The phrenic nerve plays a key role in breathing (respiration). It makes your diaphragm contract and expand, letting your lungs inhale and exhale air. Nerve damage can cause a paralyzed diaphragm. You may feel short of breath and have problems sleeping. An irritated phrenic nerve can cause long-lasting (persistent) hiccups.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
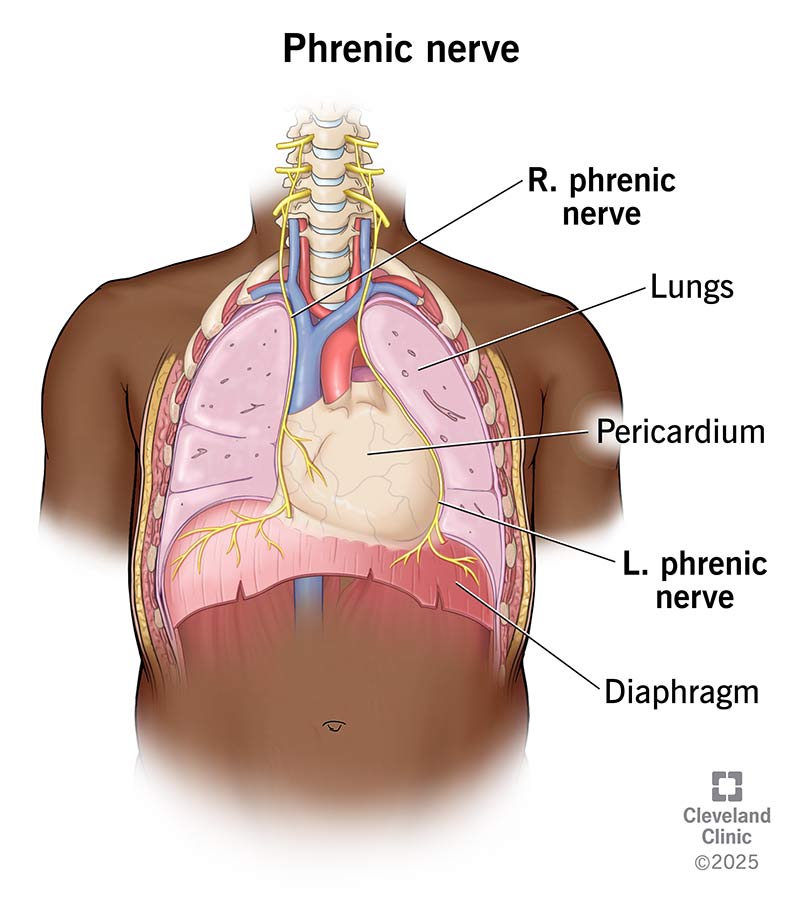
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/phrenic-nerve)
The phrenic nerve controls your diaphragm and is essential to your ability to breathe. The nerve sends signals that make your diaphragm contract (become thicker and flatter). This movement gives your lungs room to expand and take in air (inhalation). After this, the phrenic nerve relaxes your diaphragm, and your lungs return to their starting position, pushing out air (exhalation) and becoming smaller.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Your phrenic nerve is an important part of your respiratory system that helps you breathe. It’s the only nerve that gives your diaphragm movement (motor function). It sends the signals that make your diaphragm expand and contract when you breathe.
Your phrenic nerve also provides touch and pain sensations to your:
Your phrenic nerve starts in your neck and runs down through your chest to reach your diaphragm. It starts near the C3 vertebra in your neck (your cervical spine) and connects to the C4 and C5 vertebrae. It travels past your heart and lungs in your chest before reaching your diaphragm. It’s connected to nerve roots in your spinal cord along its path.
You actually have two phrenic nerves — a left and a right. Each one performs the same job. The left phrenic nerve controls the left side of your diaphragm. The right nerve controls your diaphragm’s right side.
Anything that damages your phrenic nerve can weaken or paralyze your diaphragm. If your phrenic nerve can’t control your diaphragm as it should, it won’t be able to change shape to let your lungs move and work correctly. This can make it hard to breathe.
Advertisement
Paralysis can affect one side of your diaphragm (unilateral) or both sides (bilateral). If you experience severe bilateral diaphragm paralysis, you may need a ventilator (mechanical ventilation) to breathe.
Causes of diaphragm paralysis include:
Symptoms of a paralyzed diaphragm usually include:
Symptoms of a paralyzed diaphragm can be hard to notice. That’s especially true if you have unilateral diaphragm paralysis. Visit a healthcare provider if it feels like you can’t catch your breath or you notice any new pain or other symptoms.
Sometimes, an irritated phrenic nerve causes hiccups that last for days or even a month or longer. Surgical procedures, tumors and other issues may irritate your phrenic nerve and cause persistent hiccups.
Persistent hiccups can be uncomfortable and annoying. They can affect your ability to talk, sleep and eat. Treatments for persistent hiccups include:
These steps can keep your phrenic nerve (and the rest of your nervous system) healthy:
Visit a healthcare provider if you notice any new symptoms that affect your breathing, including:
Advertisement
Your phrenic nerve helps you almost constantly. It moves your diaphragm when you breathe, which lets your lungs work the way they should. You may never need to think about your phrenic nerve. But don’t ignore changes in your breathing. Even if it’s not a phrenic nerve issue, you should see a healthcare provider if you feel like something’s making it harder to breathe.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
If you have a neurological condition, you want expert advice. At Cleveland Clinic, we’ll work to create a treatment plan that’s right for you.
