylococcus. There are more than 30 strains (types) of Staphylococcus bacteria. The most common human pathogen is Staphylococcus aureus. A pathogen is an organism that causes disease.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Healthcare providers prescribe antibiotics to treat staphylococcal infections. In severe cases, a staph infection can cause serious health complications and death.
Different types of staph bacteria cause problems in various parts of your body. Staphylococcal infection can affect the:
Advertisement
There are millions of skin staph infections in the U.S. every year. Most of them are mild and can be treated with antibiotics. Even if you are healthy, Staphylococcus bacteria commonly live in your nose or on the skin. If the bacteria get inside your body, they can cause problems. When they do, they create many thousands of serious cases of S. aureus infections in the U.S. every year.
While anyone can get a staph infection, certain people are at higher risk than others. People who work in hospitals are more likely to have the bacteria on their skin. Staph infections occur most often in people who:
Children often get staph infections that we know by other names, like impetigo and styes. These infections, along with wounds that may get infected, are often seen in infants and children. In addition to causing blisters and pimple-like lumps, staph infections in kids can cause chills, fevers and general feelings of being unwell. It’s important to check in with your healthcare provider about any of these types of conditions.
Symptoms of a staph infection vary depending on the area of your body where the infection occurs. Staph infections occur most often on your skin. They often look like pimples — red and angry and filled with pus. They may leak fluid. You might think you have some kind of bite or ingrown hair.
Signs and symptoms of staph infection on your skin include:
These types of staph infections often start with areas that are tender, warm and red. As they get worse, you may see pus or drainage, with red areas getting bigger. Some staph infections of the skin can become open wounds.
When staph infections occur in areas of your body other than your skin, it causes certain conditions with different symptoms of their own. These conditions and their symptoms include:”
Advertisement
Staph infections spread in the ways that other infections spread, through coughs and sneezes, as well as other ways, including:
Advertisement
The way your provider determines if you have a staph infection depends on what area of the body is affected. It’s easy to see staph infections on your skin. However, providers often rely on Gram stain testing and bacterial culture tests to diagnose the presence of bacteria and the type.
If you have symptoms of a staph infection, contact your healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment. See your provider if you or your child has an area of skin that is blistered, irritated or red, especially if there’s also a fever. Only healthcare providers can diagnose and treat a staph infection.
Advertisement
One thing you can do is draw a circle around the red area with a pen so you can see if it continues growing. If the redness gets bigger than the outline, you should definitely call your provider.
Most cases of staph infection on the skin can be treated with a topical antibiotic (applied to your skin). Your healthcare provider may also drain a boil or abscess by making a small incision (cut) to let the pus out.
Healthcare providers also prescribe oral antibiotics (taken by mouth) to treat staph infections inside your body and on your skin. The antibiotic will vary depending on the type of infection. In severe staph infections, providers use IV (intravenous) antibiotics to kill the bacteria.
If you have a more serious staph infection that requires an IV, your provider may suggest that you go to the hospital for a period of time.
If you’re taking antibiotics, you shouldn’t be contagious after 48 hours. It may take longer than that to feel better though.
Side effects vary depending on the type of antibiotic used to treat the staph infection. Side effects from topical ointments can include stinging, itching, and redness in the affected area. Common side effects of oral antibiotics include nausea, vomiting and diarrhea.
If left untreated, staph infections can be deadly. Rarely, staph germs are resistant to the antibiotics commonly used to treat them. This infection, called methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), causes severe infection and death.
This is one reason that it’s important to take your entire prescription of antibiotics. One factor in creating resistance has been that people only take the medication until they feel better, which means that the germs aren’t entirely gone.
It’s important to seek medical help if you think you might have a staph infection. To relieve the symptoms of staph infection on your skin, clean the affected area with soap and water. You can try cold compresses and over-the-counter pain relievers to help with discomfort.
In cases of food poisoning, drink plenty of liquids while you’re recovering to reduce your risk of dehydration.
Massage and warm compresses can relieve the symptoms of mastitis.
Most times, the outlook is favorable for people who have staph infections and are treated properly. As with most conditions, the best outlooks usually happen when the infection is diagnosed and treated early.
The outlook varies when a staph infection is more serious. You’ll recover more quickly from a superficial skin infection than from a bigger wound or from an infection that develops inside your body.
If the staph infection is systemic (throughout the body, in an organ system), the recovery time is going to take a much longer time. This is why it’s so important to get medical help. Untreated staph infections can be fatal.
Prevention depends on the type of infection. To reduce your risk of a staph infection, you should follow these tips:
Since a staph infection can become serious very quickly, you should contact your provider right away if you have signs of a staph infection. Only a healthcare provider can diagnose and treat a staph infection.
They aren’t different. MRSA stands for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. MRSA is one type of staph infection, but it’s one that is harder to treat.
Yes, you can. Some of the risk factors include:
Make sure to keep your belly button clean and dry. This will help to keep bacterial and fungal build-up to the minimum. If you have any discomfort or see signs of infection, call your healthcare provider.
Minor staph infections may clear up on their own, but it’s better not to rely on that happening. You should contact your provider because staph infections can get worse quickly and can be serious.
There are some “natural” things that have been used in the past to fight staph infections, like honey, essential oils, ginger, turmeric and garlic. Researchers are doing studies on these older antimicrobial agents (called ancientbiotics by some). Interest in these substances is rising, in part because some germs have become resistant to some types of medications.
At this point in the research, though, it’s unwise to rely only on honey or garlic or anything of that nature for a cure. See your provider to make sure that you’re diagnosed and treated correctly.
You’ve probably heard about staph infections. You may have already had one. While they aren’t necessarily something to panic about, you do need to contact your healthcare provider if you have signs or symptoms of something being wrong. The most obvious staph infections are seen on the skin.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Need care fast? Cleveland Clinic’s Express Care and Urgent Care locations treat everything from sprains to sinus infections — no appointment needed.
