Mastitis is breast inflammation that can lead to infection. If you're breastfeeding, you may get mastitis. You may have a red, swollen, painful breast and flu-like symptoms.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
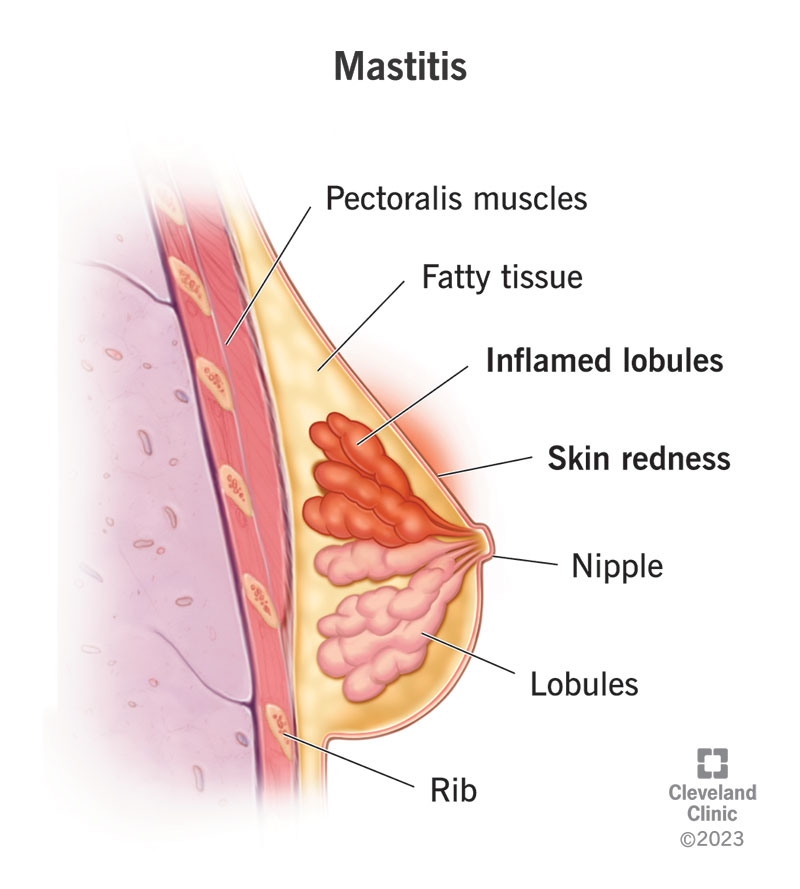
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/15613-mastitis)
Mastitis is painful inflammation in your breast tissue that can lead to a bacterial infection.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Anyone can get mastitis. It’s most common in women who breastfeed. Men and women who don’t breastfeed can also get it, but this is rare.
Mastitis affects up to 10% of women in the United States. It may affect up to 30% of breastfeeding women worldwide. It’s most common in the first three months of breastfeeding.
Mastitis is inflammation. This means your breasts may be swollen, tender or warm to touch. Your breasts may become engorged. You may also experience:
Engorgement is most common in the first few days after you give birth, but can occur as long as you produce breast milk.
The most common cause of mastitis is hyperlactation or an oversupply of milk. This oversupply of milk causes your milk ducts to narrow because the surrounding tissue puts pressure on the ducts. This leads to engorgement, which is when your breasts are extremely full and swollen. This is known as inflammatory mastitis.
Inflammatory mastitis can lead to bacterial mastitis. Bacteria mastitis is when infection occurs due to inflammatory mastitis.
Advertisement
Sometimes, a bacterial infection leads to an abscess. An abscess is a collection of fluid that requires draining.
You’re at higher risk for getting mastitis if you breastfeed and have an oversupply of milk.
In recent years, healthcare providers have changed their recommendation for dealing with oversupply. The previous recommendation suggested emptying your breasts more often would treat the symptoms of oversupply.
However, current research shows that this actually makes engorgement worse. Emptying your breast more than usual (pumping or feeding) will only lead to more milk production and further aggravate the inflammation.
Your healthcare provider will do a physical exam and check your symptoms to make a diagnosis. If you aren’t breastfeeding, you may get a mammogram or breast ultrasound to rule out breast cancer or a different breast condition.
