Your nasopharynx is the top part of your throat (pharynx), connecting your nose to your respiratory system. It contains your adenoids, which help prevent infection. Your nasopharynx also contains part of your eustachian tubes, which drain fluid from your ears. Conditions that affect your nasopharynx include the common cold and enlarged adenoids.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
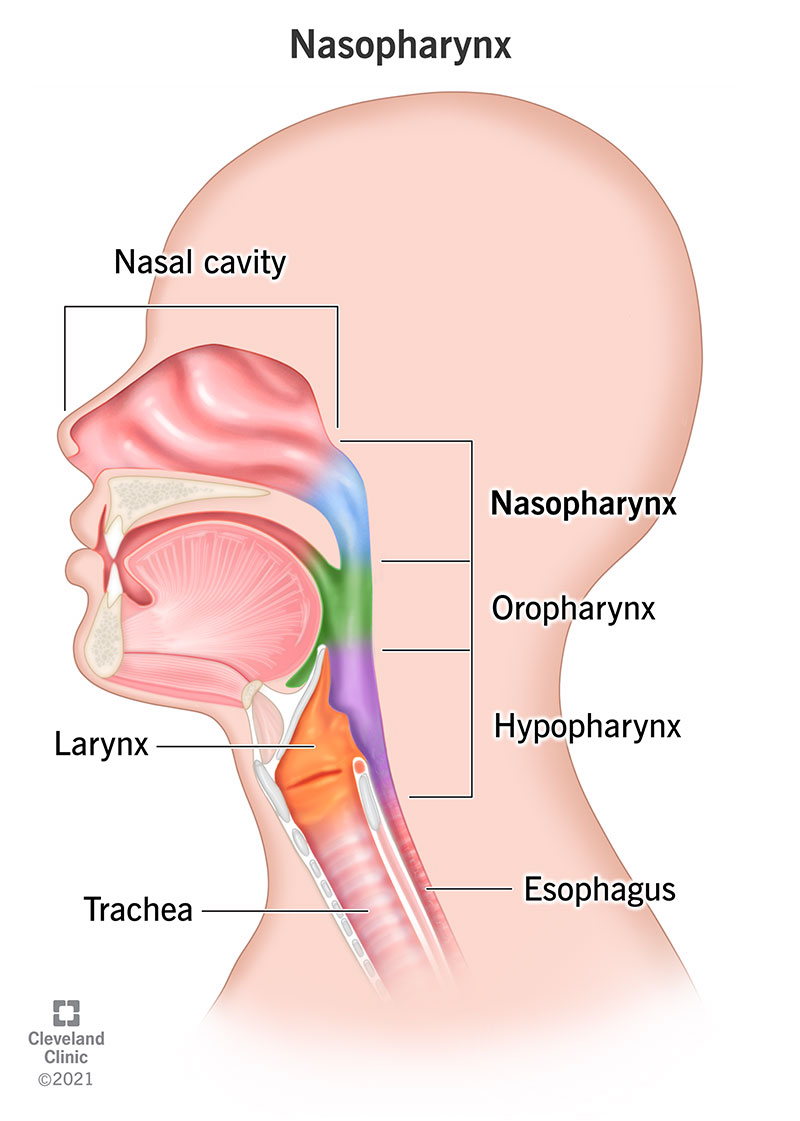
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/Images/org/health/articles/22376-nasopharynx)
Your nasopharynx is the top part of your throat (pharynx). It’s a muscular, box-shaped passageway behind your nose, just above the roof of your mouth. Your nasopharynx allows air to pass from your nose into your windpipe (trachea) and eventually, into your lungs.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
As the part of your throat closest to your nose, your nasopharynx is particularly vulnerable to germs, like the ones that cause upper respiratory infections. Taking precautions to keep from getting sick can help protect your nasopharynx.
The main function of your nasopharynx is to connect your nasal passages to the rest of your respiratory system. It’s part of a passageway that allows air to flow from your nose to your lungs.
Your nasopharynx also helps:
Your nasopharynx is located toward the bottom and back of your skull. It’s behind your nose and above the roof of your mouth.
The top of your nasopharynx connects to your nasal cavity. The bottom connects to your oropharynx (middle throat), leading to your hypopharynx (lower throat), windpipe and eventually, lungs.
Your nasopharynx includes several important structures:
Advertisement
The most common condition that affects your nasopharynx is nasopharyngitis, otherwise known as the common cold. In nasopharyngitis, a virus (often, rhinovirus) infects your nasopharynx, causing swelling of your nasal passages and throat.
Other conditions that can affect the nasopharynx include:
Common signs and symptoms include:
Signs of less common, more serious conditions (like cancer) include:
Common tests include:
Colds usually go away on their own within a week or so. Other treatments include antibiotics for bacterial infections. Your child may need surgery to remove their adenoids (adenoidectomy). Or you may need surgical removal of cysts and tumors causing symptoms.
Treatments for nasopharyngeal cancer depend on your unique diagnosis.
The best way to care for your nasopharynx is to reduce your risk of colds and other respiratory infections. You can:
Advertisement
Contact a healthcare provider if you have cold symptoms that last longer than 10 days. Let them know if you’re experiencing symptoms that may be signs of something serious.
Seek medical attention if you experience:
You can’t see your nasopharynx, but you can often feel when something’s affecting it. Common conditions, like colds and swollen adenoids, can impact this body part. Rarely, cancer or harmful benign growths can form there. This is why it’s important to talk to a healthcare provider if you have any pain or unusual symptoms related to your nasopharynx. Reach out if you or your child have cold symptoms that don’t go away after a week to 10 days.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s primary care providers offer lifelong medical care. From sinus infections and high blood pressure to preventive screening, we’re here for you.
