A right atrial appendage (RAA) is a muscular pouch that extends from your heart’s right atrium. Your RAA releases proteins to help manage blood volume. Blood from your right atrium flows into and out of your RAA. Sometimes, an abnormal heart rhythm can start in your right atrial appendage. Blood clots can form there as well.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
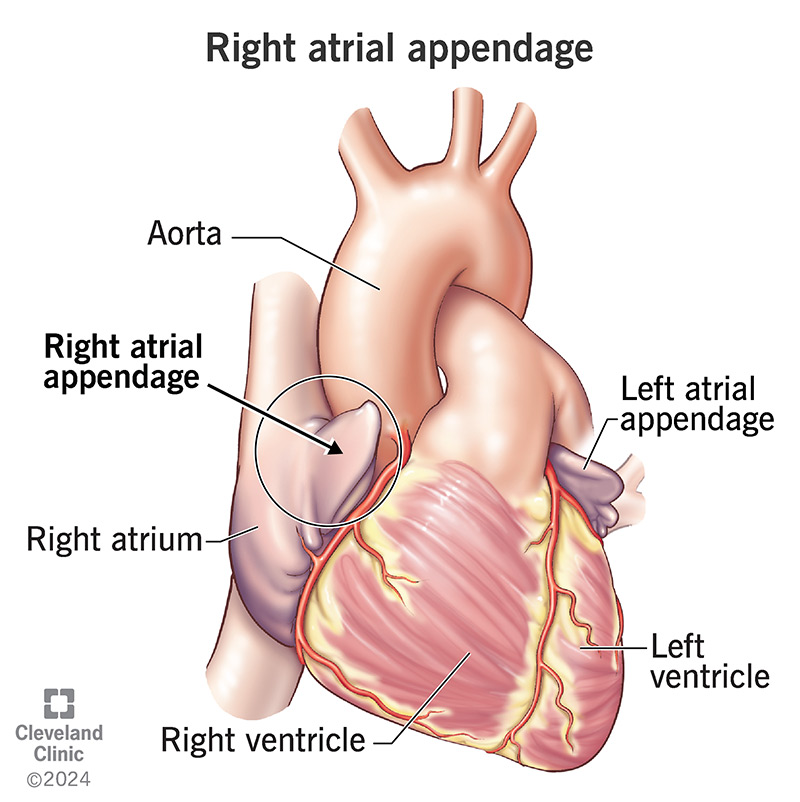
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/right-atrial-appendage)
The right atrial appendage (RAA) is a pouch that extends from the right atrium (upper chamber) in your heart. You may hear about it if a healthcare provider wants to place a pacemaker lead (wire) in your right atrial appendage. This is a good place to put a wire because a provider can get to your RAA easily. Also, it’s near the SA (sinoatrial) node that sends electrical impulses to make your heart beat.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
This unfamiliar part of your heart can cause problems for you, but treatments can help just like they do for other areas of your heart.
The right atrial appendage’s function is to release natriuretic peptides (proteins) when your RAA’s walls stretch from too much blood volume. These peptides make your blood vessels widen. They also increase the amount of salt and water your body clears out through urine (pee). These actions can bring blood volume and pressure down.
Your right atrial appendage extends out from the upper part of your heart’s right atrium. Located next to your superior vena cava, your RAA reaches over part of a groove between the right atrium and ventricle.
Your right atrial appendage anatomy consists of a pouch with an opening. Blood moves in and out of your right atrial appendage. Your RAA has ridges of muscle (the terminal crest and musculi pectinati). These create a rough surface inside your RAA.
Your right atrial appendage can consist of one or more lobes — even as many as six. Researchers estimate its area at around 3 square centimeters (about half a square inch). The RAA’s opening is about 2 centimeters (less than 1 inch).
RAA shapes may include:
Advertisement
Researchers have identified subtypes of these main types as well.
Several conditions can affect your right atrial appendage, like:
Symptoms from conditions that affect your right atrial appendage may include:
Tests to check the health of your right atrial appendage include:
Treatments for your right atrial appendage include:
Your heart is at its healthiest when it gets the everyday care it needs. Examples include:
Most people have probably never heard of a right atrial appendage (RAA). It’s not as well-known as the left atrial appendage, which may only be familiar to people with Afib. If you’re reading this because you’re getting a pacemaker, know that providers prefer the RAA as a good place for a pacemaker lead. Talk with your provider if you want to know more about pacemaker placement.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
When your heart rhythm is out of sync, the experts at Cleveland Clinic can find out why. We offer personalized care for all types of arrhythmias.