Treatment for mastitis involves reducing inflammation and pain and preventing an infection from occurring. Researchers are always learning more about lactation and mastitis, so it’s important to talk to your healthcare provider to make sure you’re getting current treatment information.
Previous treatment methods for mastitis involved heat, massage and extra pumping or feeding. Now, many providers say you should treat inflammatory mastitis like a sprained ankle. You wouldn’t massage an ankle sprain or put a heating pad on it. Mastitis should be treated similarly. The swelling in your breasts is mostly due to swelling of the structures around the milk — it’s not a “plug of milk” needing “worked out.” Rather, the inflammation needs to be decreased in order for the milk to flow better.
At-home treatment for inflammatory mastitis includes:
DO NOT:
Advertisement
If at-home treatment for inflammatory mastitis doesn’t help, it could progress to bacterial mastitis. Your healthcare provider will prescribe an antibiotic to treat a bacterial mastitis infection. They work to eliminate the bacterial infection that’s built up in your milk ducts. The infection should clear up within 10 days. However, you should begin to feel relief within 48 to 72 hours. Over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen and ibuprofen can help with pain and inflammation, but they can’t treat an infection.
If left untreated, a breast infection like mastitis can lead to a breast abscess. This type of abscess typically requires surgical treatment. Your healthcare provider will perform minor surgery or use a small needle to drain the pus.
Inflammatory mastitis usually gets completely better within 10 to 14 days. When managed correctly, symptoms improve dramatically within 24 to 72 hours. Recognizing the signs of engorgement and inflammation is key, because then you can start to implement treatment methods like ice and lymphatic drainage.
Yes, you should continue to nurse your baby. You can’t pass a breast infection to your baby through breast milk. In fact, breast milk has antibacterial properties that help babies fight infections. Antibiotics that your provider prescribes for mastitis are usually safe for your baby.
Advertisement
It may be uncomfortable to nurse when you have mastitis, but you should continue to do so.
Yes, it’s possible to get mastitis multiple times.
Mastitis is painful and uncomfortable, but it usually doesn’t cause long-term problems. At-home treatment using the methods above usually lead to positive outcomes.
If you’re nursing, you may make less milk as your body fights off the bacterial infection. Milk production should increase as you start to feel better.
Mastitis doesn’t increase your risk of breast cancer. However, mastitis symptoms are similar to inflammatory breast cancer symptoms. This rare type of breast cancer causes breast skin changes. Signs may include dimples and a breast rash that has an orange-peel texture. Like mastitis, one or both breasts may become red and swollen. Inflammatory breast cancer doesn’t usually cause breast lumps.
Inflammatory breast cancer is an aggressive cancer. It requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. Contact your healthcare provider right away any time you notice breast changes.
A good rule of thumb is to only pump what’s needed for your baby. If you’re feeding from your breast, don’t pump afterward to “drain” it.
It might be helpful to talk to a lactation consultant or attend a breastfeeding class to learn what a good latch looks like and feels like. A latch is how your baby nurses from your breasts. A good latch may help with mastitis because your body can naturally adjust your milk production to your baby’s milk intake.
Advertisement
Women who are breastfeeding can also take these steps to lower their chances of getting mastitis:
You should call your healthcare provider at-home treatment for engorgement doesn’t help. Other symptoms that may warrant a call to your provider include:
You may want to ask your healthcare provider:
It’s rare to need to go to an ER for mastitis. If your symptoms are worsening and you’re concerned about having to wait to see your healthcare provider, going to your nearest emergency room may give you peace of mind. Those already on antibiotics having worsening fevers and swelling may need imaging to rule out an abscess.
“Clogged” or “plugged” ducts are areas of inflammation or engorgement surrounding the ducts that compress the milk ducts, making it harder for the milk to come out or flow. When the inflammation isn’t treated properly, it can lead to mastitis.
Any type of breast change is a reason to call your healthcare provider. While mastitis isn’t cancerous, your healthcare provider should evaluate your symptoms. Rarely, breast infection symptoms are a sign of inflammatory breast cancer. If you develop mastitis while you’re breastfeeding, it may be helpful to talk to a lactation consultant. They can ensure proper latching and breastfeeding techniques so you don’t develop mastitis again.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
From routine pelvic exams to high-risk pregnancies, Cleveland Clinic’s Ob/Gyns are here for you at any point in life.
