Shoulder pain is a common symptom that has several possible causes. Your shoulder allows you to move your arms. Its wide range of motion makes it more at risk of injury. Some of the most common causes are arthritis, muscle strain or dislocation. Treatment could include rest, medications or surgery but it varies by the cause.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
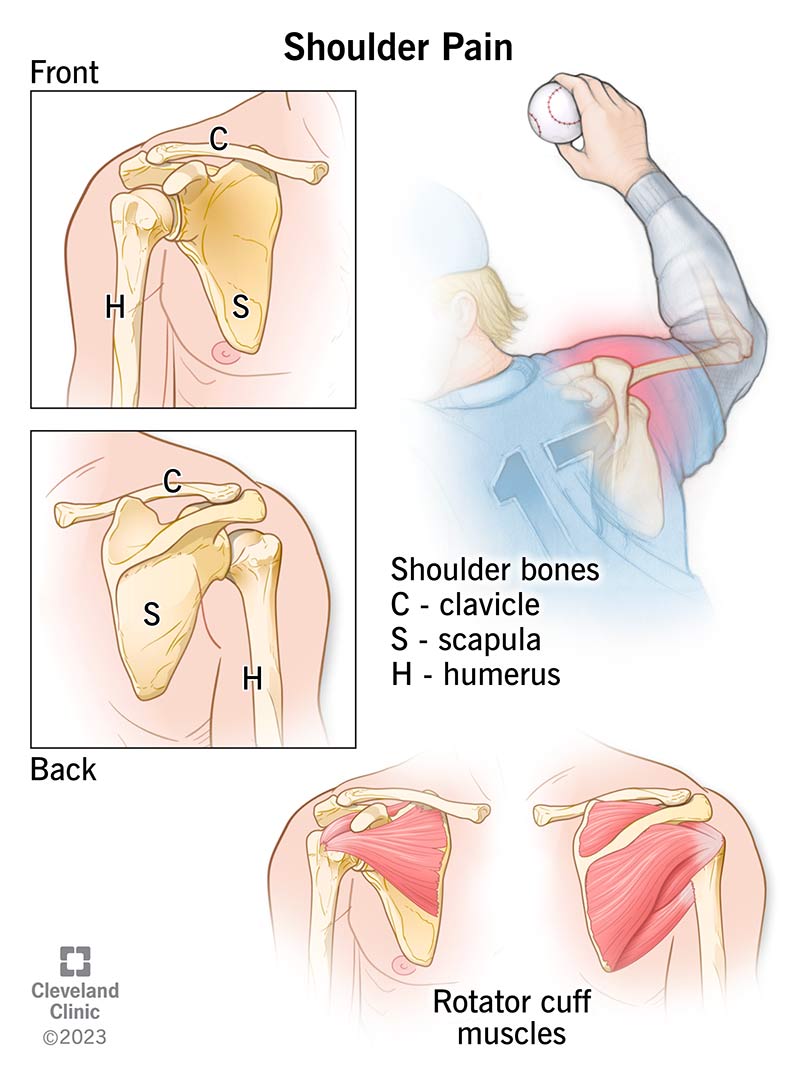
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/25122-shoulder-pain)
Shoulder pain is any discomfort you feel around your shoulder joint. The shoulder is a complex joint that allows you to throw a ball, reach for an item or give someone a high five. Because of how often you use it, your shoulder is more at risk of injury and damage, which can cause pain.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Shoulder pain varies based on the cause but you can feel the following when in motion or at rest:
Severe shoulder pain that’s usually the result of an injury may cause:
Visit a healthcare provider or the emergency room (ER) if you have severe shoulder pain.
The shoulder is a joint, or a contact point between bones, that gives your arms a wide range of motion. Your shoulders are located at the corners of your torso, at the top of your arms. You have two shoulders, one on the left and right side of your body. The shoulder joint contains three bones:
Two joints within your shoulder help it move:
The shoulder contains the following parts:
Advertisement
It’s common to have shoulder pain that spreads to other parts of your body, like your neck, for example. The anatomy of the shoulder connects your arm to your torso, so pain can radiate from your shoulder to other connected parts of your body.
Shoulder pain is common. If you have severe shoulder pain that gets worse or lasts more than a couple of days, you may have an injury to your shoulder or an underlying condition that’s causing pain. Pain with swelling can also be a sign of an injury. Visit a healthcare provider if you have severe shoulder pain that’s persistent, limits your motion or prevents you from going about your day normally.
There are several possible causes of shoulder pain. The most common include:
A healthcare provider will diagnose the cause of your pain after a review of your symptom(s) and a physical exam. A diagnosis usually involves imaging tests like a shoulder X-ray to help your provider see the bones underneath your skin.
Shoulder pain on its own isn’t a sign of a heart attack. If you have sudden, intense shoulder pain on the left side of your body and any of the following symptoms, call 911 or your local emergency services number immediately:
Certain types of lung cancer, like a Pancoast tumor in the top part of your lung, can cause shoulder blade pain in addition to upper back pain. The location of cancer in your body can affect where you have pain. For a cancer screening, visit your healthcare provider.
Symptoms of COVID-19 could include muscle weakness or aches. If you suspect you have COVID-19 or had exposure to it, complete a COVID-19 test and talk with your healthcare provider.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition that causes pain and weakness in your hand and wrist. Symptoms of carpal tunnel can affect your shoulder. Changing how you move or hold your hand or wrist can put a strain on your shoulder, leading to shoulder pain. It can be easy to overlook or ignore the pain in your shoulder when you have pain in your hand and wrist.
Treatment for shoulder pain varies based on the cause but could include:
Advertisement
Your healthcare provider will let you know what type of treatment is best for your shoulder pain after a diagnosis.
You can relieve mild shoulder pain at home by following the RICE method. RICE stands for:
This includes:
Shoulder pain can affect your ability to fall asleep and stay asleep. Try these tips to help yourself fall asleep if you have pain:
Not all cases of shoulder pain are preventable, especially if they’re the result of an accident, injury or underlying condition. You can reduce your risk of injuring your shoulder by:
Advertisement
Visit a healthcare provider if you:
Visit the emergency room if you have chest pain or difficulty breathing in addition to shoulder pain.
A chiropractor is a doctor who specializes in muscle, bone and joint pain. If you have an injury or frequent, mild shoulder pain, a chiropractor can help you feel better.
It can be difficult to get rid of shoulder pain if you don’t know what’s causing it. Your symptoms can affect your ability to move, use your arm and prevent you from getting a good night’s rest. A healthcare provider can diagnose what’s causing shoulder pain so you can feel better sooner.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Living with constant shoulder pain? Cleveland Clinic can help you get the relief you need with personalized treatment plans that match your needs.
