A cervical rib is an extra bone in your neck that some people have at birth. Very few people have this rare bone and even fewer have symptoms from it. A cervical rib can cause pain or weakness in your arm, but treatments can help. A provider can remove a cervical rib because it doesn’t have a purpose.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
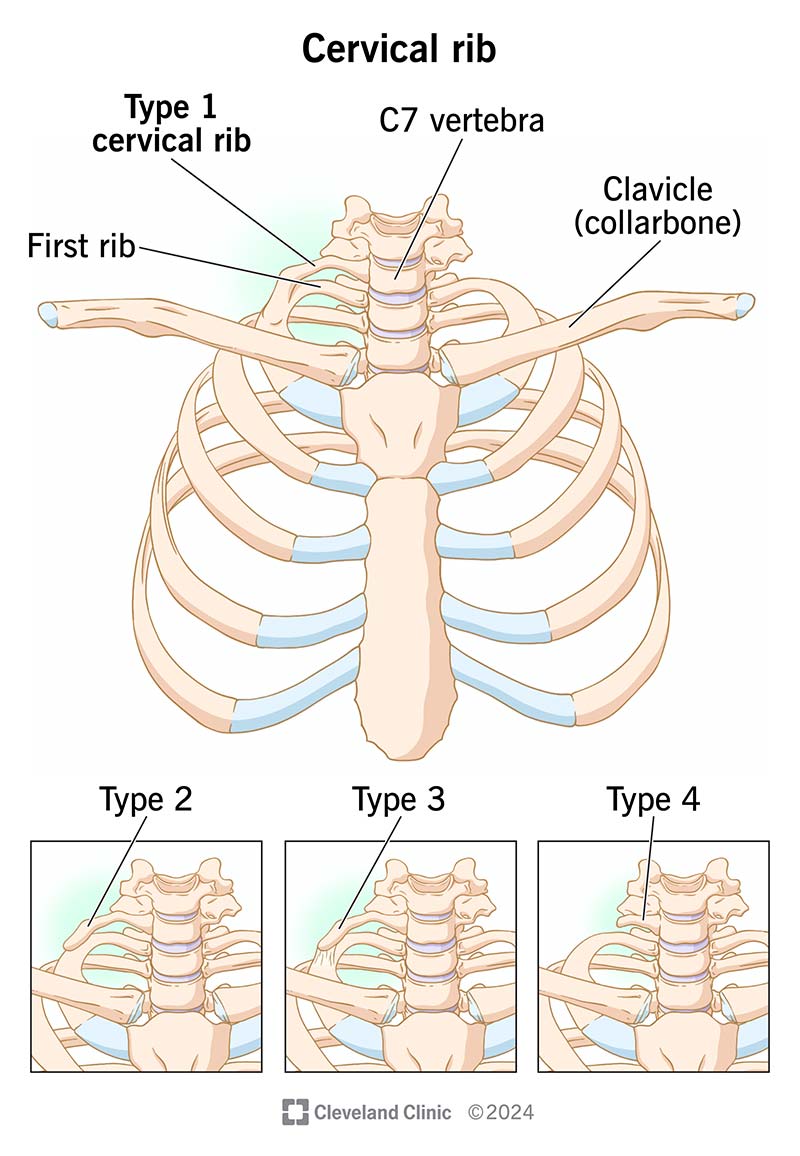
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/cervical-rib)
A cervical rib is an extra bone you may have in your neck at birth. This rare bone doesn’t look like a typical rib in your chest. It can be more vertical or diagonal instead of horizontal like the ribs in your chest. It starts from the lowest bone in your neck and can extend to the first (top) rib in your chest. A cervical rib doesn’t do anything — it doesn’t have a function.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
In most people, a cervical rib doesn’t cause issues. In others, it causes pain in their arm or difficulty using their hand to grip a pen, for example.
There are four cervical rib types:
A cervical rib (cervical rib syndrome) is rare. Up to 1% of people have one (and sometimes two) cervical ribs at birth. Cervical ribs happen more in females.
Nearly 30% of people who have thoracic outlet syndrome have cervical ribs.
Cervical rib symptoms include:
Most people don’t have symptoms of cervical rib. You’re more likely to have symptoms if you have bad posture or have experienced trauma to your upper body.
Researchers think a mutation (change) in HOX genes involved in skeletal development may cause cervical ribs. Cells in a developing fetus may form a bone in the wrong place and it becomes a cervical rib.
Advertisement
Cervical ribs can compress a nerve or your subclavian artery. A cervical rib can cause thoracic outlet syndrome, which can be dangerous without treatment.
A healthcare provider can do a physical exam that includes an Adson test. If your cervical rib is compressing your subclavian artery, a provider can feel your extended arm’s pulse get weaker when you turn your head.
Most of the time, providers find cervical ribs when they’re looking for something else. Cervical ribs can show up on a chest X-ray or cervical (neck) X-ray.
Providers may use other tests to make a diagnosis, like:
If you don’t have symptoms, you won’t need treatment.
If you have symptoms, treatments may include:
If you have symptoms, they can get worse without treatment. You can also get blood clots in your subclavian artery or brain.
The outlook is good for people who have surgery to remove a cervical rib. Their affected arm works normally again and symptoms rarely return after surgery.
No, you can’t prevent cervical ribs because they develop before birth.
Follow your provider’s instructions for getting medical treatment. If nonsurgical treatments don’t help you, ask your provider if surgery would be right for you.
If your cervical rib starts causing symptoms, contact your provider.
If you have surgery to treat a cervical rib, you’ll need follow-up appointments with your provider. They’ll want to see how well your body is healing and make sure you’re not having any issues. You may also need to do physical therapy for a number of weeks after your operation.
Questions to consider asking your healthcare provider include:
Maybe you had no idea there was an extra bone in your neck, but you can’t ignore the pain in your arm. That pain isn’t normal and you don’t have to suffer with it. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best treatment for you. Be sure to ask questions if there’s anything you don’t understand about your condition or treatment.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Everyday things like turning your head shouldn’t be a pain in the neck. Cleveland Clinic medical spine experts can find ways to ease your cervical neck pain.
